🔸 在 Kubernetes 部署應用程式時,設定檔(Configuration)與敏感資訊(Secrets)是不可或缺的部分。
🔸 傳統上我們可能會把這些資訊硬寫在程式碼或映像檔中,但這樣做不僅不安全,也會降低靈活性。
🔸 K8s 提供了 ConfigMap 與 Secret 兩個核心資源,分別用來管理「非敏感」與「敏感」的設定,幫助我們在部署中達到 配置與程式解耦 的目標。
kubectl create configmap 指令建立apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: demo-config
data:
APP_ENV: "dev"
API_URL: "http://example.com"
app.conf: |
# Sample configuration file
setting1 = value1
setting2 = value2
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: demo-secret
type: Opaque
data:
USERNAME: ZGV2X3VzZXI= # base64(dev_user)
PASSWORD: MTIzNDU2 # base64(123456)
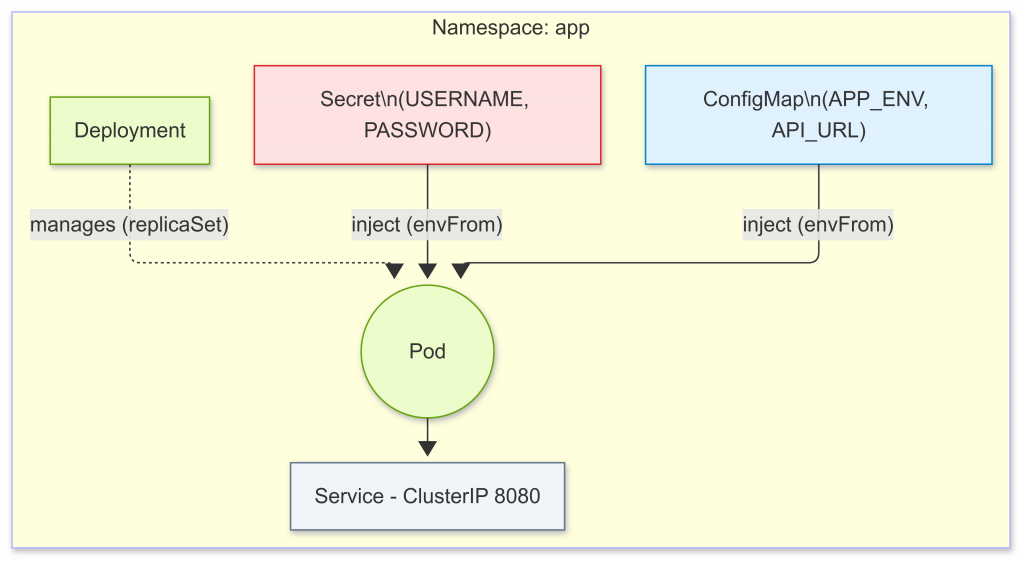
envFrom 載入 ConfigMap 與 Secret,驗證注入是否成功apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: demo-app
spec:
selector:
matchLabels: { app: demo-app }
template:
metadata:
labels: { app: demo-app }
spec:
containers:
- name: app
image: busybox
command: ["sh", "-c", "printenv | grep -E 'APP_ENV|API_URL|USERNAME|PASSWORD'; sleep 3600"]
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: demo-config
- secretRef:
name: demo-secret
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: demo-svc
spec:
selector:
app: demo-app
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
type: ClusterIP




minikube kubectl -- apply -f .

printenv
ls /etc/...

kubectl delete -f .

🔸 ConfigMap 適合非敏感資料;Secret 用於敏感資料
🔸 Secret 雖然用 Base64 存放,但不是加密,建議搭配 Vault 或 KMS
🔸 建立 Secret 時要注意權限控管(RBAC)
🔸 ConfigMap 與 Secret 更新後,Pod 不會自動重啟,需搭配 Checksum Annotation 或 kubectl rollout restart
🔸 ConfigMap 與 Secret:分別處理設定檔管理與敏感資訊管理
🔸 Deployment 與 Service:確保應用程式能正常運作與存取
🔸 透過這些資源,我們能將程式碼與環境設定解耦,提升靈活性與安全性
Day 15|Helm Chart 入門(實作)
