昨天已大致了解路由的建立,但是如果我們有好幾個方法都要共用一個路由呢?
這就是今天要討論的重點!
以 /book 作為範例,如果要因應各種請求方法做回覆,最基本的寫法為:
// app.js
app.get('/book', (req, res) => {
res.send('Get a book')
})
app.post('/book', (req, res) => {
res.send('Post a book')
})
app.delete('/book', (req, res) => {
res.send('Delete the book')
})
以上方式也可以順利完成請求回覆,但缺點就是有太多冗長的程式,
如果要把路由 /book 改成 /books 就要一次改 GET / POST / DELETE 等地方,
維護起來相對不容易,以下提供兩個方式做優化:
可以從昨天寫的 app.METHOD() 延伸,相同的路徑底下寫不同的方法:
// app.js
app.route('/book')
.get((req, res) => {
res.send('Get a book')
})
.post((req, res) => {
res.send('Post a book')
})
.delete((req, res) => {
res.send('Delete the book')
})
更好的方式,就是今天要著重介紹的路由模組化。
說到模組化,就要先說到 express.Router() 這個模組:
express.Router() 是一個路由系統,只要建立起 Router 物件,
然後設定這個物件的路由規則,就可以針對這系列的路由做管理。
我們實做看看會更有感覺:
ironman 專案底下建立一個 routes 資料夾。routes 資料夾建立 modules 資料夾和 index.js 的檔案(負責管理 modules 裡面所有路由)。modules 資料夾建立 book.js 檔案(負責管理 book 的相關路徑)。book.js 檔案引用 express.Router() 模組。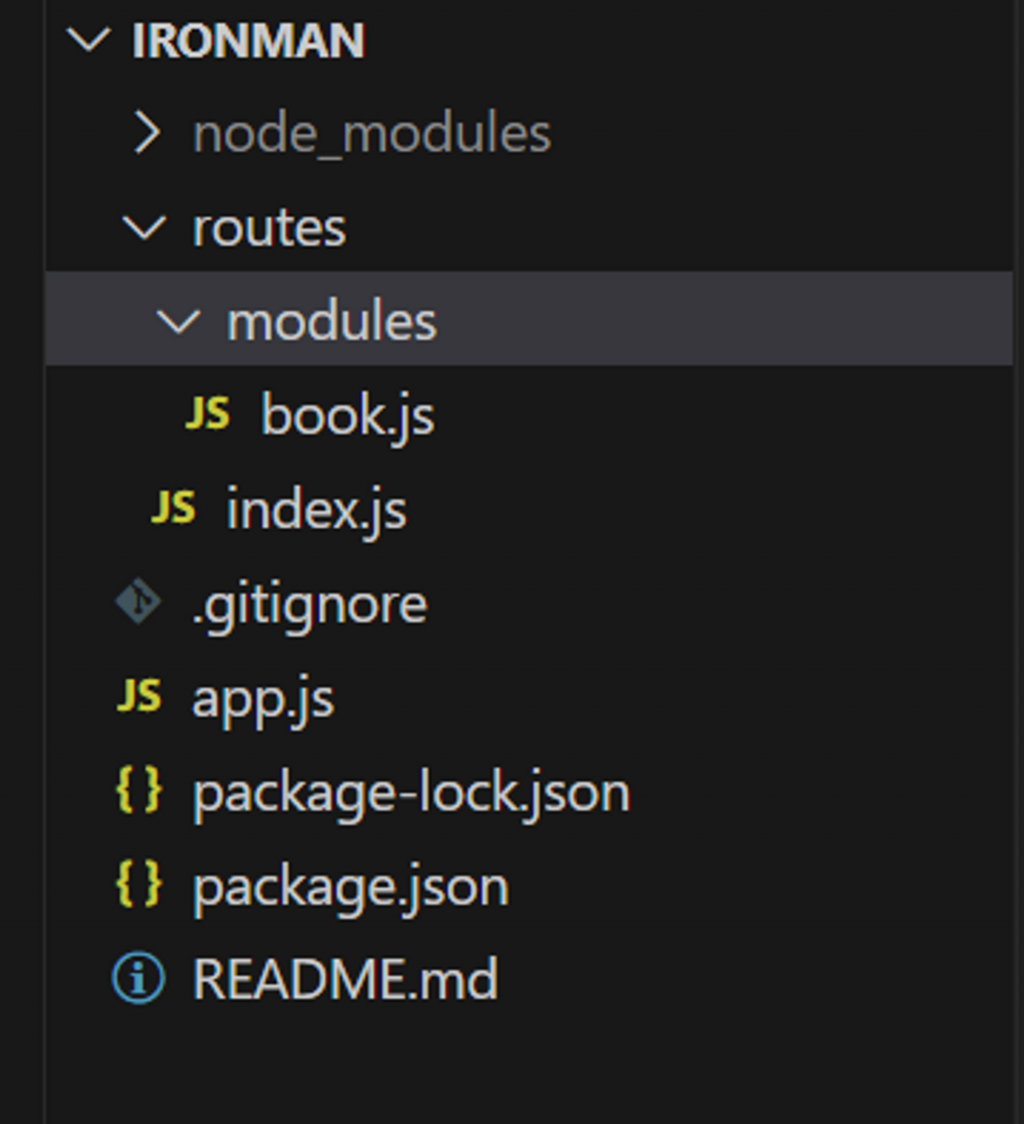
將 book 路由的方法寫在底下,有關 book 路由的架構就初步完成了!
(注意,這裡的 path 是接續 /book 之後要串連的路徑,如果沒有的話就設定 /)
// book.js
const express = require('express')
const router = express.Router()
// define the book page route by get method
router.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Get a book')
})
// define the book route by post method
router.post('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Post a book')
})
// define the book route by delete method
router.delete('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Delete the book')
})
module.exports = router
之後就要將整個路由的流程引入 routes 資料夾底下的 index.js 和我們的主程式 app.js。
// /routes/index.js
const express = require('express')
const router = express.Router()
const book = require('./modules/book') // book 路由
router.use('/book', book)
module.exports = router
// app.js
const express = require('express')
const router = require('./routes') // 引用 router 模組
const app = express()
const port = 3000
app.use(router) // 使用 router
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`)
})
將伺服器開起來後打開瀏覽器,也可以順利取得 book 頁面資料啦!
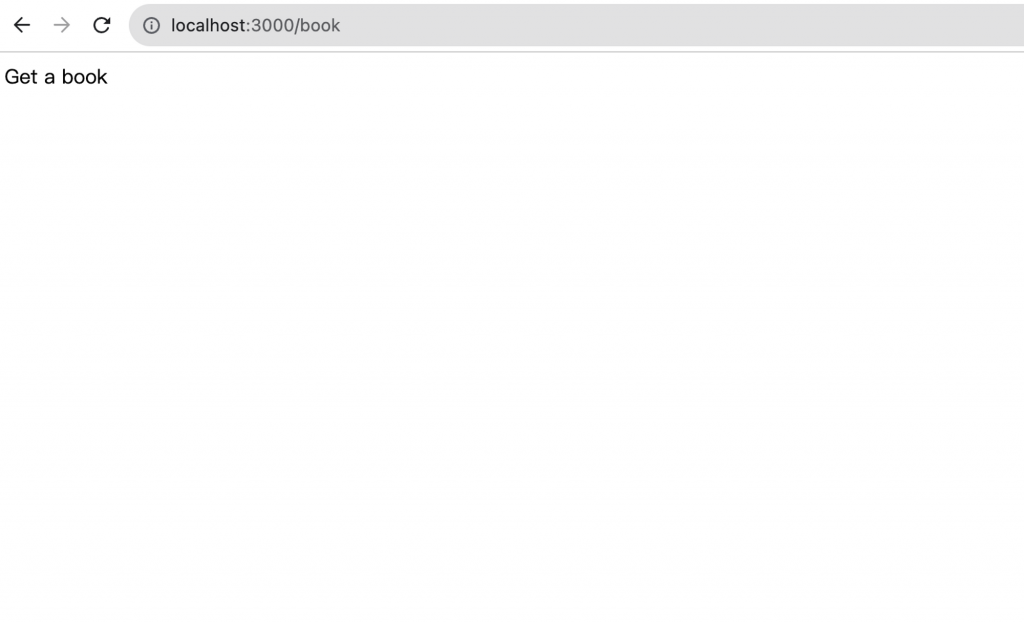
雖然感覺在寫的過程中比較繁複,但是將每個環節進行拆解之後,對於以後維護或除錯會很有幫助,
你會很感激當時有建立起模組化的自己![]()
對於路由的介紹就到這裡結束,大家明天見~
