新的CPU會需要新的compiler toolchain,而compiler toolchain的開發通常會使用現有的compiler toolchain去修改,所以我們今天會介紹如何從現有的compiler toolchain開發出新的compiler toolchain。
Compiler toolchain是一套複雜的軟體,新技術、新硬體推陳出新速度快,為每一套新系統打造一套compiler toolchain需要實作、重複驗證相同的功能、非常耗時。
因此,新系統打造的compiler toolchain大部分是從open source的compiler toolchain更改過來,open source的compiler toolchain會持續被system software developer更新、加入新功能、修復bug且獲得使用者的feedback。
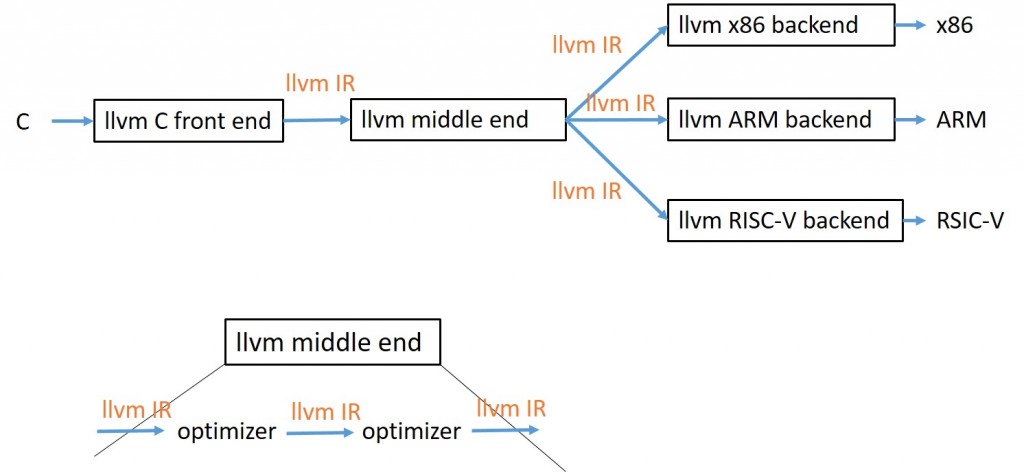
現行最大的兩套open source compiler toolchain分別是GCC和LLVM系統,其中LLVM系統的架構讓system software developer很容易依照需求改造,我們之後會再提到。
Upstream是指source code來源的管理員/作者,通常system software developer修改source code做了新功能、bug fix後會想往upstream提交。
例如: system software developer對LLVM的修改、bug fix想要提交給LLVM project,LLVM project和管理員就是upstream。
如果upstream接受了修改,則之後新出的版本都會包含這些修改,可以讓所有人受用。如果upstream不接受,則修改者必須要一直維護local版本並且一直merge到新版本的source code當中。
我們今天認識了compiler toolchain是如何依照我們的需求開發。然而,build compiler toolchain、system software的結果都會受到environment的影響,所以我們明天會介紹build environment的相關內容。
