Day29-字串的輸出入
那今天我們要教的是字串的輸出入
輸出字串函式為puts()函式,這個函式上一篇練習題也使用到,不知道大家還記不記得
puts()語法:
int puts(const char*str);
這個函式接受一個字元指標的引數,他從該位址開始將字元輸出直到遇到\0字元後停止
puts()函式與使用printf()函式再加上換行字元的意義相同
gets()函式是將整行字串儲存入引數,也就是字元指標開頭的陣列,並且回傳字串陣列的位址
那C語言提供許多標準的字串處理函式,在使用時記得將string.h標頭檔含括進來
#include<string.h>
strcat()和strncat()函式:連接字串
語法:
char *strcat (char *str1,const char *str2);
char *strncat (char *str1,const char *str2,size_t len);
範例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(void){
char s1[]="Hello!";
char s2[10];
printf("What is your name?");
gets(s2);
strncat(s1,s2,10);
printf("%s\n",s1);
system("pause");
}
印出: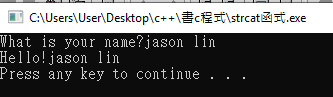
strchr()和strrchr()函式:尋找字元(在字串中尋找一個字元)
語法:
char *strchr(const char *str,int ch);
char *strrchr(const char *str,int ch);
範例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(void){
char s[]="string is fun!";
char key;
printf("The string is[string is fun!]. Which Character?");
scanf("%c",&key);
if(strchr(s,key))
printf("Founf %c in string! The address is %d.\n",key,strchr(s,key));
else
printf("Can't find %c in string!\n",key);
system("pause");
}
印出: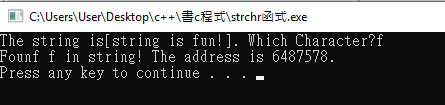
解釋:
ch為char型態
strcmp()和strncmp()函式:比較字串(比較兩個字串,根據結果回傳不同的值)
語法:
int strcmp(const char*str1,const char *str2);
int strncmp(const char*str1,const char *str2,size_t len);
範例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main (void){
char s1[]="string is fun!";
char s2[]="string is";
if(!strcmp(s1,s2))
printf("s1 and s2 are same(by strcmp)\n");
if(!strncmp(s1,s2,5))
printf("s1 and s2 are same(by strncmp)\n");
system("pause");
}
印出: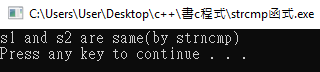
解釋:
使用strcmp()函式比較會發現兩個字串並不相同,
但使用strncmp()函式時,因只比較前5個字元,程式認為兩字串相同
strcpy()和strncpy()函式:複製字串
語法:
char *strcpy(char *to,const char *from);
char *strncpy(char *to,const char *from,size_t len);
範例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main (void){
char s1[]="string is fun!";
char s2[]="string ";
strcpy(s1,s2);
printf("%s\n",s1);
system("pause");
}
印出: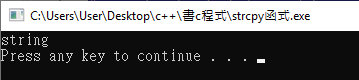
strlen()函式:計算字串長度
語法:size_t strlen(const char*str);
範例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main (void){
int len;
char s[]="string is fun!";
len=strlen(s);
printf("string s is %d long\n",len);
system("pause");
}
印出: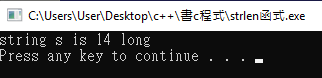
解釋:字串長度含空格
那今天就先到這拉
謝謝大家今天的閱讀
