今天大概會聊到的範圍
- AnnotatedString
- Text
在 Compose 中顯示文字時,我們可以使用 Text 這個 Composable。但沒有任何一個文字是單獨存在的,所有的文字都會搭配著字型、大小、顏色來顯示。
讓我們來看看 Text 的 function 定義:
@Composable
fun Text(
text: String,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
color: Color = Color.Unspecified,
fontSize: TextUnit = TextUnit.Unspecified,
fontStyle: FontStyle? = null,
fontWeight: FontWeight? = null,
fontFamily: FontFamily? = null,
letterSpacing: TextUnit = TextUnit.Unspecified,
textDecoration: TextDecoration? = null,
textAlign: TextAlign? = null,
lineHeight: TextUnit = TextUnit.Unspecified,
overflow: TextOverflow = TextOverflow.Clip,
softWrap: Boolean = true,
maxLines: Int = Int.MAX_VALUE,
onTextLayout: (TextLayoutResult) -> Unit = {},
style: TextStyle = LocalTextStyle.current
)
Text 這個 Composable 是一個參數很多的 Composable ,text 和 modifier 算是最好理解的,另外很多參數可以用來調整、美化這個文字。
剛剛提到的字型、大小及顏色,分別就是 fontFamily 代表字型,color,代表文字顏色。fontSize 就是文字大小。
除了這些之外,fontStyle 就是常見的斜體,可以透過 fontStyle = FontStyle.Italic 設定。
那粗體呢?粗體可以透過 fontWeight 設定。fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold 可以設定成常見的粗體。但 fontWeight 還有不同的級距,從 FontWeight.Thin ~ FontWeight.Black,同時也代表 FontWeight.W100 ~ FontWeight.W900,數字越大字越粗。
字元間距可以透過 letterSpacing 設定,行高可以透過 lineHeight 設定。如果想要做刪除線或底線,可以透過 textDecoration 進行裝飾。
如果文字很長時,可以透過 overflow 設定當文字超出框時是要截斷還是留三個點、透過 softWrap 決定是否要換行,最後透過 maxLines 設定換行後最多可以有幾行。
如果有常用的文字格式,可以透過 TextStyle 將上述說到的各種參數設定好後,在透過 style 參數一次設定整個格式。要注意的是 style 與外部的其他參數同時設定時,會被外部的參數給覆寫掉
Text(
text = "AAAAA",
color = Color.Green,
style = TextStyle(
color = Color.Red
)
)
雖然 TextStyle 內有設定
color = Color.Red,但會被外部的color = Color.Green覆蓋掉,顯示綠色
剛剛其實刻意簡化了 text 這個參數,text 除了可以接收 String 之外,還能接受 AnnotatedString。
AnnotatedString 其實很類似原本 android.text 的 SpannableString。 可以逐字的調整文字的 style。
Text(
text = AnnotatedString(
"BBBBB",
spanStyle = SpanStyle(
color = Color.Green
)
)
)
這樣 BBBBB 會顯示為綠色
這樣好像和直接設定顏色沒什麼差異?那 AnnotatedString 的好處到底在哪裡呢?
Text(
text =
AnnotatedString(
"BBBBB",
spanStyle = SpanStyle(
color = Color.Green
)
) + AnnotatedString(
"BBBBB",
spanStyle = SpanStyle(
color = Color.Red,
fontWeight = FontWeight.Black
)
)
)

AnnotatedString 可以互相串接。同一個 Text component 內可以有多個不同的 style
Text(
text = buildAnnotatedString {
append(
AnnotatedString("CCCCC", spanStyle = SpanStyle(Color.Red))
)
append(
AnnotatedString("CCCCC", spanStyle = SpanStyle(Color.Green))
)
append(
AnnotatedString("CCCCC", spanStyle = SpanStyle(Color.Blue))
)
}
)

也可以透過 builder 做到一樣的事情,將不同的 AnnotatedString 加在一起。也可以 append 沒有 style 的文字
Text(
text = buildAnnotatedString {
append(
AnnotatedString("Red", spanStyle = SpanStyle(Color.Red))
)
append(" is not ")
append(
AnnotatedString("Blue", spanStyle = SpanStyle(Color.Blue))
)
}
)
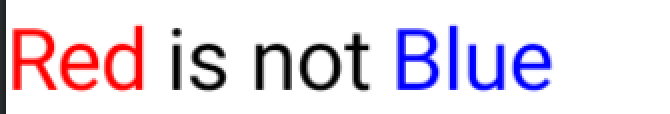
一樣是透過 builder,我們可以先設定一個字串,在對特定的位置設定特定的 style。Style 重複設定在一樣的位置上。例如這邊我想將第一個字和第二個字設定為不同顏色,但是兩個字都要有底線:
Text(
text = buildAnnotatedString {
append("Multiple style in one text")
addStyle(
style = SpanStyle(
color = Color.Red,
fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold,
fontStyle = FontStyle.Italic
),
start = 0,
end = 8
)
addStyle(
style = SpanStyle(
color = Color.Blue,
fontFamily = FontFamily.Monospace,
),
start = 9,
end = 14
)
addStyle(
style = SpanStyle(
textDecoration = TextDecoration.Underline
),
start = 0,
end = 14
)
},
)
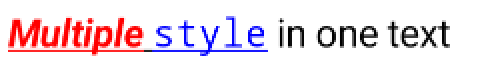
在使用原本的 Android TextView 時,我們若要做到一樣的動作,會需要使用 SpannableString。但是 SpannableString 之所以可以運作,是因為 TextView 的內部,會去判斷目前的文字是否是 Spannable ,並且特殊處理。但在 Compose 中,Text 不會去判斷 SpannableString,因此無法使用原先在 Android 專案中建立好的 SpannableString。
因此,在使用 Compose 時,會需要重新建構 AnnotatedString。但為了滿足好奇,還是研究了一下如何將 SpannableString 轉換成 AnnotatedString。
fun SpannableStringBuilder.toAnnotatedString(): AnnotatedString {
// ...
}
我在 SpannableStringBuilder 上建立一個 toAnnotatedString 的 extension function,並預期這個 function 回傳 AnnotatedString
data class SpanCollection(val start: Int, val end: Int, val spanStyles: List<CharacterStyle>)
fun SpannableStringBuilder.toAnnotatedString(): AnnotatedString {
var idx = 0
var next: Int
val spanCollections = mutableListOf<SpanCollection>()
while (idx < this.length) {
// find the next span trasition
next = nextSpanTransition(idx, this.length, CharacterStyle::class.java)
// get all spans in this range
val charStyleSpans = getSpans(idx, next, CharacterStyle::class.java)
spanCollections.add(SpanCollection(idx, next, charStyleSpans.toList()))
idx = next
}
// ...
}
在開始組成 AnnotatedString 之前,先透過 while loop 將 SpannableStringBuilder 中的每個 SpanStyle 抓出來,並且將 style 與其影響的位置存放在一個 list 中。
fun SpannableStringBuilder.toAnnotatedString(): AnnotatedString {
var idx = 0
var next: Int
val spanCollections = mutableListOf<SpanCollection>()
while (idx < this.length) {
// find the next span trasition
next = nextSpanTransition(idx, this.length, CharacterStyle::class.java)
// get all spans in this range
val charStyleSpans = getSpans(idx, next, CharacterStyle::class.java)
spanCollections.add(SpanCollection(idx, next, charStyleSpans.toList()))
idx = next
}
return buildAnnotatedString {
append(this@toAnnotatedString.toString())
spanCollections.forEach { spanCollection ->
val (start, end, spans) = spanCollection
spans.forEach {
when (it) {
is ForegroundColorSpan -> {
val span = it
addStyle(
style = SpanStyle(color = Color(span.foregroundColor)),
start = start,
end = end
)
}
// .. other SpanStyle
}
}
}
}
}
最後,透過 builder 將 style 一一加入,建構 AnnotatedString。這邊比較麻煩的是要將所有 SpanStyle 列舉出來,並逐一轉換成對應的 AnnotatedString 的 SpanStyle
Text 可能會是最常用的元件之一。雖然並不是所有的樣式都會很常用到,但了解這個最基礎元件的用法,也許會在有需要的時候有點幫助。
Reference:
