Postgresql 使用 fdw 連接MySQL 將階層資料移轉並使用 ltree 產生路徑實例
昨天回答了邦友關於 MySQL 5.7 處理階層式資料.雖然開發了兩個 procedure,
但是畢竟不如使用有 CTE 及 Path Enumerations (ltree) 的 Postgresql
來的方便.
https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/questions/10195812
我知道有許多單位因為種種原因,一時無法升級到 MySQL 8 ,
而且 MySQL 8 要做 Path Enumerations也要自己 Hardcode.
換成 Postgresql 呢? 換資料庫可是件大工程.
所以我想將使用 Postgresql 使用 fdw 的功能,將 Postgresql 怎樣連接 MySQL ,
並將 Adjacency List 型態的資料,使用之前介紹過的 ltree, 將資料變成
Path Enumerations 與 Adjacency List 共存,甚至回寫到 MySQL 的一整個
過程,與大家分享.
階層式資料的處理,算是難度較高,也是一些ERP的重要核心,例如 BOM 展開,工序,組織,
物料關係等等.
來開始愛與勇氣的冒險吧.
--
先來看昨天的邦友的資料. https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/questions/10195812
我們在 Postgresql 這邊建立一個鏡像的 table.過程如下:
# in PostgreSQL
# 先建立一個 連線的 server , 取名為 mysql_server
create server mysql_server
foreign data wrapper mysql_fdw
options (host '127.0.0.1', port '3306');
# 建立一個 mapping user, for 現在登入的 pg user
# 密碼以及 mysql 的 user, 要記得置換.
create user mapping for miku
server mysql_server
options (username 'miku1', password 'your$passwd');
--
# 接著使用 Postgresql 特殊的 import foreign schema
# 來建立對應的 table.
# 一般是用來匯入整個 schema , 有選項可以指定 table.
# 所以這次只匯入 ithelp191024
import foreign schema miku1
limit to (ithelp191024)
from server mysql_server
into miku;
[miku]# \dE
List of relations
+--------+--------------+---------------+-------+
| Schema | Name | Type | Owner |
+--------+--------------+---------------+-------+
| miku | ithelp191024 | foreign table | miku |
+--------+--------------+---------------+-------+
[miku]# \dS ithelp191024
Foreign table "miku.ithelp191024"
+-----------+---------+-----------+----------+---------+-------------+
| Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | FDW options |
+-----------+---------+-----------+----------+---------+-------------+
| id | integer | | not null | | |
| parent_id | integer | | | | |
+-----------+---------+-----------+----------+---------+-------------+
Server: mysql_server
FDW options: (dbname 'miku1', table_name 'ithelp191024')
select *
from ithelp191024;
+----+-----------+
| id | parent_id |
+----+-----------+
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 3 |
...
| 26 | ¤ |
+----+-----------+
(15 rows)
# 這樣不用手動建立 mapping table, import foreign schema
# 幫我們建立好了.很方便.
# 接著建立 Postgresql 這邊有 ltree 型態的 table
create table p191025a (
id int primary key
, parentid int
, path ltree
);
create unique index
on p191025a
using btree(path);
create index
on p191025a
using gist(path);
create or replace function p191025a_get_path(id int)
returns ltree as
$code$
select case when p.parentid is null
then p.id::text::ltree
else p191025a_get_path(p.parentid) || p.id::text
end
from p191025a p
where p.id = $1;
$code$
language sql;
create or replace function trig_upin_p191025a()
returns trigger as
$code$
begin
if TG_OP = 'UPDATE' then
if (coalesce(old.parentid, 0) != coalesce(new.parentid, 0)
or new.id != old.id) then
update p191025a
set path = p191025a_get_path(id)
where old.path @> p191025a.path;
end if;
elsif TG_OP = 'INSERT' then
update p191025a
set path = p191025a_get_path(new.id)
where p191025a.id = new.id;
end if;
return new;
end
$code$
language plpgsql volatile;
create trigger trig_upin_p191025a
after insert or update of id, parentid
on p191025a for each row
execute procedure trig_upin_p191025a();
-----
# 建立好 trigger 後,我們直接透過 CTE 將 MySQL 的 資料
# insert 到 p191025a
--
insert into p191025a(id, parentid)
with recursive tree as (
select id
, parent_id
from ithelp191024
where parent_id is null
union all
select i.id
, i.parent_id
from ithelp191024 i
inner join tree t
on (i.parent_id = t.id)
)
select id, parent_id
from tree;
select *
from p191025a;
+----+----------+-------------+
| id | parentid | path |
+----+----------+-------------+
| 26 | ¤ | 26 |
| 20 | 26 | 26.20 |
| 10 | 26 | 26.10 |
| 37 | 26 | 26.37 |
| 19 | 10 | 26.10.19 |
| 5 | 10 | 26.10.5 |
| 22 | 20 | 26.20.22 |
| 45 | 37 | 26.37.45 |
| 36 | 37 | 26.37.36 |
| 3 | 5 | 26.10.5.3 |
| 9 | 5 | 26.10.5.9 |
| 17 | 19 | 26.10.19.17 |
| 21 | 19 | 26.10.19.21 |
| 1 | 3 | 26.10.5.3.1 |
| 2 | 3 | 26.10.5.3.2 |
+----+----------+-------------+
(15 rows)
---
# 很優雅的顯示出來路徑了.
# 接著我們要把路徑資料轉給 MySQL,讓 MySQL 那邊也能方便使用,無需一個一個生成.
# 轉回去之前先在 MySQL 建立新的 table.
-- in MySQL
create table ithelp191025 (
id int unsigned NOT NULL primary key
, parent_id int unsigned DEFAULT NULL
, path text
);
# 接著在 Postgresql 建立 mapping table
-- in Postgresql
import foreign schema miku1
limit to (ithelp191025)
from server mysql_server
into miku;
# 將 p191025a 的資料 insert 給 ithelp191025
# 注意到將 ltree 轉型為 text
-- in Postgresql
insert into ithelp191025 (id, parent_id, path)
select id
, parentid
, path::text
from p191025a;
# 注意, 最好做 commit 確保成果.
這時候在 MySQL 的 ithelp191025 已經有了 path 的資料了.
也就是說可以透過 fdw , 直接更新 MySQL 的資料.
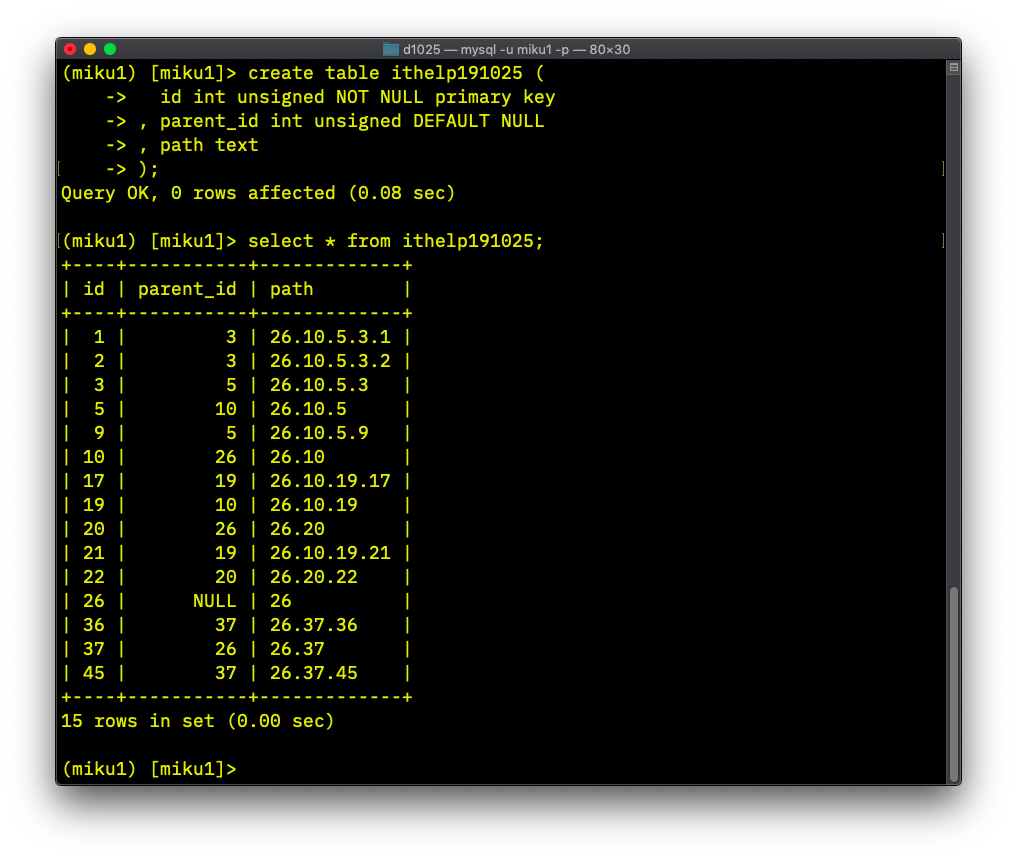
上面在 Postgresql 的 table , 我們使用了 trigger, 此
trigger 會遞迴呼叫 function. 然後我們再透過 CTE 遞迴
insert 到 table, 此時 trigger 會產生 path.也就是有
兩組遞迴;也許有人會擔心執行效能的問題.
先來看這道 SQL Command 及其執行結果.
with recursive tree as (
select id
, parent_id
, array[]::int[] as path
, id::text as path2
from ithelp191024
where parent_id is null
union all
select i.id
, i.parent_id
, path || i.id
, path2 || '.' || i.id::text
from ithelp191024 i
inner join tree t
on (i.parent_id = t.id)
)
select *
from tree;
+----+-----------+------------+-------------+
| id | parent_id | path | path2 |
+----+-----------+------------+-------------+
| 26 | ¤ | {} | 26 |
| 20 | 26 | {20} | 26.20 |
| 10 | 26 | {10} | 26.10 |
| 37 | 26 | {37} | 26.37 |
| 19 | 10 | {10,19} | 26.10.19 |
| 5 | 10 | {10,5} | 26.10.5 |
| 22 | 20 | {20,22} | 26.20.22 |
| 45 | 37 | {37,45} | 26.37.45 |
| 36 | 37 | {37,36} | 26.37.36 |
| 3 | 5 | {10,5,3} | 26.10.5.3 |
| 9 | 5 | {10,5,9} | 26.10.5.9 |
| 17 | 19 | {10,19,17} | 26.10.19.17 |
| 21 | 19 | {10,19,21} | 26.10.19.21 |
| 1 | 3 | {10,5,3,1} | 26.10.5.3.1 |
| 2 | 3 | {10,5,3,2} | 26.10.5.3.2 |
+----+-----------+------------+-------------+
(15 rows)
當 table 已經有 id, parent_id ,卻無 path 時,
可以使用 CTE 方式批次產生,此時是可以將 trigger 改成
在 insert 時不觸發.
trigger 主要是確保,更新時,能夠保持其一致性.
當批次更新完成後,可以改回 insert 跟 update 時均觸發.
這樣輸入更新都能確保正確性,平時輸入的語法也單純.

一向都使用 Mysql,沒有接觸 Postgresql , 不知道它有這麼多強大的功能。
看完這系列文章,發現它的確有很多【特異功能】可以簡便地解決 mysql 要花費大量精神才能得到相同的結果,比如在資料型態方面,多采多姿,遠比 mysql 完整而豐富。
受教了,感恩。
兩者定位不同
PostgreSQL: The World's Most Advanced Open Source Relational Database
MySQL: The World’s Most Popular Open Source Database