作者:小美娜娜
連接:https://juejin.im/post/6844903808200343559
來源:掘金
本篇文章有提到node EventLoop,但我僅針對瀏覽器去做分析
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log(1)
},0)
Promise.resolve().then(()=>{
console.log(2)
})
console.log(3)
1. 遇到setTimeout放入宏任務隊列,碰到Promise then將它放進微任務隊列
2. 打印3
3. 同步執行完畢

宏任務與微任務隊列:
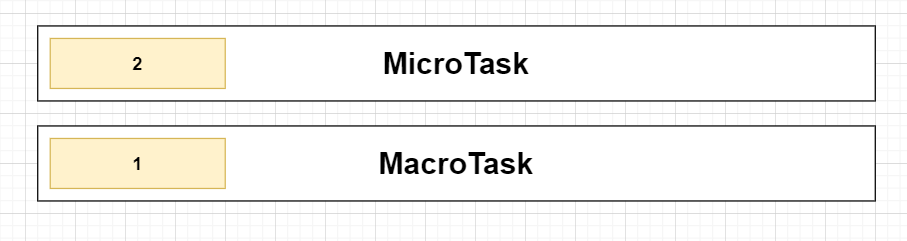
1. 觀察微任務隊列,發現有2
2. 打印2
3. 微任務全數完成,執行宏任務打印出1
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(1)
}, 0)
let a = new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log(2)
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log('Promise3')
}).then(() => {
console.log('Promise4')
})
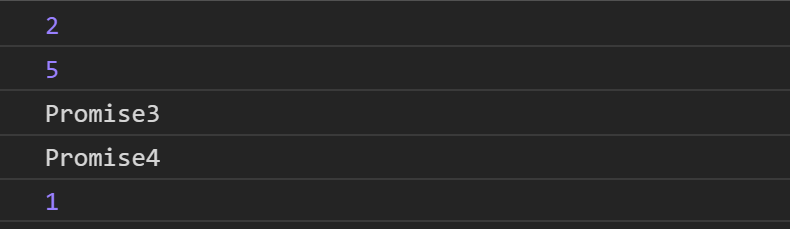
console.log(5)
- 看到setTimeout將它放進宏任務隊列
- new了一個Promise實例,但Promise的executer是同步,因此這裡打印出2,接下來看到Promise3 then 將它放進微任務隊列繼續執行(因為第二個then需等第一個完成,因此會先無視它)
- 打印出5
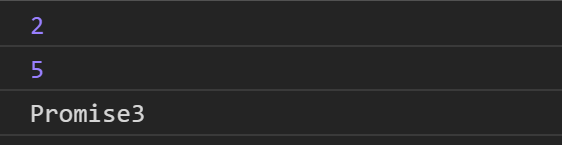
宏任務與微任務隊列:
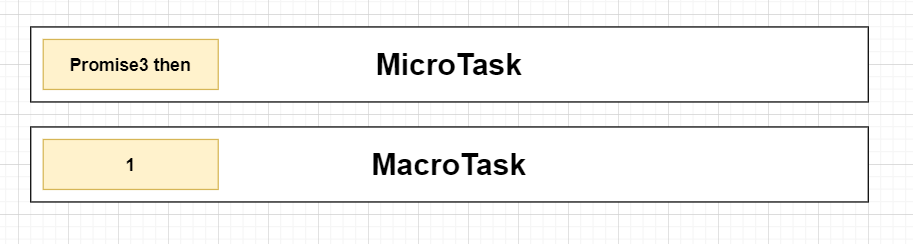
- 觀察微任務隊列,有Promise3 then,執行它,打印出Promsie3。
- 打印出Promise3之後發現下面還有一個Promise4 then(鍊式調用),將它放進微任務隊列
目前宏任務與微任務隊列:
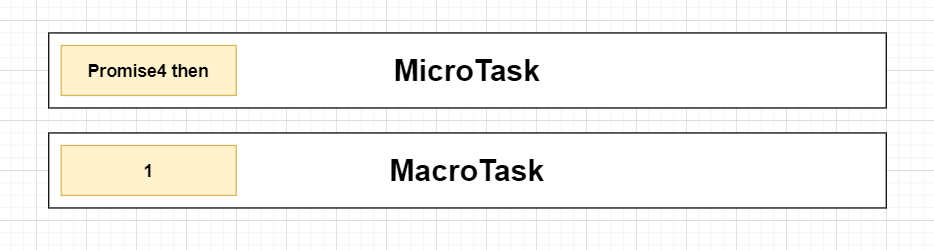
- 檢查微任務隊列是否為空,發現Promise4 then,執行它打印出Promise4
- 微任務隊列終於變空的,執行宏任務隊列(注意每執行完一個宏任務就要檢查為任務隊列是否為空)打印出1
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log("promise1")
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log("then11")
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log("promise2")
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log("then21")
}).then(() => {
console.log("then23")
})
}).then(() => {
console.log("then12")
})
- Promsie executor,所以打印promise1,並將then11放進微任務

目前宏任務與微任務隊列:
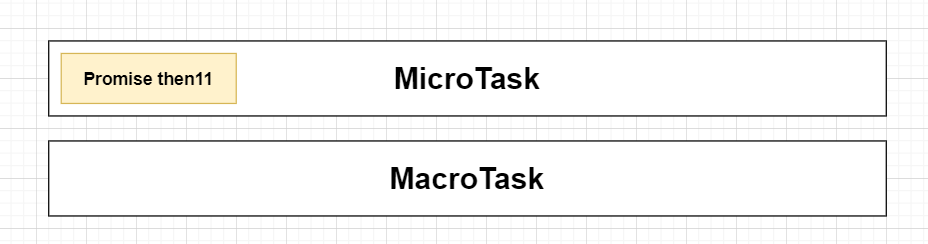
- 執行then11區塊,並打印出then11
- 又創建了一個Promise實例,因為executor為同步,所以在此打印promise2
- 碰到then21,所以將它放進微任務隊列裡,第二個then23因為要等then21區塊執行完先跳過
- then11區塊執行完成,因此將Promise then12放進微任務隊列裡面
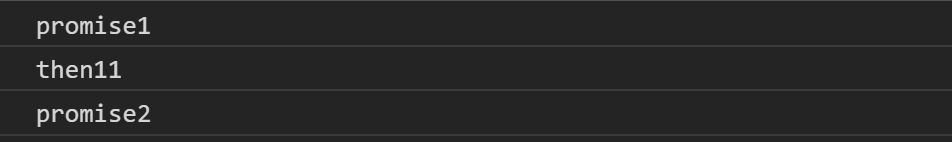
目前宏任務與微任務隊列:

- 照隊列邏輯,先進先出,因此先執行Promise then21區塊,打印出then21,然後出隊列
- 因為Promise the21執行完成,因此發現then23 將它放到隊列裡
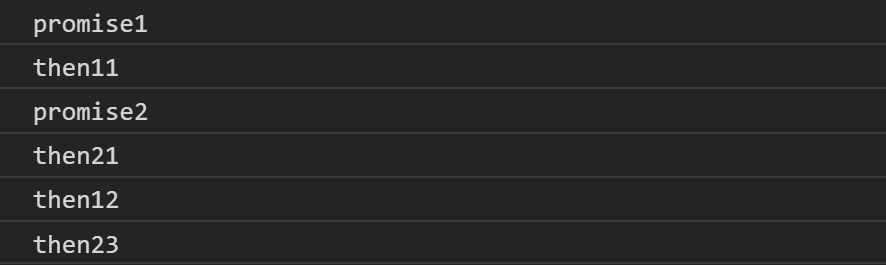
- 順著下來執行Promise then12 區塊,因此又打印出then12
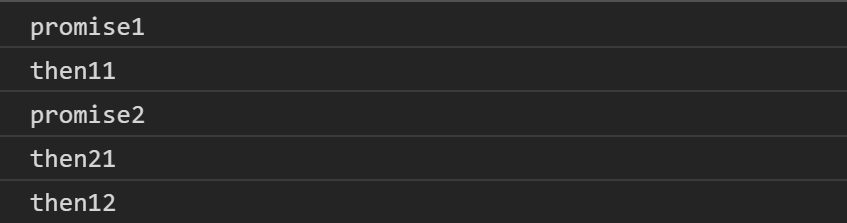
目前宏任務與微任務隊列:
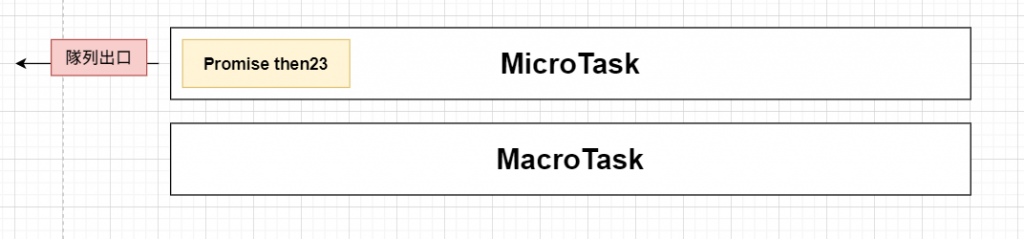
- 觀察微任務隊列,發現Promise then23,執行它並打印出then23
- 隊列皆為空,完成
async function async1() {
console.log("async1 start");
await async2();
console.log("async1 end");
}
async function async2() {
console.log( 'async2');
}
console.log("script start");
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("settimeout");
},0);
async1();
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log("promise1");
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("promise2");
});
console.log('script end');
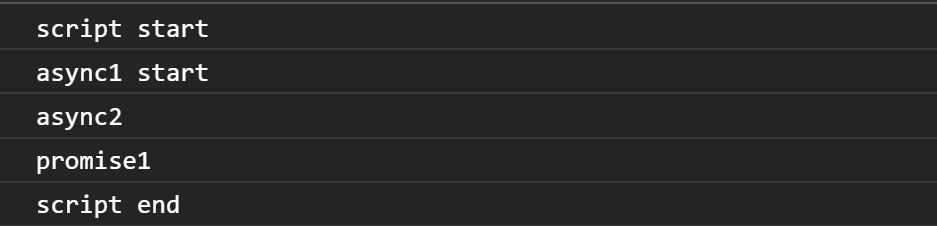
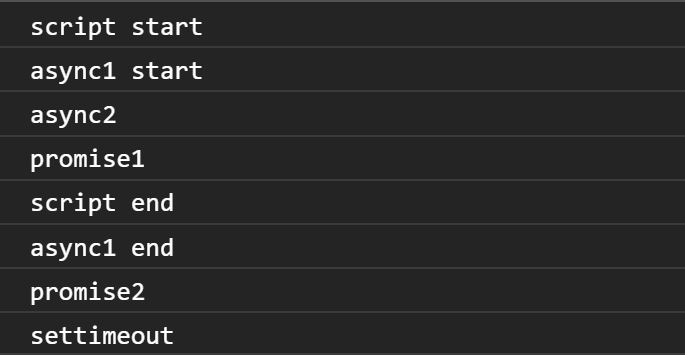
聲明了兩個函數,然後打印 script start
接下來碰到宏任務setTimeout,將它放進宏任務隊列
執行async1,回去找他聲明時候的樣子,接著打印出async1 start以及async2,並將以下為異步放進為任務隊列裡
async function async1() { // 這裡以下為同步函數(包括await後面) console.log("async1 start"); await async2(); // 以下為異步 console.log("async1 end"); } async function async2() { console.log( 'async2'); }
打印 promise1,並將promise2 then放入微任務隊列裡
打印 script end
目前宏任務與微任務隊列:
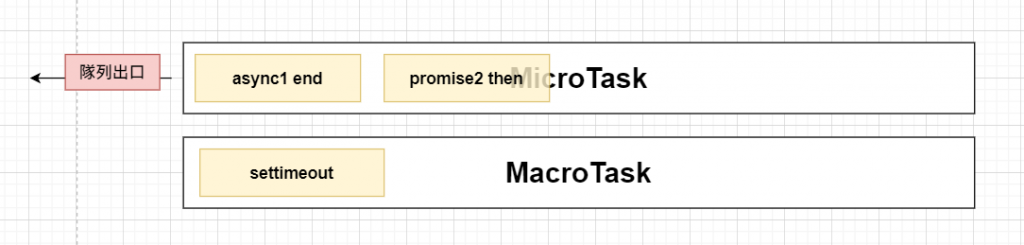
- 執行async1 end的區塊,並打印出async1 end
- 微任務隊列裡還有proimse2 then,執行它
- 打印出promise2
- 執行宏任務,並打印出settimeout
因此題提到node的EventLoop,因此我暫時跳過。有興趣的人可以解看看
async function async1() {
console.log("async1 start");
await async2();
console.log("async1 end");
}
async function async2() {
console.log( 'async2');
}
console.log("script start");
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("settimeout");
});
async1()
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log("promise1");
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("promise2");
});
setImmediate(()=>{
console.log("setImmediate")
})
process.nextTick(()=>{
console.log("process")
})
console.log('script end');
