MAUI使用了URI-based的navigation,來當做我們app中的routes。使我們能透過route流覽至app中的任何頁面,而不需要遵循設定的navigation hierarchy,並且提供navigate backwards,使我們不需瀏覽navigation stack上的所有頁面。
而有關於Navigation的屬性被定義在Shell底下
The BackButtonBehavior, CurrentItem, and CurrentState properties are backed by BindableProperty objects, which means that these properties can be targets of data bindings.
BackButtonBehavior、CurrentItem和CurrentState properties的properties都以BindableProperty物件為backed,所以這些屬性也可以做為資料繫結的目標,並且導覽室透過呼叫GoToAsync方法執行的,當瀏覽執行時,Navigating會觸發事件,並在Navigated瀏覽完成引發事件
一般我們可以透過Router屬性在TabBar、Tab和ShellContent object上的FlyoutItem坐定義
ex.
<Shell ...>
<FlyoutItem ...
Route="animals">
<Tab ...
Route="domestic">
<ShellContent ...
Route="cats" />
<ShellContent ...
Route="dogs" />
</Tab>
<ShellContent ...
Route="monkeys" />
<ShellContent ...
Route="elephants" />
<ShellContent ...
Route="bears" />
</FlyoutItem>
<ShellContent ...
Route="about" />
...
</Shell>
我們可以使用Routing.RegisterRoute來註冊我們的Router
像是我們的專案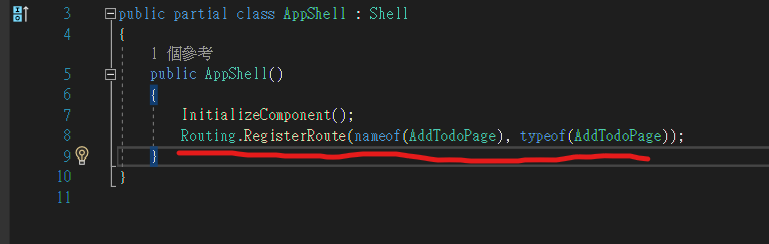
並且我們就能從app的任何位置,來瀏覽這些以 URI 為基礎的詳細資料頁,而這種頁面的router,叫做全域路由
我們可以透過呼叫GotoAsync方法來執行導覽, 此方法會導覽至ShellNavigationState,並在導覽動畫完成後傳回將會完成的Task
像是我們的TodoViewModel中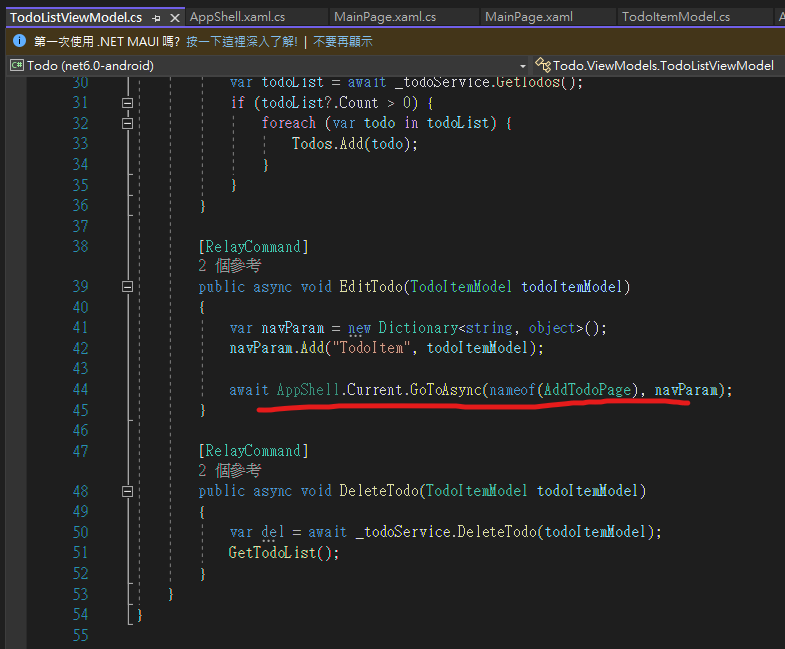
直行我們註冊過的AddTodoPage路由並傳遞參數
await AppShell.Current.GoToAsync(nameof(AddTodoPage), navParam);
v1.0今天簡單的介紹一下路由,我們明天見
