今天是紀錄LeetCode解題的第二十三天
又來看一題困難題
第二十三題題目:You are given an array of k linked-lists lists, each linked-list is sorted in ascending order.
Merge all the linked-lists into one sorted linked-list and return it.
給定k個鏈結串列,每個鏈結串列按升序排列,將所有鏈結串列合併成一個並回傳
分治法(Divide and Conquer)
最小堆(Min-Heap/Priority Queue)
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[Optional[ListNode]]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not lists:
return None
return self.mergeRange(lists,0,len(lists)-1)
def mergeRange(self,lists,left,right):
if left == right:
return lists[left]
mid = (left + right) // 2
l1 = self.mergeRange(lists,left,mid)
l2 = self.mergeRange(lists,mid + 1,right)
return self.mergeTwoList(l1,l2)
def mergeTwoList(self,l1,l2):
dummy = ListNode(0)
tail = dummy
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val < l2.val:
tail.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
else:
tail.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
tail = tail.next
tail.next = l1 if l1 else l2
return dummy.next
初始狀態
分治過程
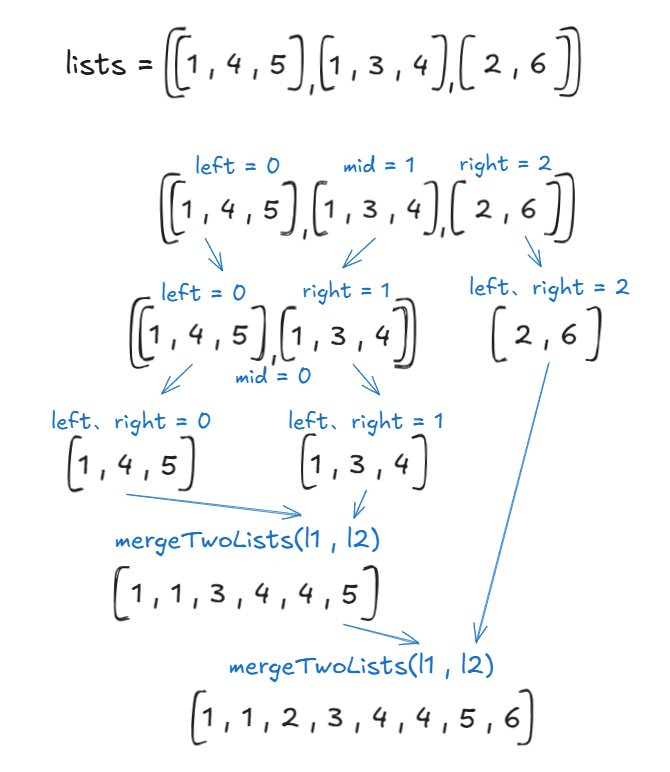
合併過程
import heapq
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[Optional[ListNode]]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
heap = []
dummy = ListNode(0)
tail = dummy
for i,node in enumerate(lists): #加上i來避免node.val相同時無法比較node物件
if node:
heapq.heappush(heap,(node.val,i,node)) #初始先把鏈結串列的最小值都加入到heap中
while heap:
val,idx,node = heapq.heappop(heap) #取出最小的值
tail.next = node
tail = tail.next
if node.next:
heapq.heappush(heap, (node.next.val, idx, node.next)) #把剛加入的最小值的下一個節點加入到heap裡
return dummy.next
heapq是Python內建的模組,可以把list當作最小堆操作
| 函式 | 說明 |
|---|---|
heapq.heappush(heap, item) |
把一個元素放進最小堆中 |
heapq.heappop(heap) |
取出並移除堆中「最小」的元素 |
heapq.heapify(lst) |
把 list 轉成最小堆 |
初始狀態
第一次執行
第二次執行
第三次執行
第四次執行
第五次執行

依此類推直到heap為空為止就合併排序好所有鏈結串列了
分治法
不斷將鏈結串列拆分,分為左半邊left ~ mid及右半邊mid + 1 ~ right,再將拆分的範圍傳入函式繼續拆分,直到拆分到只剩下一個鏈結串列,也就是left = right時,回傳鏈結串列,接著做合併
最小堆
先取出每個鏈結串列中最小的節點並放進heap裡,再從heap中取出最小的節點放到結果鏈結串列中,接著把該最小節點的下一個節點放進heap,循環往復直到heap為空(小細節:取出的節點值要記錄索引值,避免節點的值相同的情況下無法比較node物件大小)
