This chapter will continue to introduce advanced topics related to inheritance. If you have any questions about the previous content, you can go back and review it.this and super are two object keywords commonly used in inheritance.
The usage of the two is roughly the same, but the main difference is in the things they represent:
this represents accessing the properties of the “own class”; super represents accessing the properties of the “parent class”
The advantage of using these two keywords is that
The declaration of this is in the following format:
this.attribute of its own class (argument passed in);
/*First File : Student.java*/
class Student{
String name;
int group;
char gpa;
static int count = 0;
Student(){
name = "Unknowen";
group = 1;
gpa = 'C';
count++;
}
Student(String name){
this(); //初始化內容
this.name = name;
}
Student(String name, int group){
this(name);
this.group = group;
}
Student(String name, int group, char gpa){
this(name,group);
this.gpa = gpa;
}
void printout_info(){
System.out.println("Student ID : " + count);
System.out.println("Student name : " + name);
System.out.println("Student group : " + group);
System.out.println("Student gpa : " + gpa);
}
}
/*Second File : Grade.java*/
class Grade{
public static void main(String[] args){
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.printout_info();
Student s2 = new Student("c");
s2.printout_info();
Student s3 = new Student("ch",2);
s3.printout_info();
Student s4 = new Student("chi",3,A);
s4.printout_info();
}
}
Output :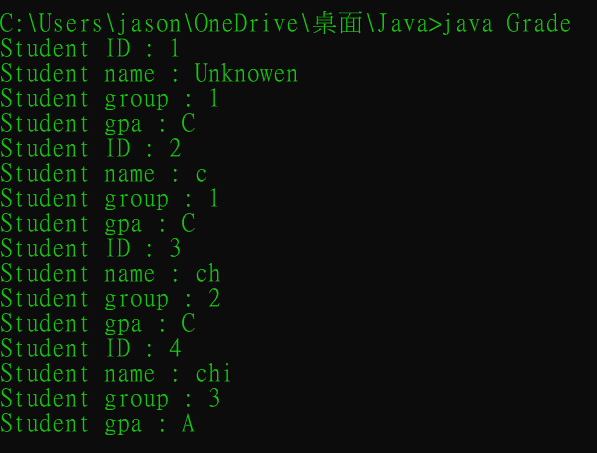
this is the keyword that represents “its own class”
super is declared in the same way as this. In this section, we combine the two keywords and use inheritance observation.
class Sum
{
protected int num;
protected int total;
public void show_num(){
System.out.println("num = " + num);
}
Sum(int a, int b){
this.total = a + b;
}
void printout_sum(){
System.out.println(this.total);
}
}
class Add extends Sum
{
Add(int a, int b){
super(a,b);
}
int num;
public void show_num(){
super.num = 126;
this.num = 136;
System.out.println("num = "+ num);
super.show_num();
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
Add new_obj = new Add(46,29);
new_obj.printout_sum();
new_obj.show_num();
}
}
Outcome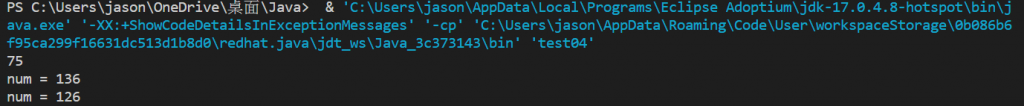
super sets the variable in the parent class, and this sets the variable in this class. Therefore, the num printed on the next line is the variable in the subclass, and then the parent class.super to print it.super is the keyword for “parent class”.
Resource:[Java]super() 與 this()、Java備忘筆記
