JS 有許多原生方法都是 impure 的,而 mutable data 容易產生預期外的 side Effect 也是造成 Bug 的主要來源之一,當然你可以直接用上一篇推薦的 ImmutableJS 來避免變動資料,但若不想要額外引入 Library 又必須用到那些不純函式的方法怎麼辦?
這一篇會來介紹如何將 Mutable array/object 改成 Immutable array/object
去年鐵人賽在介紹 陣列 Array ,有列出所有常見 Array Method 經過運算後回傳什麼跟原本陣列是否變動
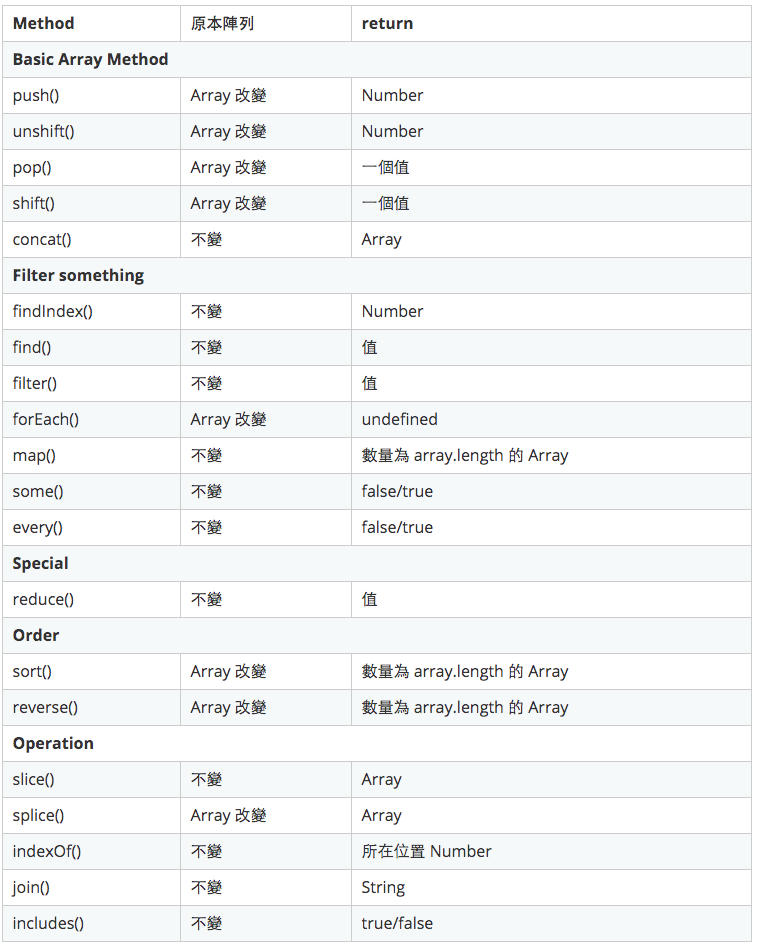
以下就來嘗試把 Mutable array operations 改成 immutable 吧
// 初始值,以下範例都會共用這個 -----
const colors = ['red', 'yellow', 'blue'];
在 Array "後面" 加上新值
// native method mutable array
const newColor = colors.push('purple', 'green');
console.log(colors) // ['red', 'yellow', 'blue', 'purple', 'green']
console.log(newColor) // 5 <- 陣列長度
// immutable
const purePush = (arr, newEntry) => [...arr, ...newEntry];
const newColor = purePush(colors, ['purple', 'green'])
console.log(colors) // ['red', 'yellow', 'blue']
console.log(newColor) // ['red', 'yellow', 'blue', 'purple', 'green']
在原本的 Array "前面"加上新值
// native method mutable array
const newColor = colors.unshift('purple', 'green');
console.log(colors) // ['purple', 'green', 'red', 'yellow', 'blue' ]
console.log(newColor) // 5 <- 陣列長度
// immutable
const pureUnshift = (arr, newEntry) => [ ...newEntry, ...arr ];
const newColor = pureUnshift(colors, ['purple', 'green'])
console.log(colors) // ['red', 'yellow', 'blue']
console.log(newColor) // ['purple', 'green', 'red', 'yellow', 'blue' ]
移除原本陣列"最後面"的第一個值
// native method mutable array
const newColor = colors.pop();
console.log(colors) // ['red', 'yellow']
console.log(newColor) // 'blue'
// immutable
const purePop = arr => arr.slice(0, -1)
const newColor = purePop(colors)
console.log(colors) // ['red', 'yellow', 'blue']
console.log(newColor) // ['red', 'yellow']
移除原本陣列"最前面"的第一個值
// native method mutable array
const newColor = colors.shift();
console.log(colors) // ['yellow', 'blue' ]
console.log(newColor) // 'red'
// immutable
const purePop = arr => arr.slice(1)
const newColor = purePop(colors)
console.log(colors) // ['red', 'yellow', 'blue']
console.log(newColor) // ['yellow', 'blue']
排序,若沒有 compareFunction,會先自動 .toString() 轉成字串,回傳一個根據 Unicode 排序 array.length 長度的 array 。
// native method mutable array
const newColor = colors.sort();
console.log(colors) // ['blue', 'red', 'yellow']
console.log(newColor) // ['blue', 'red', 'yellow']
// immutable,無替代語法,只能拷貝出新陣列作 sort
const pureSort = (arr, compareFunction) => [ ...arr ].sort(compareFunction)
const newColor = pureSort(colors)
console.log(colors) // ['red', 'yellow', 'blue' ]
console.log(newColor) // '['blue', 'red', 'yellow']
Note. 若不想使用原生 sort 解法,可以看以下 良葛格 的補充留言
回傳反過來長度為 array.length 的陣列
// native method mutable array
const newColor = colors.reverse();
console.log(colors); // ['blue', 'yellow', 'red']
console.log(newColor); // ['blue', 'yellow', 'red']
// immutable,無替代語法,只能拷貝出新陣列作 reverse
const pureReverse = arr => [ ...arr ].reverse();
const newColor = pureReverse(colors)
console.log(colors); // ['red', 'yellow', 'blue']
console.log(newColor); // ['blue', 'yellow', 'red']
感謝良葛格補充不使用原生 reverse 的解法
const pureReverse = arr => [ ...arr ].reduceRight((accumulator, elem) => accumulator.concat([elem]), []);
const newColor = pureReverse(colors);
console.log(colors); // ['red', 'yellow', 'blue']
console.log(newColor); // ['blue', 'yellow', 'red']
Object 相對來說容易一些
// mutable
const state = {
selected: 'apple',
quantity: 13,
fruits: ['orange', 'apple', 'lemon', 'banana']
};
state.selected = 'orange';
state.quantity = 5;
state.origin = 'imported from Spain';
/*
state = {
selected: 'orange',
quantity: 5,
fruits: ['orange', 'apple', 'lemon', 'banana'],
origin: 'imported from Spain'
}
*/
// immutable
const state = {
selected: 'apple',
quantity: 13,
fruits: ['orange', 'apple', 'lemon', 'banana']
};
const newState = {
...state,
selected: 'orange',
quantity: 5,
origin: 'imported from Spain'
};
/*
newState = {
fruits: ['orange', 'apple', 'lemon', 'banana'],
selected: 'orange',
quantity: 5,
origin: 'imported from Spain'
}
*/
// mutable
const state = {
selected: 'apple',
quantity: 13,
fruits: ['orange', 'apple', 'lemon', 'banana']
};
delete state.quantity;
/*
state = {
selected: 'apple',
fruits: ['orange', 'apple', 'lemon', 'banana']
}
*/
// immutable
const state = {
selected: 'apple',
quantity: 13,
fruits: ['orange', 'apple', 'lemon', 'banana']
};
const { quantity, ...newState } = state;
/*
quantity = 13
newState = {
selected: 'apple',
fruits: ['orange', 'apple', 'lemon', 'banana']
}
*/
這篇概念其實相當簡單卻很重要! 但還是要強調雖然變成 Immutable data 可以減少發生預期外的 Side Effect,但因為每次都需要先 Clone 一個 Array/Oject 出來,若處理大量資料時是相當耗費記憶體空間的!
自己這樣寫到第七天也學到並沒有一種寫法是絕對好壞,而是要了解他然後在不同的情況選擇最適合的方式運用。
如有錯誤或需要改進的地方,拜託跟我說。
我會以最快速度修改,感謝您
歡迎追蹤我的部落格,除了技術文也會分享一些在矽谷工作的甘苦。

感謝分享 已訂閱
幫忙抓一下 Typo XD
...但若不想要額外引入
Librabry又必須...
...需要先 Clone 一個 Array/
Oject出來,若處理大量資料時是相當好(多字?)耗費記憶體空間的!
辛苦了 加油!![]()
感謝眼尖,已修正囉
不使用 Array.prototype.reverse 的方式:
const colors = ['red', 'yellow', 'blue'];
const pureReverse = arr => [ ...arr ].reduceRight((accumulator, elem) => accumulator.concat([elem]), []);
const newColor = pureReverse(colors);
console.log(colors); // ['red', 'yellow', 'blue']
console.log(newColor); // ['blue', 'yellow', 'red']
排序的話比較麻煩:
// quick sort
function sorted(array, comp) {
if(array.length === 0) {
return array;
}
const head = array[0];
const tail = array.slice(1);
const before = sorted(tail.filter(elem => comp(head, elem) >= 0), comp);
const after = sorted(tail.filter(elem => comp(head, elem) < 0), comp);
return before.concat([head]).concat(after);
}
const numbers = [5, 9, 3, 6, 4];
console.log(sorted(numbers, (e1, e2) => e1 - e2)); // [3, 4, 5, 6, 9]
console.log(sorted(numbers, (e1, e2) => e2 - e1)); // [9, 6, 5, 4, 3]
謝謝補充,我再加上去 ![]()
以下就來嘗試把 Immutable array operations 改成 immutable 吧
這邊應該前面是Mutable?
最近才開始拜讀這系列文章, 收穫良多, 真心感激啊!!
對沒錯,已更新 謝謝你