介紹完constructor建構子,今天起講一個可能是封裝方面最重要的主題:封裝的「保護層級」。
p開頭。#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Tree
{
public:
string breed; // public attribute(公開屬性)
// constructor建構子(也是公開)。
Tree(string breed, int age, int height)
{
cout << ".在Constructor中..." << endl;
this->breed = breed;
this->age = age;
this->height = height;
cout << " 所有屬性的初值都已設定。" << endl;
}
void ShowInfo() // public method(公開方法)
{
cout << " breed(public) : " << breed << endl;
cout << " age(protected) : " << age << endl;
cout << " height(private): " << height << endl;
}
protected:
int age;
private:
int height;
};
int main()
{
// Create an instance(object) without using the 'new' operator.
Tree Laozi("cedar", 2593, 59);
// C++的constructor只能在「創建物件」時由C++的compiler自動調用,不可外顯呼叫。
// Laozi.Tree("cedar", 2593, 59); // 這樣會引發執行時期錯誤。
cout << "\n.透過呼叫Laozi.ShowInfo()方法取值。protected/private的屬性均可存取:\n";
Laozi.ShowInfo();
cout << "\n.用object.attribute(物件.屬性)表示法取值。只能存取public層級的屬性:\n";
cout << " Laozi's breed(public) : " << Laozi.breed << endl;
// cout << " Laozi's age(protected) : " << Laozi.age << endl;
// cout << " Laozi's height(private): " << Laozi.height << endl;
}

講完C++, Java, C#等C-like語言,回頭看Python:
Python的封裝層級,表面上也有public / protected / private這三個p's。
可是protected只是「約定俗成」,並未實際支援,所以實際上只有public和private兩層。
和上面C++類似的Python code如下:
class Tree():
def __init__(self, breed, age, height): # constructor
self.breed = breed # public: 名稱前面沒有底線。
self._age = age # protected: 前綴一條底線(無實質保護效果)。
self.__height = height # private: 前綴兩條底線(有實質保護效果)。
def show_info(self):
print(f' breed(public): {self.breed}')
print(f' age(protected): {self._age}')
print(f' height(private): {self.__height}')
# Create an object(instance) based on class Tree.
laozi = Tree('cedar', 2593, 59)
print('\n.透過呼叫laozi.show_info()方法取值。private屬性也可存取:')
laozi.show_info()
print('\n.用「物件.屬性」表示法取值。只能存取public和protected層級屬性:')
print(f" laozi's breed(public): {laozi.breed}")
print(f" laozi's age(protected): {laozi._age}")
# print(f" laozi's height(private): {laozi.__height}")
輸出: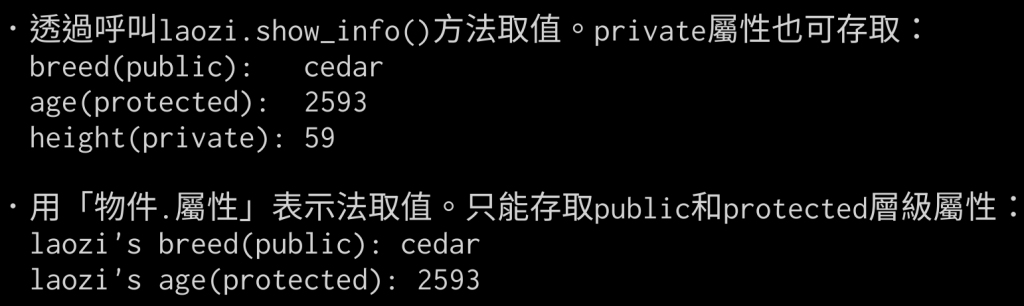
剛才講的類別內部、外部,以及「物件.屬性」的表示法的進一步解釋,就留待明天再說。
註1:所謂子孫,是Subclasses之意,屬於繼承(Inheritance)範疇。講繼承時詳談。
