這次要介紹邊緣檢測和霍夫轉換一樣參考[1],而邊緣檢測的Sobel為本次重點,因Sobel運算在往後取得方向和角度是非常方便的一個算式。
這次也修正了坐標和矩形相關的程式邏輯如下。
endX和endY為實際索引位置,舉例endX公式為,x + width - 1,若width等於0回傳-1。DrawLine8bit修正為自動換算畫出線。[1]邊緣運算主要有Sobel、Scharr和Laplace,它們差異在於乘上的"核"不同,這裡使用Sobel中的3x3的一階核運算來當範例。
Sobel垂直方向3x3一階"核": 。
。
Sobel水平方向3x3一階"核":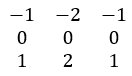 。
。
而垂直方向與水平方向計算出來結果映射在二維系座標,可以取得角度、方向和長度等等。假設垂直方向為x,水平方向為y,則依照三角函數性質可得到tan = 對邊 / 斜邊 = y / x,反三角函數atan則可得到角度,而距離公式使用歐幾里得距離公式(L2算法),sqrt(x^2 + y^2),以上為合併後的性質,接著繼續看Sobel的運算步驟。
Library.h
這裡只使用一階3x3運算,dx和dy為使用開關。
/*
Sobel8bit Parameter:
src = source of image
pur = purpose of image
width = Image width
height = Image height
dx = x gradient switch
dy = y gradient switch
*/
void Sobel8bit(C_UCHAE* src, int32_t* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, const bool dx, const bool dy);
Library.cpp
void Library::Sobel8bit(C_UCHAE* src, int32_t* data
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, const bool dx, const bool dy)
{
// 1. padding
C_UINT32 padWidth = width + 2;
C_UINT32 padHeight = height + 2;
UCHAE* padSrc = new UCHAE[padWidth * padHeight];
ImagePadding8bit(src, padSrc, width, height, 1);
// 2. set kernel
Image srcImage(padSrc, padWidth, padHeight, MNDT::ImageType::GRAY_8BIT);
int32_t kernels[9];
SetSobelKernels(kernels
, dx, dy);
// 3. calculate convolution
for (UINT32 row = 1; row < padWidth - 1; row++)
{
for (UINT32 col = 1; col < padHeight - 1; col++)
{
int32_t sum = 0;
UINT32 kernelsIndex = 0;
for (int32_t blockRow = -1; blockRow <= 1; blockRow++)
{
for (int32_t blockCol = -1; blockCol <= 1; blockCol++)
{
UCHAE pix = srcImage.image[row + blockRow][col + blockCol];
sum += (static_cast<int32_t>(pix) * kernels[kernelsIndex]);
kernelsIndex++;
}
}
*data = sum;
data++;
}
}
delete[] padSrc;
padSrc = nullptr;
}

24bit垂直x

24bit水平y
邊緣檢測主要是使用水平和垂直的絕對值(L1算法)合計後,再去做正規化顯示即是邊緣檢測。而邊緣檢測方式有很多種例如,Laplacian和Canny等等,但其原理大同小異,部分的差別只在於"核"的不同,這邊使用上述的Sobel運算子取得邊緣。
Library.h
/*
SobelEdgeView8bit Parameter:
src = source of image
pur = purpose of image
width = Image width
height = Image height
*/
void SobelEdgeView8bit(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height);
Library.cpp
void Library::SobelEdgeView8bit(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height)
{
// 1. get sobel
int32_t* Gx = new int32_t[width * height];
int32_t* Gy = new int32_t[width * height];
C_UCHAE* srcEnd = src + width * height;
Sobel8bit(src, Gx
, width, height
, true, false);
Sobel8bit(src, Gy
, width, height
, false, true);
// 2. calculate abs and get max
int32_t max = 0;
int32_t* data = new int32_t[width * height];
int32_t* dataPointer = data;
int32_t* GxPointer = Gx;
int32_t* GyPointer = Gy;
while (src < srcEnd)
{
*dataPointer = abs(*GxPointer) + abs(*GyPointer);
max = max < *dataPointer ? *dataPointer : max;
dataPointer++;
src++;
GxPointer++;
GyPointer++;
}
delete[] Gx;
Gx = nullptr;
delete[] Gy;
Gy = nullptr;
// 3. normalization
C_UCHAE* purEnd = pur + width * height;
dataPointer = data;
while (pur < purEnd)
{
*pur = *dataPointer * 255 / max;
dataPointer++;
pur++;
}
delete[] data;
data = nullptr;
}
參考[2]的OpenCV代碼,主要將最後改為全部重新計算一次在畫出結果。
霍夫轉換是計算x和y在0~180角度的極座標(離散值),使用三角函數cos = 鄰邊 / 斜邊,sin = 對邊 / 斜邊,而cos乘上斜邊得取x,sin乘上斜邊得取y,使用圖片的位置乘上cos和sin,cos(theta) * x取得x在霍夫分布和sin(theta) * y取得y分布,兩者相加即是霍夫轉換的離散值,如下圖一,圖二則是實際圖片輸出的分布有興趣可找函數DrawHoughPolar。
輸入資料[x, y]由上而下[7, 7], [5, 5], [3, 3], [1, 1],可以清楚的看到都相交於弧度2.35(135度)位置,利用此特性統計直線的角度,將可能為直線的角度列出就可以減少計算量。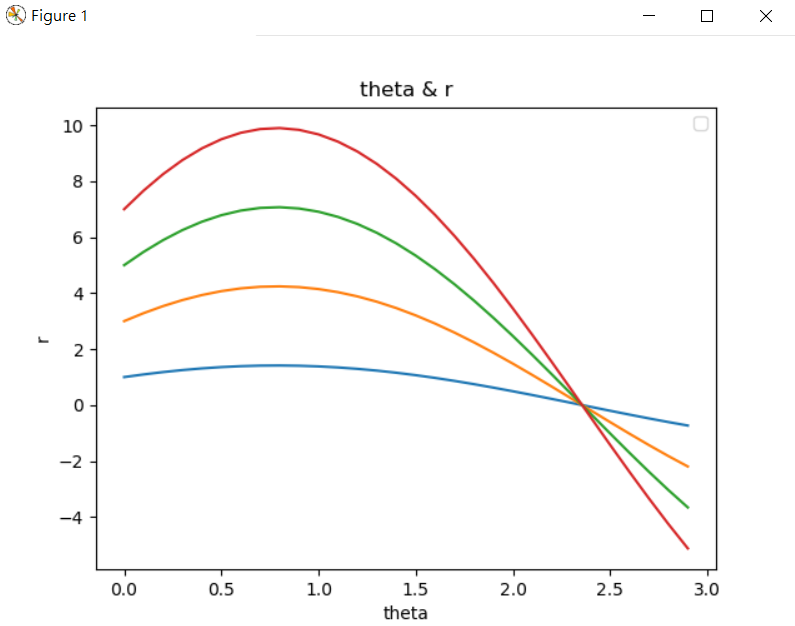
圖一。
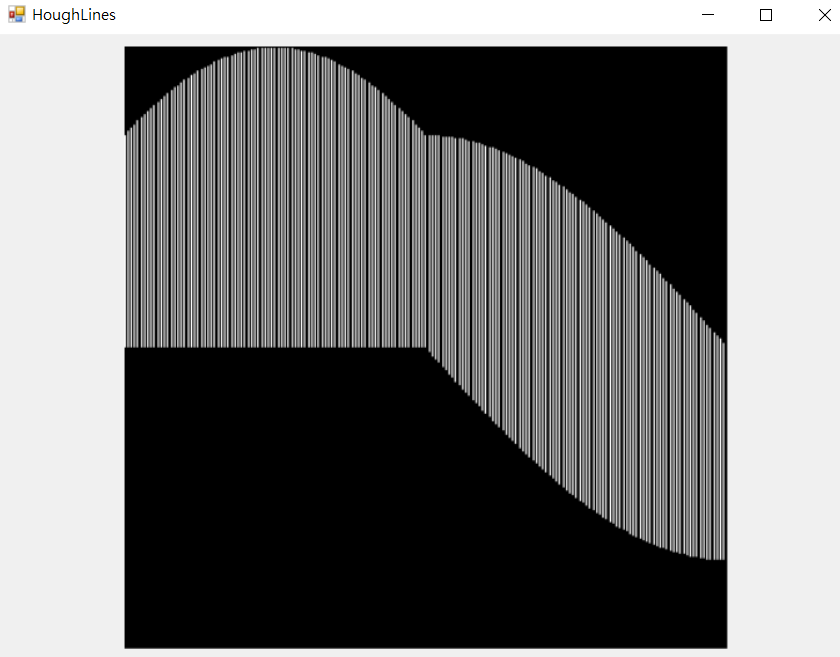
圖二,整張圖片實際畫出的線。
thetaSize:分割數量。PI除theta,theta為每個切割弧度大小。fixRho:三角函數倍率。1除rho,rho為倍率參數。originalR:最大離散值。最大為長寬乘上0.7...(45度)或者高或寬乘上1。maxR:修正的最大離散值。為了算鄰近,加上填補和修正索引位置。xAxisOffset:負數的偏移位置。主要用來將離散值分為正和負兩部分,所以每一個分割角度的範圍是[-originalR,originalR],。Library.h
/*
HoughLines Parameter:
src = source of image
pur = purpose of image
width = Image width
height = Image height
rho = calculation sin and cos
theta = calculation split parmas
threshold = calculation output parmas
*/
void HoughLines(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_FLOAT rho, C_FLOAT theta, C_UINT32 threshold);
void HoughLineNeighboursUpdate(UINT32* count
, C_UINT32 thetaSize, C_UINT32 maxR
, C_UINT32 threshold);
Library.cpp
void Library::HoughLines(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_FLOAT rho, C_FLOAT theta, C_UINT32 threshold)
{
// 1. init params
C_FLOAT fixRho = 1.0f / rho;
C_UINT32 thetaSize = static_cast<UINT32>(MNDT::PI / theta);
float* fixSin = new float[thetaSize];
float* fixCos = new float[thetaSize];
for (UINT32 index = 0; index < thetaSize; index++)
{
fixSin[index] = MNDT::FixValue(sin(theta * index)) * fixRho;
fixCos[index] = MNDT::FixValue(cos(theta * index)) * fixRho;
}
// 2. hough total
Image srcImage(const_cast<UCHAE*>(src), width, height, MNDT::ImageType::GRAY_8BIT);
C_DOUBLE originalR = std::max((width + height) * sin(MNDT::PI / 4.0), static_cast<double>(std::max(width, height)));
C_UINT32 maxR = static_cast<UINT32>(originalR * fixRho) + 1 + 2;
C_UINT32 xAxisOffset = maxR * (thetaSize + 2);
UINT32* count = new UINT32[xAxisOffset * 2]{ 0 };
for (UINT32 row = 0; row < height; row++)
{
for (UINT32 col = 0; col < width; col++)
{
if (srcImage.image[row][col] > 0)
{
for (UINT32 index = 0; index < thetaSize; index++)
{
int32_t r = static_cast<int32_t>(fixSin[index] * row + fixCos[index] * col);
r = r < 0 ? abs(r) + xAxisOffset : r;
count[maxR * (index + 1) + r + 1]++;
}
}
}
}
//// draw hough
//DrawHoughPolar(pur
// , width, height
// , count
// , theta, maxR);
// 3. update neighbours
HoughLineNeighboursUpdate(count
, thetaSize, maxR
, threshold);
// 4. draw line
Image purImage(pur, width, height, MNDT::ImageType::GRAY_8BIT);
for (UINT32 row = 0; row < height; row++)
{
for (UINT32 col = 0; col < width; col++)
{
if (srcImage.image[row][col] > 0)
{
for (UINT32 index = 0; index < thetaSize; index++)
{
int32_t r = static_cast<int32_t>(fixSin[index] * row + fixCos[index] * col);
r = r < 0 ? abs(r) + xAxisOffset : r;
if (count[maxR * (index + 1) + r + 1] > 0)
{
purImage.image[row][col] = 255;
}
}
}
}
}
delete[] fixSin;
fixSin = nullptr;
delete[] fixCos;
fixCos = nullptr;
delete[] count;
count = nullptr;
}
void Library::HoughLineNeighboursUpdate(UINT32* count
, C_UINT32 thetaSize, C_UINT32 maxR
, C_UINT32 threshold)
{
// 4鄰比較
C_UINT32 xAxisOffset = maxR * (thetaSize + 2);
for (UINT32 index = 0; index < thetaSize; index++)
{
C_UINT32 offset = maxR * (index + 1);
for (UINT32 countIndex = offset + 1; countIndex < offset + maxR - 1; countIndex++)
{
// x axis -> + and -
for (UINT32 axis = 0; axis < 2; axis++)
{
UINT32* nowCountPointer = count + countIndex + xAxisOffset * axis;
if (*nowCountPointer < threshold
|| *nowCountPointer < *(nowCountPointer - 1)
|| *nowCountPointer < *(nowCountPointer + 1)
|| *nowCountPointer < *(nowCountPointer - maxR)
|| *nowCountPointer < *(nowCountPointer + maxR))
{
*nowCountPointer = 0;
}
}
}
}
}

原圖
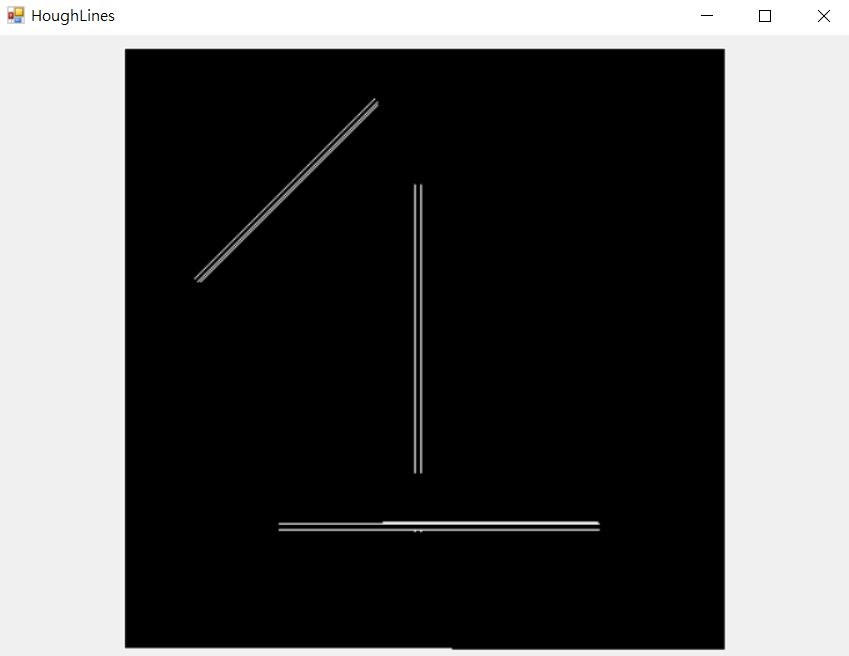
結果
參考[3]的OpenCV代碼,在用更直觀方式實現。
圓的方式與直線相同,公式改為,r^2 = x^2 + y^2,而在OpenCV當中先統計有可能為圓心的位置,在去判別哪些是真正的圓心。首先找到大於0的像素,依照Sobel運算可取得梯度,而在這裡的梯度方向即是切線的法線(與切線垂直),如此一來只需要往梯度方向和反方向累加通過的可能圓心點即可,如下圖一原圖,圖二為累加的所有路徑。
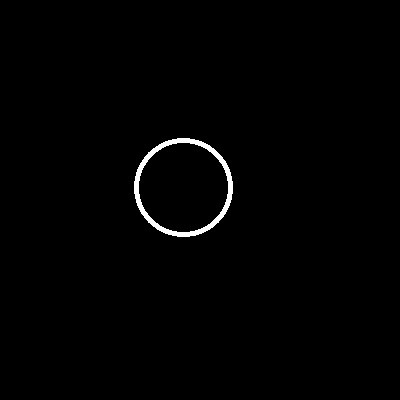
圖一

圖二
count陣列統計像素大於0從minRadius到maxRadius經過的直線。這裡多用一個函數計算點到點之間經過的距離。count大於0的座標從minRadius到maxRadius判斷360度的位置是否為大於0的像素,若360度都是即是原心。(可以改為依照count數量排序後,依照取得前N個再去跑迴圈效率會較高)。Library.h
/*
HoughCircles Parameter:
src = source of image
pur = purpose of image
width = Image width
height = Image height
minRadius = min radius
maxRadius = max radius
threshold = calculation output parmas
*/
void HoughCircles(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_FLOAT minRadius, C_FLOAT maxRadius, C_UINT32 threshold);
void HoughCirclesCount(C_UCHAE* src
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, UINT32* count
, C_FLOAT minRadius, C_FLOAT maxRadius);
void HoughCirclePointCount(UINT32* count
, C_UINT32 width
, const Point& p1, const Point& p2);
void HoughCircleNeighboursUpdate(UINT32* count
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_UINT32 threshold);
Library.cpp
void Library::HoughCircles(C_UCHAE* src, UCHAE* pur
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_FLOAT minRadius, C_FLOAT maxRadius, C_UINT32 threshold)
{
// 1. total
UINT32* count = new UINT32[(width + 2) * (height + 2)]{ 0 };
HoughCirclesCount(src
, width, height
, count
, minRadius, maxRadius);
// 2. update neighbours
HoughCircleNeighboursUpdate(count
, width, height
, threshold);
// 3. draw
Image srcImage(const_cast<UCHAE*>(src), width, height, MNDT::ImageType::GRAY_8BIT);
Image purImage(pur, width, height, MNDT::ImageType::GRAY_8BIT);
for (UINT32 row = 0; row < height; row++)
{
C_UINT32 rowIndex = (row + 1) * width;
for (UINT32 col = 0; col < width; col++)
{
C_UINT32 nowIndex = rowIndex + col + 1;
if (count[nowIndex] == 0)
{
continue;
}
for (float radius = minRadius; radius <= maxRadius; radius++)
{
bool nCircle = false;
for (float pi = 0; pi <= MNDT::PI * 2; pi += 0.2f)
{
int32_t y = static_cast<int32_t>(static_cast<float>(row) + MNDT::FixValue(sin(pi)) * radius);
int32_t x = static_cast<int32_t>(static_cast<float>(col) + MNDT::FixValue(cos(pi)) * radius);
if (x < 0 || y < 0
|| (unsigned)x >= width || (unsigned)y >= height
|| srcImage.image[y][x] == 0)
{
nCircle = true;
break;
}
}
if (nCircle)
{
continue;
}
for (float pi = 0; pi <= MNDT::PI * 2; pi += 0.2f)
{
C_UINT32 y = static_cast<UINT32>(row + MNDT::FixValue(sin(pi)) * radius);
C_UINT32 x = static_cast<UINT32>(col + MNDT::FixValue(cos(pi)) * radius);
purImage.image[y][x] = 255;
}
}
}
}
delete[] count;
count = nullptr;
}
void Library::HoughCirclesCount(C_UCHAE* src
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, UINT32* count
, C_FLOAT minRadius, C_FLOAT maxRadius)
{
assert(count != nullptr);
// get gradient
Library lib;
int32_t* Gx = new int32_t[width * height];
int32_t* Gy = new int32_t[width * height];
lib.Sobel8bit(src, Gx
, width, height
, true, false);
lib.Sobel8bit(src, Gy
, width, height
, false, true);
// calculate gradient total
Image srcImage(const_cast<UCHAE*>(src), width, height, MNDT::ImageType::GRAY_8BIT);
for (UINT32 row = 0; row < height; row++)
{
C_UINT32 rowIndex = row * width;
for (UINT32 col = 0; col < width; col++)
{
C_UINT32 index = rowIndex + col;
if (srcImage.image[row][col] > 0)
{
C_FLOAT magnitude = static_cast<float>(sqrt(Gx[index] * Gx[index] + Gy[index] * Gy[index] + 0.0001f));
float offsetX = Gx[index] / magnitude;
float offsetY = Gy[index] / magnitude;
for (UINT32 sign = 0; sign < 2; sign++)
{
float x = col + minRadius * offsetX;
float y = row + minRadius * offsetY;
for (float radius = minRadius; radius <= maxRadius; radius++)
{
if (x < 0 || y < 0
|| x >= width || y >= height)
{
continue;
}
//MNDT::DrawLine8bit(purImage, Point(col, row), Point(static_cast<UINT32>(x), static_cast<UINT32>(y)));
HoughCirclePointCount(count, width, Point(col, row), Point(static_cast<UINT32>(x), static_cast<UINT32>(y)));
x += offsetX;
y += offsetY;
}
offsetX = -offsetX;
offsetY = -offsetY;
}
}
}
}
delete[] Gx;
Gx = nullptr;
delete[] Gy;
Gy = nullptr;
}
void Library::HoughCirclePointCount(UINT32* count
, C_UINT32 width
, const Point& p1, const Point& p2)
{
C_UINT32 absDiffX = abs(static_cast<int32_t>(p1.X()) - static_cast<int32_t>(p2.X()));
C_UINT32 absDiffY = abs(static_cast<int32_t>(p1.Y()) - static_cast<int32_t>(p2.Y()));
C_UINT32 base = absDiffX > absDiffY ? absDiffY : absDiffX;
C_INT32 diffX = static_cast<int32_t>(p1.X()) - static_cast<int32_t>(p2.X());
C_INT32 diffY = static_cast<int32_t>(p1.Y()) - static_cast<int32_t>(p2.Y());
C_INT32 baseX = diffX < 0 ? 1 : -1;
C_INT32 baseY = diffY < 0 ? 1 : -1;
int32_t x = p1.X();
int32_t y = p1.Y();
for (UINT32 index = 0; index < base; index++)
{
count[static_cast<UINT32>(static_cast<UINT32>(y + 1) * width + x + 1)]++;
x += baseX;
y += baseY;
}
}
void Library::HoughCircleNeighboursUpdate(UINT32* count
, C_UINT32 width, C_UINT32 height
, C_UINT32 threshold)
{
// 4鄰比較
for (UINT32 row = 0; row < height; row++)
{
C_UINT32 rowIndex = (row + 1) * width;
for (UINT32 col = 0; col < width; col++)
{
C_UINT32 nowIndex = rowIndex + col + 1;
UINT32* nowCountPointer = count + nowIndex;
if (*nowCountPointer < threshold
|| *nowCountPointer < *(nowCountPointer - 1)
|| *nowCountPointer < *(nowCountPointer + 1)
|| *nowCountPointer < *(nowCountPointer - width - 2)
|| *nowCountPointer < *(nowCountPointer + width + 2))
{
*nowCountPointer = 0;
}
}
}
}

原圖
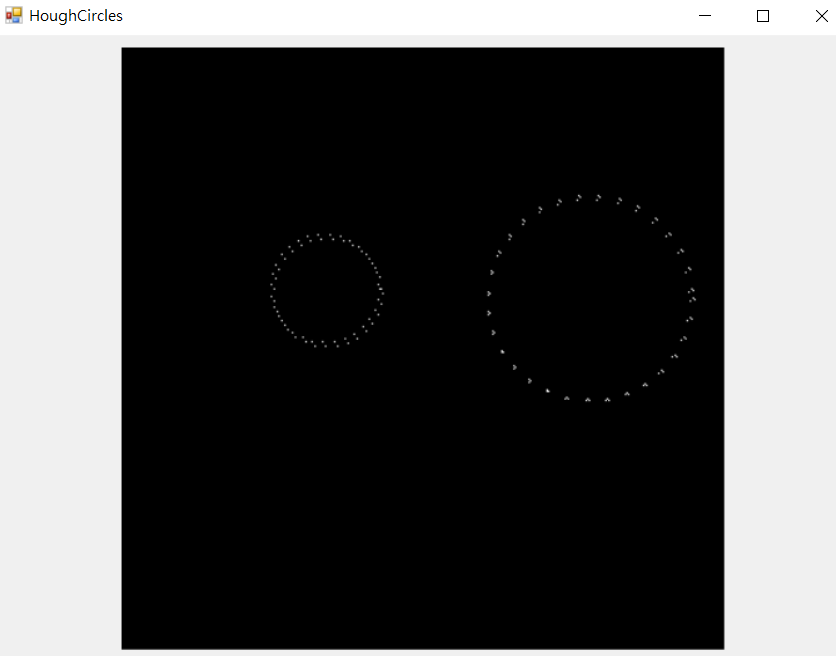
結果圖
這次做的霍夫轉換直接把全部的可能輸出效率會較差,但對於理解原理沒有太大的影響。在[1]有提到分水嶺算法它是利用邊緣製作出一個標記表,再利用像素差進行合併,由此可知Sobel運算子運用的地方非常廣泛,接下來會介紹影像特徵取得,希望在月底能把AdaBoost做完![]() 。若有問題或錯誤歡迎留言指教。
。若有問題或錯誤歡迎留言指教。
[1]阿洲(2015). OpenCV教學 | 阿洲的程式教學 from: http://monkeycoding.com/?page_id=12 (2018.11.21).
[2]viewcode(2012) 霍夫变换直线检测houghlines及opencv的实现分析 from: https://blog.csdn.net/viewcode/article/details/8090932 (2018.11.21).
[3]zhaocj(2016). Opencv2.4.9源码分析——HoughCircles from: https://blog.csdn.net/zhaocj/article/details/50454847 (2018.11.22)
