時間過得非常快已經快要11月了,有點混所以進度算有點小落後![]() 。這次主要介紹
。這次主要介紹meanShift原理從直方圖循序了解,藉由本篇文章介紹主要能達到對於原理的理解並解實作。
在介紹直方圖之前,首先要先建立一個標頭檔專門在繪製直線與方塊。而直線主要是有點到點所以先建立Point,矩形則是參考OpenCV方式給予點和長寬所以建立Rect。
新增Point.h
#pragma once
#ifndef POINT_H
#define POINT_H
#include "general.h"
#include "Image.h"
class Point {
public:
Point(C_UINT32 x, C_UINT32 y) :_x(x), _y(y) {};
void X(C_UINT32 x);
UINT32 X() const;
void Y(C_UINT32 y);
UINT32 Y() const;
private:
UINT32 _x;
UINT32 _y;
};
#endif // !POINT_H
新增Point.cpp
#include "Point.h"
void Point::X(C_UINT32 x) {
_x = x;
}
UINT32 Point::X() const {
return _x;
}
void Point::Y(C_UINT32 y) {
_y = y;
}
UINT32 Point::Y() const {
return _y;
}
新增Rect.h
#pragma once
#ifndef RECT_H
#define RECT_H
#include "general.h"
#include "Image.h"
class Rect {
public:
Rect(C_UINT32 x, C_UINT32 y, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height) :_x(x), _y(y), _width(width), _height(height) { };
void X(C_UINT32 x);
UINT32 X() const;
void Y(C_UINT32 y);
UINT32 Y() const;
void Width(C_UINT32 width);
UINT32 Width() const;
void Height(C_UINT32 height);
UINT32 Height() const;
UINT32 EndX() const;
UINT32 EndY() const;
private:
UINT32 _x;
UINT32 _y;
UINT32 _width;
UINT32 _height;
};
#endif // !RECT_H
新增Rect.cpp
#include "Rect.h"
void Rect::X(C_UINT32 x)
{
_x = x;
}
UINT32 Rect::X() const
{
return _x;
}
void Rect::Y(C_UINT32 y)
{
_y = y;
}
UINT32 Rect::Y() const
{
return _y;
}
void Rect::Width(C_UINT32 width)
{
_width = width;
}
UINT32 Rect::Width() const
{
return _width;
}
void Rect::Height(C_UINT32 height)
{
_height = height;
}
UINT32 Rect::Height() const
{
return _height;
}
UINT32 Rect::EndX() const
{
return _x + _width;
}
UINT32 Rect::EndY() const
{
return _y + _height;
}
新增draw.h
#pragma once
#ifndef DRAW_H
#define DRAW_H
#include "general.h"
#include "Image.h"
#include "Point.h"
#include "Rect.h"
namespace MNDT {
inline void DrawLine8bit(const Image& image, const Point& p1, const Point& p2, C_UCHAE& color)
{
assert(image.Width() > p1.X() && image.Width() > p2.X());
assert(image.Height() > p1.Y() && image.Height() > p2.Y());
C_UINT32 diffX = abs(static_cast<int32_t>(p1.X()) - static_cast<int32_t>(p2.X()));
C_UINT32 diffY = abs(static_cast<int32_t>(p1.Y()) - static_cast<int32_t>(p2.Y()));
C_UINT32 base = diffX > diffY ? diffX : diffY;
C_FLOAT baseX = static_cast<float>(diffX) / static_cast<float>(base);
C_FLOAT baseY = static_cast<float>(diffY) / static_cast<float>(base);
float x = static_cast<float>(p1.X());
float y = static_cast<float>(p1.Y());
for (UINT32 index = 0; index < base; index++)
{
image.image[static_cast<UINT32>(y)][static_cast<UINT32>(x)] = color;
x += baseX;
y += baseY;
}
}
inline void DrawLine8bit(const Image& image, const Point& p1, const Point& p2)
{
DrawLine8bit(image, p1, p2, 255);
}
inline void DrawRect8bit(const Image& image, const Rect& rect, C_UCHAE& color)
{
C_UINT32 endX = rect.EndX();
C_UINT32 endY = rect.EndY();
for (UINT32 x = rect.X(); x < endX; x++)
{
image.image[rect.Y()][x] = color;
image.image[endY][x] = color;
}
for (UINT32 y = rect.Y(); y < endY; y++)
{
image.image[y][rect.X()] = color;
image.image[y][endX] = color;
}
}
inline void DrawRect8bit(const Image& image, const Rect& rect)
{
DrawRect8bit(image, rect, 255);
}
}
#endif // !DRAW_H
在八位元影像當中,是由0到255像素所組成的,而直方圖顧名思義就是計算0到255的數量。
步驟
1.走訪圖片每個像素並記錄。
Library.h加入
/*
SetHistogram8bit Parameter:
src = source of image
pur = purpose of image
width = Image's width
height = Image's height
minRange = min pixel
maxRange = max pixel
bin = histogran split size
*/
void SetHistogram8bit(C_UCHAE* src, int32_t* histogram
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height);
void SetHistogram8bit(C_UCHAE* src, int32_t* histogram
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_UCHAE minRange, C_UCHAE maxRange
, C_UCHAE bin);
Libary.cpp
void Library::SetHistogram8bit(C_UCHAE* src, int32_t* histogram
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height)
{
C_UINT32 size = width * height;
for (UINT32 count = 0; count < size; count++)
{
histogram[*src]++;
src++;
}
}
void Library::SetHistogram8bit(C_UCHAE* src, int32_t* histogram
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_UCHAE minRange, C_UCHAE maxRange
, C_UCHAE bin)
{
assert(maxRange > minRange);
C_UCHAE diffRange = maxRange - minRange;
C_UCHAE interval = diffRange / bin;
C_UINT32 size = width * height;
for (UINT32 count = 0; count < size; count++)
{
histogram[*(src + count) / interval]++;
}
}
[1]使用OpenCV的規一化有多種方法,這裡使用最大值規一化。
步驟
1.取得size大小中最大值。
2.將size個都規一化。
Library.h加入
/*
SetNormalizedHistogram8bit Parameter:
histogram = histogram data
size = histogram size
base = max pixel
*/
void SetNormalizedHistogram8bit(int32_t* histogram
, C_UINT32 size
, C_UCHAE base);
Library.cpp加入
void Library::SetNormalizedHistogram8bit(int32_t* histogram
, C_UINT32 size
, C_UCHAE base)
{
int32_t max = 0;
for (UINT32 index = 0; index < size; index++)
{
max = max < histogram[index] ? histogram[index] : max;
}
float normalizedBase = static_cast<float>(base) / max;
for (UINT32 index = 0; index < size; index++)
{
histogram[index] = static_cast<int32_t>(histogram[index] * normalizedBase);
}
}
使用上述取得值方圖資料後再規一化,並畫在256 * 256大小圖片上。
步驟
1.計算像素直方圖數量。
2.規一化直方圖數據。
3.畫出0到255直方圖。
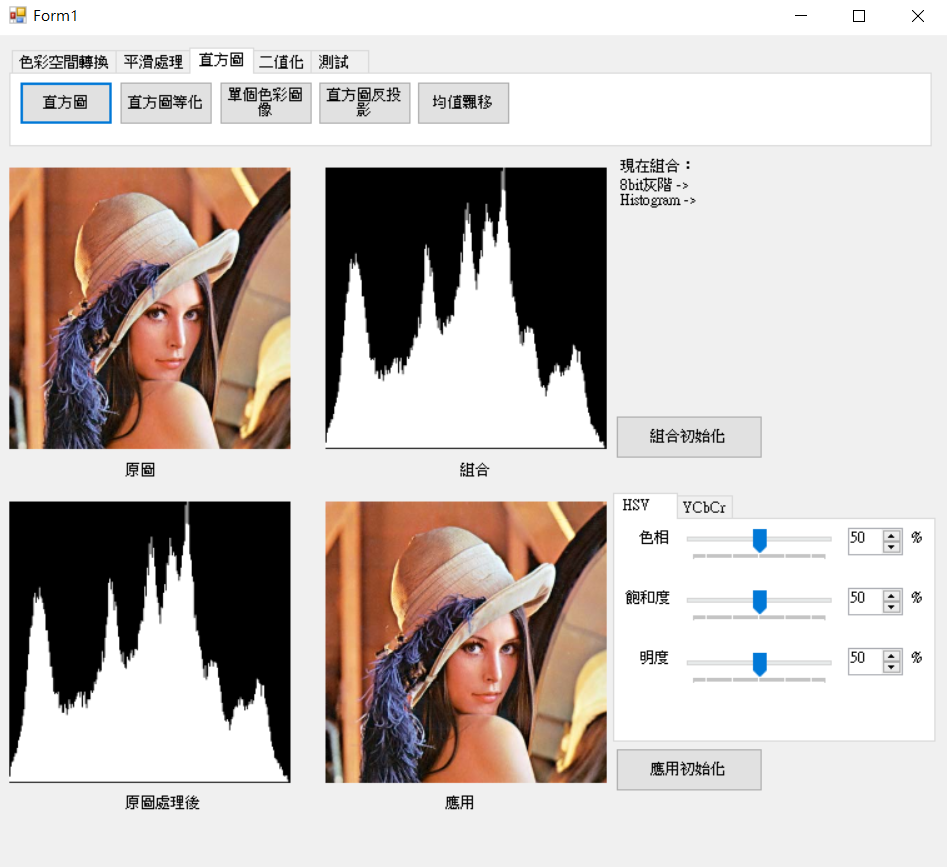
結果圖。
Library.h加入
/*
Histogram8bit Parameter:
src = source of image
pur = purpose of image
width = Image's width
height = Image's height
*/
void Histogram8bit(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height);
Library.cpp加入
void Library::Histogram8bit(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height)
{
int32_t* histogram = new int32_t[256]{ 0 };
int32_t max = 0;
SetHistogram8bit(src, histogram, width, height);
SetNormalizedHistogram8bit(histogram, 256, 255);
Image purImage(pur, 256, 256, MNDT::GRAY_8BIT);
for (UINT32 index = 0; index < 256; index++)
{
Point start(index, (255 - histogram[index]));
Point end(index, 255);
MNDT::DrawLine8bit(purImage, start, end);
}
delete[] histogram;
}
直方圖等化主要是使用累積分布函數來去改變圖片性質,圖一為直方圖數量,圖二為依序累積後的數量,然而最後依照原數量除上累積總數量則是累積分布的結果。
結果測試圖片來源[2],公式相關參考之前上課老師所提供的講義。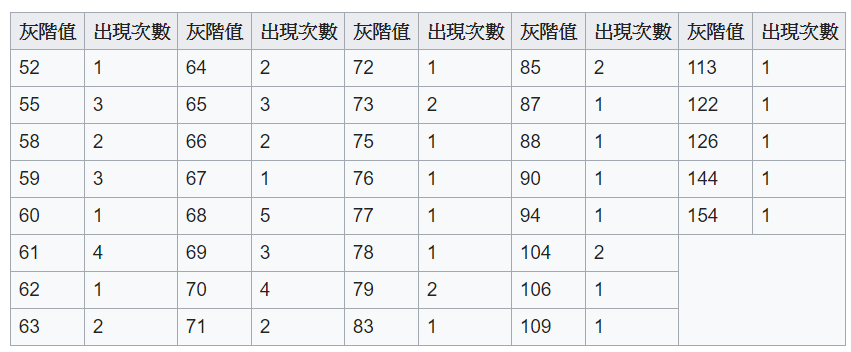
圖一來源:[2]。
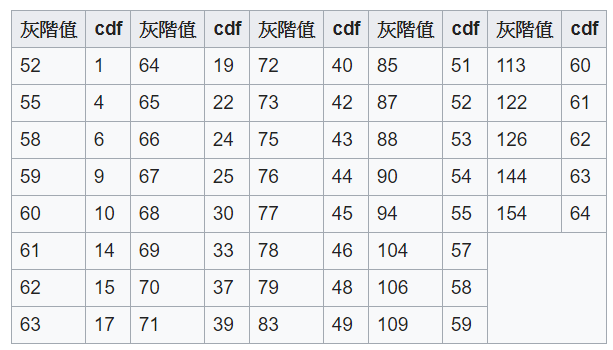
圖二來源:[2]。
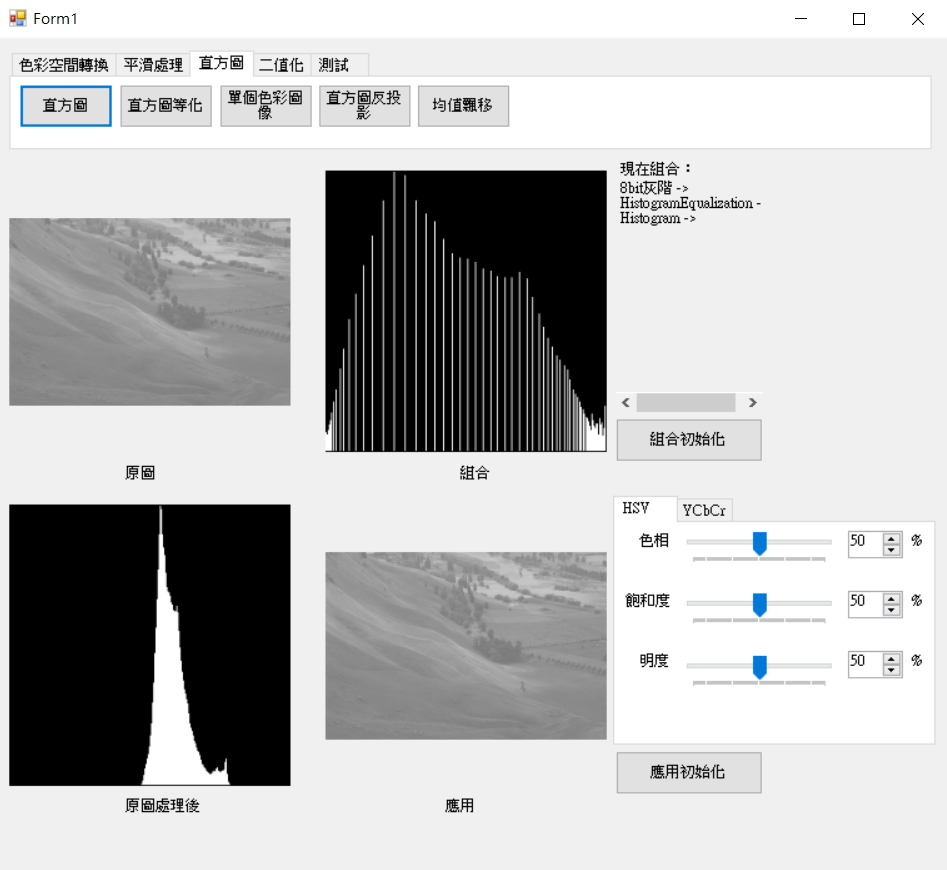
結果圖。
步驟
1.計算像素直方圖數量。
2.計算每個累積分布機率在乘上255做規一化。
3.計算後的直方圖帶入原始圖像。
Library.h加入
/*
HistogramEqualization8bit Parameter:
src = source of image
pur = purpose of image
width = Image's width
height = Image's height
*/
void HistogramEqualization8bit(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height);
Library.h加入
void Library::HistogramEqualization8bit(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height)
{
C_UINT32 size = width * height;
int32_t* histogram = new int32_t[256]{ 0 };
SetHistogram8bit(src, histogram, width, height);
float base = 0;
for (UINT32 index = 0; index < 256; index++)
{
if (histogram[index] > 0)
{
base += static_cast<float>(histogram[index]) / static_cast<float>(size);
histogram[index] = static_cast<int32_t>(base * 255);
}
}
for (UINT32 index = 0; index < size; index++)
{
*(pur + index) = histogram[*(src + index)];
}
delete[] histogram;
}
[1]有介紹OpenCV有多種比較方法,這邊使用直方圖相減去計算誤差,設定為越接近1代表誤差越小。
步驟
1.取得兩張圖片的直方圖。
2.兩個直方圖相減計算累加。
3.一扣掉累積除上像素數量。
Library.h加入
/*
CompareHistogram Parameter:
src = source of image
pur = purpose of image
width = Image's width
height = Image's height
*/
double CompareHistogram(C_UCHAE* src, C_UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height);
Library.cpp加入
double Library::CompareHistogram(C_UCHAE* src, C_UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height)
{
int32_t* srcHistogram = new int32_t[256]{ 0 };
int32_t* purHistogram = new int32_t[256]{ 0 };
SetHistogram8bit(src, srcHistogram, width, height);
SetHistogram8bit(pur, purHistogram, width, height);
int32_t diff = 0;
for (UINT32 index = 0; index < 256; index++)
{
diff += abs(srcHistogram[index] - purHistogram[index]);
}
return 1.0 - static_cast<double>(diff) / static_cast<double>(width * height);
}
這邊介紹取出單一通道影像,因後面meanShift會使用到。主要用途為將BGR或其他色彩通道指定取得單一通道,例如BGR,通道1為只取出B色彩圖像,通道2為只取出G色彩圖像,通道3為只取出R色彩圖像。
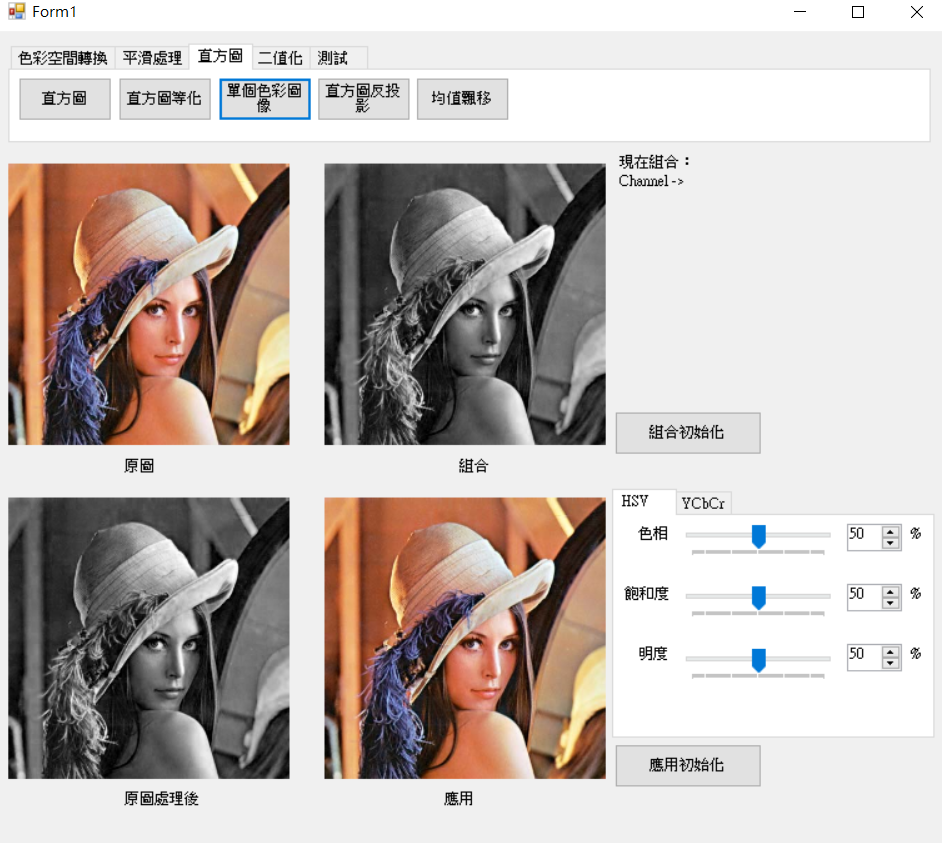
取出B通道結果圖。
Library.h加入
/*
Channel Parameter:
src = source of image
pur = purpose of image
width = Image's width
height = Image's height
channel = color channel
*/
void Channel(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_UINT32 channel);
Library.cpp加入
void Library::Channel(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_UINT32 channel)
{
assert(src != nullptr && pur != nullptr);
assert(width > 0 && height > 0);
assert(channel > 0 && channel < 4);
C_UCHAE* purEnd = pur + width * height + 1;
src += (channel - 1);
while (pur < purEnd)
{
*pur = *src;
pur++;
src += 3;
}
}
主要將輸入圖片依照輸入的分布直方圖去做輸出,簡單來說先計算一張圖片的直方圖資料,再將另一張圖片像素使用計算好的直方圖資料做投影,也就是套上直方圖資料在輸入圖像的機率分布,而這邊使用HSV的H,因為H代表色度比較能代表圖片的特徵。
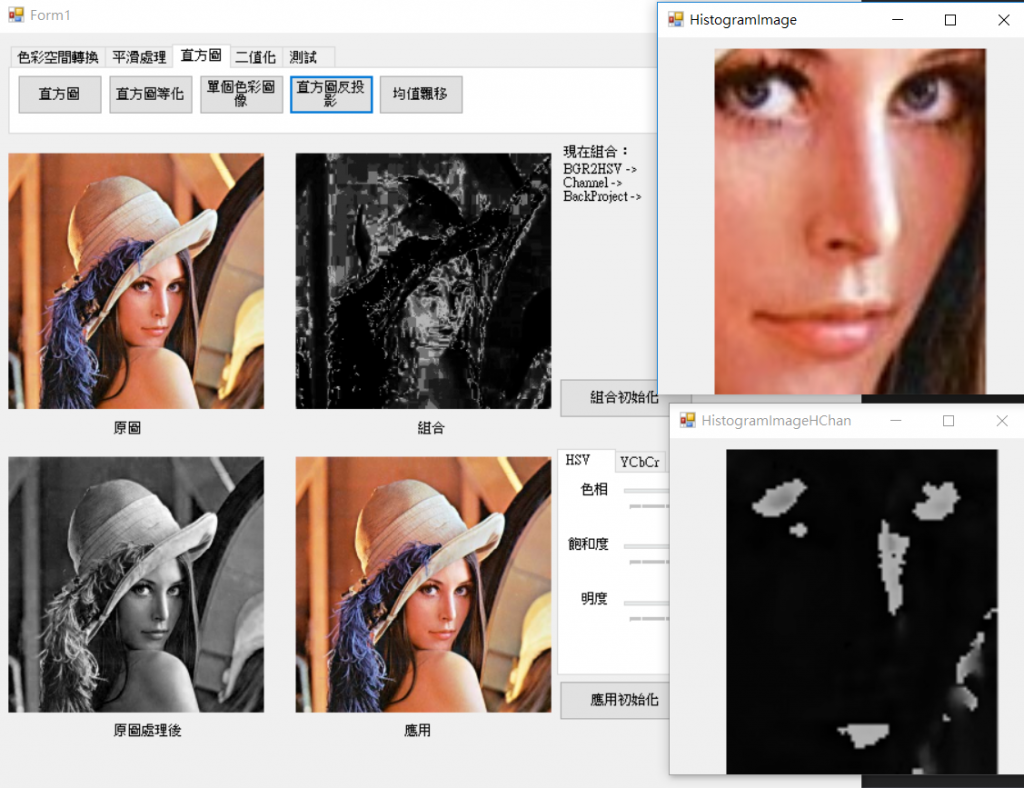
結果圖。
取得直方圖步驟-使用C#
1.將一張圖片轉為HSV。
2.使用Channel取得H。
3.計算直方圖資料。
4.直方圖資料規一化。
步驟
1.將每個像素轉為bin區間,並轉為輸入直方圖的值。
C#取得直方圖資料
hisData與之前輸入圖片原理相同,hisPtr為H通道圖像的指標。
IntPtr hisPtr = hisData.Scan0;
int[] histogram = new int[bin];
mndtSetHistogram8bit(hisPtr, histogram
, hisImage.Width, hisImage.Height
, 0, bin
, bin);
mndtSetNormalizedHistogram8bit(histogram, bin, bin);
Library.h加入
/*
BackProjection Parameter:
src = source of image
pur = purpose of image
width = Image's width
height = Image's height
histogram = histogram data
minRange = min pixel
maxRange = max pixel
bin = histogran split size
*/
void BackProjection(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_UINT32* histogram
, C_UCHAE minRange, C_UCHAE maxRange
, C_UCHAE bin);
Library.cpp加入
void Library::BackProjection(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_UINT32* histogram
, C_UCHAE minRange, C_UCHAE maxRange
, C_UCHAE bin)
{
assert(src != nullptr && pur != nullptr);
assert(width > 0 && height > 0);
C_UCHAE* purEnd = pur + width * height + 1;
C_UCHAE diffRange = maxRange - minRange;
C_UCHAE interval = diffRange / bin;
while (pur < purEnd)
{
*pur = histogram[(*src) / interval];
pur++;
src++;
}
}
這邊均值漂移作法叫簡單,如下圖一,只需要已中心計算範圍內的值即可求出移動量和方向,而圖一的紅點在圖片上即是像素,像素也則代表對移動和方向的影響量。上面使用反向投影求出分布圖後,在使用均值漂移則可以求出新圖片的目標位置。
註:實際上均值漂移也是一種機器學習,通常會使用高斯核來去計算分群目標[4]。
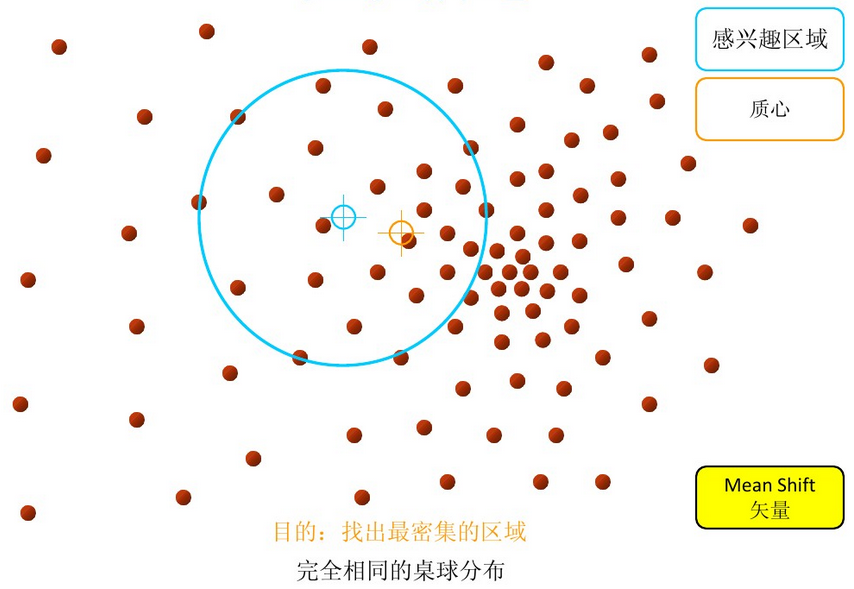
圖一來源:[4]。
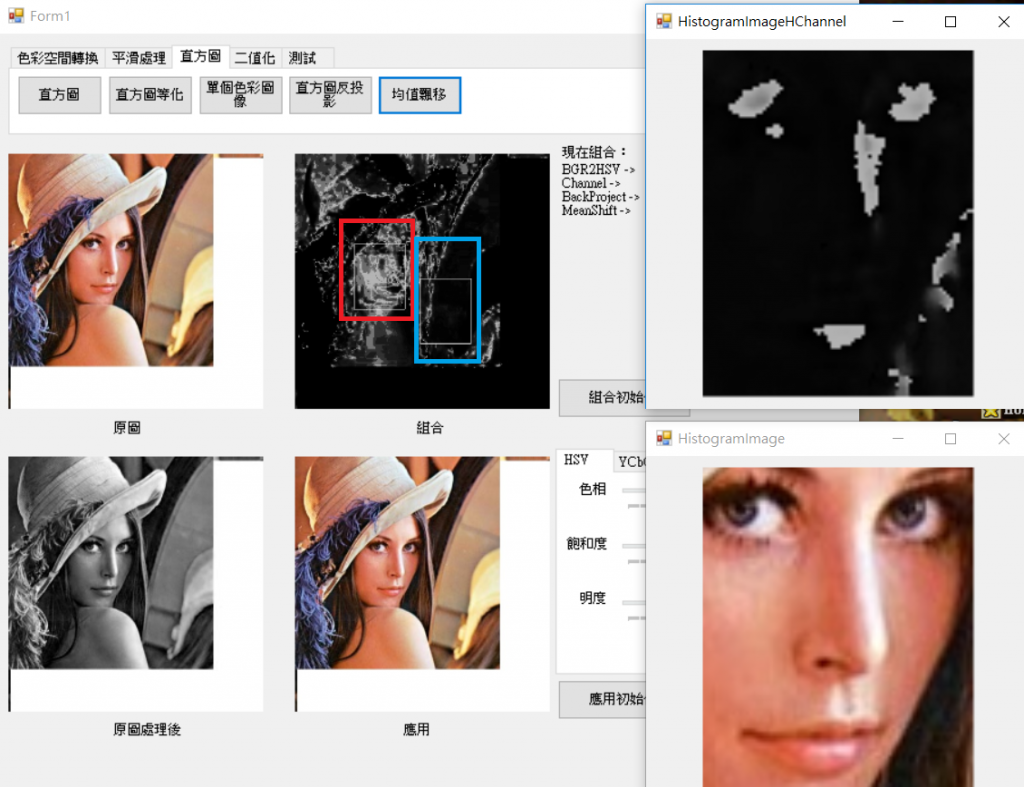
結果圖,藍色為原始位置,紅色為搜尋到的位置。
公式簡介
參考[3]和OpenCV的meanShift原始碼。假設矩形大小為120 * 60,則中心位置為(60, 30)。矩形內每個座標已中心為原點(二維座標系)去累加計算x和y乘上像素(影像度),最後在除上總像素計算x和y的位移量。
原點(60, 30)。
二維座標為,G(x) = x - 60,G(y) = y - 30。
步驟
1.計算矩形內的x像素、y像素和像素總和。
2.取得x和y位移量並且修正數值。
3.偏移達到threshold或time則結束。
Library.h加入
/*
MeanShift Parameter:
src = source of image
pur = purpose of image
width = Image's width
height = Image's height
rectPoint = original rect point
time = trans time
threshold = diff threshold
*/
void MeanShift(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_UINT32* rectPoint
, C_UINT32 times
, C_DOUBLE threshold);
Library.cpp加入
void Library::MeanShift(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_UINT32* rectPoint
, C_UINT32 times
, C_DOUBLE threshold)
{
assert(src != nullptr && pur != nullptr);
assert(width > 0 && height > 0);
memcpy(pur, src, width * height * sizeof(UCHAE));
Image srcImage(const_cast<UCHAE*>(src), width, height, ColerType::BGR2GRAY_8BIT);
Image purImage(const_cast<UCHAE*>(pur), width, height, ColerType::BGR2GRAY_8BIT);
Rect rect(rectPoint[0], rectPoint[1], rectPoint[2], rectPoint[3]);
MNDT::DrawRect8bit(purImage, rect);
for (UINT32 time = 0; time < times; time++)
{
C_UINT32 endX = rect.EndX();
C_UINT32 endY = rect.EndY();
int32_t centerX = (rect.Width() >> 1) + rect.X();
int32_t centerY = (rect.Height() >> 1) + rect.Y();
int32_t sumX = 0;
int32_t sumY = 0;
int32_t sumBase = 0;
for (UINT32 y = rect.Y(); y < endY; y++)
{
for (UINT32 x = rect.X(); x < endX; x++)
{
if (srcImage.image[y][x] > 0)
{
C_INT32 xDiff = x - centerX;
C_INT32 yDiff = y - centerY;
sumX += (xDiff * srcImage.image[y][x]);
sumY += (yDiff * srcImage.image[y][x]);
sumBase += srcImage.image[y][x];
}
}
}
C_DOUBLE offsetX = (static_cast<double>(sumX) / static_cast<double>(sumBase));
C_DOUBLE offsetY = (static_cast<double>(sumY) / static_cast<double>(sumBase));
int32_t updateX = rect.X() + static_cast<int32_t>(offsetX);
int32_t updateY = rect.Y() + static_cast<int32_t>(offsetY);
updateX = std::min(std::max(updateX, 0), static_cast<int32_t>(width - 1));
updateY = std::min(std::max(updateY, 0), static_cast<int32_t>(height - 1));
rect.X(updateX);
rect.Y(updateY);
// loss
if ((offsetX * offsetX + offsetY * offsetY) <= threshold) break;
}
MNDT::DrawRect8bit(purImage, rect);
}
C#視窗原始碼
C++函數原始碼
感覺時間過得很快,今年又快過完了,但還有很多東西都還沒學到一個段落,看來要努力加把勁了,希望大家今年也能完成自己的目標準備朝向新的一年前進。文章若有文題歡迎留言提問謝謝。
[1]阿洲(2015). OpenCV教學 | 阿洲的程式教學 from: http://monkeycoding.com/?page_id=12 (2018.10.19).
[2]維基百科(2018). 直方图均衡化 from:https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%9B%B4%E6%96%B9%E5%9B%BE%E5%9D%87%E8%A1%A1%E5%8C%96 (2018.10.10).
[3]CamShift算法--Mean Shift算法 from:http://www.voidcn.com/article/p-rekabebj-zs.html
[4]简单易学的机器学习算法——Mean Shift聚类算法 from:https://blog.csdn.net/google19890102/article/details/51030884
