在前幾天的學習中,已經認識了 Transformer 的基本結構,也了解了 LLM 迭代以及訓練三階段,從今天開始我們將自己手搓大模型,從零開始實現一個 LLaMA2 模型。
Meta 在 2023 年推出了 LLaMA 與 LLaMA2 系列,成為開源模型中重要的基礎模型,我們會實作一個簡化版,理解他的核心模組。
在任何模型建立之前,我們都需要定義一些超參數,例如:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from transformers import PretrainedConfig
class ModelConfig(PretrainedConfig):
model_type = "Tiny-K"
def __init__(
self,
dim: int = 768, # 模型維度
n_layers: int = 12, # 層數
n_heads: int = 16, # 注意力頭數
n_kv_heads: int = 8, # key/value 頭數
vocab_size: int = 6144, # 詞彙表大小
hidden_dim: int = None,
multiple_of: int = 64,
norm_eps: float = 1e-5,
max_seq_len: int = 512,
dropout: float = 0.0,
flash_attn: bool = True,
**kwargs,
):
self.dim = dim
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.n_heads = n_heads
self.n_kv_heads = n_kv_heads
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.multiple_of = multiple_of
self.norm_eps = norm_eps
self.max_seq_len = max_seq_len
self.dropout = dropout
self.flash_attn = flash_attn
super().__init__(**kwargs)
LLaMA 採用的不是之前所介紹到的 LayerNorm,而是改用了 RMSNorm,他的特色在於,使用平方均值來正規化,避免梯度爆炸或消失,γ 為可學習縮放參數,這種方法可以更穩定,尤其在深層模型中。
公式如下: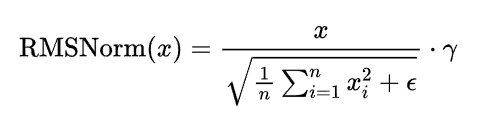
class RMSNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim: int, eps: float):
super().__init__()
self.eps = eps
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(dim)) # 可學習縮放參數
def _norm(self, x):
# x: [batch, seq_len, dim]
return x * torch.rsqrt(x.pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True) + self.eps)
def forward(self, x):
output = self._norm(x.float()).type_as(x)
return output * self.weight
# 建立設定
config = ModelConfig()
# 建立 RMSNorm
norm = RMSNorm(config.dim, config.norm_eps)
# 測試輸入
x = torch.randn(1, 50, config.dim) # [batch=1, seq_len=50, dim=768]
output = norm(x)
會注意到輸出的 shape 與輸入一致,這樣是正確的,因為正規化不會改變 shape。
參考連結:
https://datawhalechina.github.io/happy-llm/#/
