30 kang thiau-chiàn CompTIA Security SY0—701
Dimain 1.0: General Security Concepts
1.2 Summarize fundamental security concepts
1.2 Summarize 基本的安全觀念(ki-pún ê an-choân koan-liām)
1. Confidentiality, Integrity, Available(CIA)
mā-sī CIA Triad
-
Confidentiality:
資料 kan-na 被授權的人會用得提取 lih。
Encryption, access control, authentication 來維持 confidentiality°
-
Integrity:
Kan-na 被授權的人會用得修改資料。
資料佇伊 ê 性命週期 sī accurate, consistent, trustworthy。
用 hashing, checksum, digital signature 來保證 data integrity。
-
Available:
被授權 ê 使用者需要 ê sî-chūn 會用得馬上提取資訊。
Redundancy, failover solutions, regular backups 來維持 available。
2. Nonrepudiation
預防 denial of actions
個人 ia̍h-sī 系統 袂使 m̄ 承認 i 進前做kòe ê 代誌,chheⁿ-chhiūⁿ 傳送訊息、簽署文件。
3. Authentication, Authorization, Accounting (AAA)
-
Authentication(驗證 Giām-chèng):
證明使用者、電腦裝置 tī 電腦系統 ê 身份。目的 sī beh 保證 kan-na 被授權的 chiah ē-êng-lit 使用電腦系統。
用 username password、biometrics、one-time tokens、digital certificate 來驗證。
-
Authenticating People
- Something You Know: 使用 knowledge-based 驗證 chhiūⁿ passwords、PINs。
- Something You Have: 使用 possession-based 驗證 chhiūⁿ smart card(智慧卡)、security token、mobile device。
- Something You Are: 使用 biometric(生物辨識技術) 驗證 chhiūⁿ fingerprints、retina scans、facial recognition。
- Somewhere You Are: 依靠 location-based 驗證 chhiūⁿ GPS、IP 位址。
-
Authenticating System
使用 certificates、device biometrics、unique identifiers chhiūⁿ MAC 位址佮 TMP(Trusted Platform Module)。
相互驗證:Ūi-tio̍h 安全的通訊 client 佮 server 互相驗證對方 ê 身份 chhiūⁿ SSL/TLS handshakes。
-
Authorization(授權 Siū-koân):
使用者 ê 身份驗證 liáu-āu,下一步 to̍h-sī 授權。決定通過驗證 ê 使用者 ū hō͘ 允準 ē-êng-lit 使用電腦系統內底 ê tó chi̍t-ê 資源 ia̍h-sī 功能。
-
Authorization Models:
-
Discretionary Access Control(DAC): 物件(a file or folder) ê 主人決定 siâng ē-sái-tit 提取 i ê 物件 kah ē-êng-tit 對 choai 物件做 siáⁿ-mih 動作。Windows 佮 Linux 作業系統用這 ê 方法。
-
Role-based Access Control(RBAC): 根據使用者 tī 組織 ê 部門 kah 負責 ê khang-khòe 設定 in ê 角色。角色確定 in ē-tàng 提取 siáⁿ-mih 電腦資源。chhiūⁿ 銷售人員 kan-na ē-êng-tit 提取客戶資料 bē-sái 進入財務系統。
-
Mandatory Access Control(MAC): 有實權 ê 人 chhiūⁿ 系統管理者(system administrator) 控制提取 ê 授權。Tī MAC,使用者 kah 資源(files, folder, or databases) lóng 有 chi̍t-ê 標籤(label),就是安全標籤(security label)。使用者 ê 標籤 ài 符合資源的標籤 kah 有效力 ê 提取資源 ê 理由,chiah ē 通過授權。資安人員確定 siâng ē-sái-tit 提取 siáⁿ-mih 物件 liáu-āu,系統自動執行 chit-kóa 規則。軍隊 kah 政府單位需要嚴格控制資安 ē 用這 ê 方法。
-
Attribute-base Access Countrol(MAC): 提取 ê 授權是根據使用者、資源 kah 環境 ê 特性 chhiūⁿ 使用者 ê 角色、檔案 ê 敏感性、提取 ê 時間。提取 ê 規則 ē-êng 包括狀況 chhiūⁿ 使用者是 m̄ 是 tī HR 部門 kah 是 m̄ 是上班時間。Chi̍t-ê 方法適合用 tī 需要詳細控制 ê 複雜 ê 環境。
-
Accounting(or Audit):
紀錄使用者 ê 活動,chheⁿ-chhiūⁿ 使用 ê 資源、執行 ê 動作 kah 系統 ê 使用方式。
Login and logout logs、command execution logs。
4. Gap Analysis
比較組織目前 ê 資安情形 kah 已經建立 ê 資安標準 hām 產業界 ê 做法。
Gap Analysis ê 過程包括:用已經確定資安標準 kah frameworks,來評估組織目前 ê 安全控制、政策、程序,辨認需要改進 ê 所在,kā chit-kóa 辨認出來 ê gaps 根據 in ê 嚴重程度 kah 對組織 ê 影響,排定優先處理 ê 順序,建立改進 ê 計畫。
5. Zero Trust
Zero Trust 是 chi̍t-ê tī "never trust, always verify" 原則 ē-kha 運作 ê 資安觀念 kah framework。
Zero Trust kā 網路分成 control plane(控制層) kah data plane(資料層)。
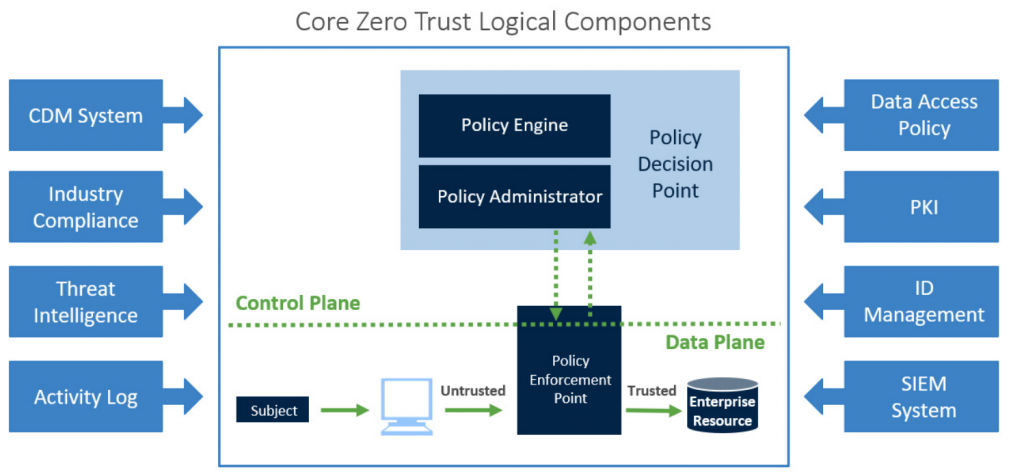
source:https://www.syntax.com/blog/zero-trust-and-sase/
-
control plane(控制層): 根據政策、安全控管、規則決定資料是 m̄ 是 ē-eng-tit tī 資料層流動。Policy Engine 確定使用者 kah 裝置 ê 授權 liáu-āu,Policy Administrator 傳達授權決定 hō͘ 資料層 ê Policy Enforcement Point。
-
Adaptive identity: 用 context-based ê 方法驗證使用者,tio̍h-sī 驗證 ê 時陣考慮使用者 log-in ê 地點 kah 時間、使用 ê 裝置。
-
Threat scope reduction: 限制 subject 活動 ê 範圍 iah-sī 對資源 ê access(提取),來降低錯誤 ê 發生。方法包括 segmenting networks 佮 least privilege。
-
Policy-driven access control: Policy Engine 根據政策來做決定。
-
Policy Administrator(PA): 執行 Policy Engine 做出來 ê 決定。
-
Policy Engine: 根據建立 ê 政策來評估所有 ê access(提取) 請求,決定同意 iah-sī 拒絕請求。
-
data plane(資料層): 使用者 ê 資料 kah 應用程式流動 ê 所在。Policy Enforcement Point 根據來自控制層 ê 授權決定,允許 iah-sī 阻擋使用者 ê 請求。
kā chit-kóa 功能分開,Zero Trust ê 構造建立 chi̍t-ê khah 安全 ê 控制 access(提取) 資源 ê 方法。
-
Implicit trust zone: 認為網路內底組成份子是 ē-eng-tit 信任 lih,所以 bô 經過嚴格 ê 驗證 kah 檢驗 tio̍h hō͘ in 互相溝通。
-
Subject/system: Subject 是使用者、裝置、應用程式,tio̍h 是提出 access(提取) 請求 ê 個體。System 是 Subject 想 beh access(提取) ê 資源 iah-sī 服務,chhiūⁿ 資料庫、雲端服務、Servers。
-
Policy Enforcement Point(PEP): PEP 根據 Policy Engine 設定、Policy Administrator 執行 ê 政策,同意 iah-sī 拒絕 access(提取) 請求。PEP ē-eng tī bô 仝款 ê 所在 chhiūⁿ firewall、gateways iah-sī endpoints。伊保證 kan-ná 授權 ê 請求 ē-tàng 通過進入 Enterprise Resource (企業資源)。
Physical Security 實體安全
保護建築物、土地、資產 bōe 受 tio̍h 外人侵入 kah 可能 ê 傷害。
-
Bollards: 短 ê 柱仔,Chhāi tī 出入口,阻止車輛駛入來。
-
Access Control Vestibule: sī chi̍t-ê 加強安全、控制人員出入 ê 所在,ē-tit 門禁系統看 tio̍h,chi̍t-ê 人開門入 khì chi̍t 棟建築物內底,會先到管制區,保全人員檢查通過 chiah ē-sái 開第二 ê 門入 khì 伊 beh 去 ê 所在。
-
Fencing: 用鉛線網仔 kah 外部隔開,預防外人侵入。包括簡單 ê iân-sòaⁿ(鉛線)網仔 kah 安全性懸 ê 有刺鉛線網仔 iah-sī 有電流鉛線網仔。
-
Video Surveillance: 用監視器來監視 kah 紀錄建築物周圍活動,監視器主要 ē 裝 tī 停車場、出入口 kah 其他重要 ê 所在 chhiūⁿ 電腦機房、資料中心。監視器 hō͘ 負責安全 ê 人員隨時 ē 知影組織現場 ê 狀狀況,萬一 ná ū 事件發生,監視器錄影 ê 資料 ē-eng-tit 提出來當做證據,幫助調查。
-
Security Guard: 有 chi̍t-kóa 所在警衛 ê 出現是需要 kah 對安全有幫助 eh,in ē-sái 完成科技產品 bô 辦法做出來 ê 決定 kah 工課。警衛 mā ē-eng-tit 以主動 kah 被動 ê 方式來確保實體安全。 In ē-eng-tit 檢查確認主動出入人員 ê Access Badge,紀錄訪客活動 kah 出入狀況 tiàm 工作日誌本(written logs)。警衛 mā ē-tàng 被動觀察人員出入 kah 活動狀況,chhiūⁿ sī m̄ sī 有 tailgating - 未授權人員偷偷 tè 授權員工進入管制區 ê 情形發生。
-
Access Badge: ē-eng-tit 提供身分 kah 出入權利證明 ê 卡片。用2 tī 電子門禁系統。
-
Lighting: 適當 ê 照明 ē-tàng 阻擋入侵者 kah pang-chān 監視器 tī 暗時 lo̍k tio̍h 較清楚 ê 影像。
-
Sensors: 對環境改變 ê 偵測 kah 反應。
-
Infrared Sensors: 紅外線 ē-tàng 偵測人身體 ê 溫度,這 ê 功能袂受光線影響,所以 ē-eng-tit 用 tiàm 能見度 kē ê 所在。chit-má chiâⁿ-chē 監視器攏有 Infrared Sensors 來偵測入侵者。
-
Pressure Sensors: 偵測 chi̍t-ê 表面 iah-sī 區域壓力 ê 改變。用 tī 保全系統來偵測出入口 chhiūⁿ 門 iah-sī 窗仔 ê 狀況。nā ū 人 chhì beh 開門 iah-sī 踏入管制區域,壓力感應器 tio̍h ē 發出警告聲。
-
Microwave Sensors: 送出微波信號,偵測特定區域內人 iah-sī 物件活動引起頻率 ē 改變,發出警告聲。
-
Ultrasonic Sensors: 送出高頻率聲波,測量聲波 tū-tio̍h 人 iah-sī 物件反彈 tńg-lâi ê 時間,所以 ē-tang 偵測 kah 實體離 lōa-hn̄g。
了解風險觀念 Liáu-kái hong-hiám koan-liām
了解佮管理風險 對 保護一个組織的資產佮保證營業繼續 sī 真重要。
Liáu-kái kah koán-lí hong-hiám tùi pó-hō͘ chi̍t ê cho͘-chit ê chu-sán kah pó-chèng êng-gia̍p kè-sio̍k sī chin tiōng-iàu.
基本 ê 風險觀念包括 threats,vulnerabilities,佮無仝款 ê 風險管理策略。
Threat:
Sī 任何可能會利用 vulnerabilities 來引起傷害 iah-sī 危險 ê 事件 iah-sī 行動。
Threats 來自:
- Malicious actors:Hackers 佮內部威脅
- Nature disasters:水災,火災
- System failures:Hardware,software 故障
Vulnerabilities
是一个系統、網路抑是應用程式內底的錯誤、缺點會予人提來用做威脅。
是無修補的軟體、無合標準的暗號、misconfigured system造成的的結果。
Risk:
利用 vulnerabilitie 的威脅可能造成的損失抑是傷害
測量風險的方法:
- Likelihood:威脅發生的可能。
- Impact:傷害的嚴重程度。
風險公式:
Risk = Threat x Vulnerability x Impact
Risk Acceptance
Risk Mitigation
Risk Transfer
Risk Avoidance

