「重新認識 CSS」這個系列名稱的由來就如其名,我想要重新認識它。雖然以前就有學過 CSS,但這次想從 CSS Spec 中學到最原始的定義和內容,更加了解 CSS 的原理,讓我在切版的時候可以更加確定自己在做什麼,我踩到的雷只是因為我不夠了解它才會炸開。
在這 30 天的內容中,會將 Spec 內看到的資料整理成這個系列,也希望正在學 CSS 的各位可以更加了解它。另外我也會同時將文章發至我的 Blog,如果想直接看文內的程式碼 Demo 畫面,可以到我的 Blog 來看。
本文同步發表於 Titangene Blog:重新認識 CSS - Pseudo-element (偽元素)
「重新認識 CSS」系列文章發文於:
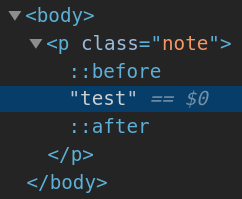
pseudo-element 代表不直接存在於 document tree 中的元素。
document language (文件語言) 不提供存取元素內容的第一個字母或第一行的機制,但是可以用 ::first-letter 和 ::first-line 這兩個 pseudo-element 選到,這樣就可以對這些元素設定樣式。
另外,pseudo-element 還可以表示原始文件 (source document) 中根本不存在的內容,例如 ::before 和 ::after 這兩個 pseudo-element 可以在任何元素的內容之前或之後插入其他內容。
pseudo-class 和 pseudo-element 都不會出現在 document source 或 document tree 中,或是不會對其進行修改。所以,pseudo-class 和 pseudo-element 都不會影響到 structural pseudo-class 或與它們的 originating (原始) 元素 或其 tree 有關的其他 selector 的解譯 (interpretation)。
Structural pseudo-class 詳情可參考我前幾天寫的「重新認識 CSS - Pseudo-class (偽類) (2)」。
Originating (原始) 元素是什麼?
pseudo-element 綁定到頁面上的某個元素,而此元素就稱為 originating 元素。例如:
div a::before { content: 'Hi '; }在 selector
div a::before中,與 selector match 的a元素就是 originating 元素。
如果想更了解 pseudo-element,可以看它在以下這些 CSS Spec 的定義:
::before and ::after::before:在 originating 元素的內容之前建立的 child pseudo-element::after:在 originating 元素的內容之後建立的 child pseudo-element::before 和 ::after 的 CSS content 屬性的初始值為 normal,計算值為 none。
當 ::before 和 ::after 的計算 content 值不為 none 時,這些 pseudo-element 就會產生 box,就好像它們是其 originating (原始) 元素的直接子元素一樣,並且可以像在 document tree 中任何 normal document-sourced (基於文件) 的元素一樣進行樣式設定
例如:
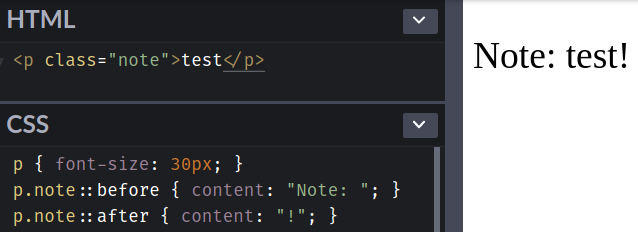
note 的 p 元素的內容之前插入字串 "Note: "note 的 p 元素的內容之後插入字串 "!"<p class="note">test</p>
p.note::before { content: "Note: "; }
p.note::after { content: "!"; }
Demo:Codepen 連結
::before 和 ::after 的 display 的初始值為 inline,所以會生成 inline box。與 p 元素的其他 inline children 一樣,它會參與 p 元素的 IFC (inline formatting context),有可能與其他內容共享一行。
就如下面範例那樣,因為 ::before 和 ::after 都是 display: inline,並且在 p 元素的內容 test 之前加上 ::before 的內容 "Note: ",以及在 test 之後加上 ::after 的內容 "!",所以在畫面上顯示的結果就變成 Note: test!。
今天介紹一些 ::before 和 ::after 這兩個 pseudo-element,接下來幾天會接續介紹其他 selector。
資料來源:
