記錄學習內容。看網路上大大們的文章和影片,做些紀錄。
還不太了解,內容可能有錯誤。
Leetcode 1192. Critical Connections in a Network
筆記:
假設有一個點是3
另一個點是4
邊的表示方法就是[3、4]
代表3 到 4
如果是 undirected graph (沒方向(箭頭)的圖)
[3、4] 就代表 3到4 、 4到3都可以 。
這題是undirected graph。
題目 給 connections = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[1,3]]
代表 0 1之間相連 、1,2之間相連 、2,0之間相連 、1,3之間相連
有4個邊(edge )
有一種邊 叫做 critical connection 。
這種邊 移除 後 , 會讓1個 圖 變成 兩個圖 , 就會讓 某些點 到 不了 某些點
如圖 ,這條紅色的邊 就叫做critical connection 。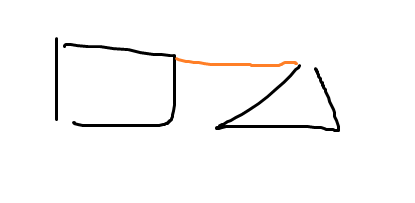
教學來源:
Critical Connections in a Network - Leet Code Hard Problem
影片解題筆記:
List<List> connections 代表 題目給的邊:
connections = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[1,3]]
ArrayList[] 就是 [ArrayList , ArrayList, ArrayList, ArrayList ]
陣列裡面放 ArrayList 資料。
先把[[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[1,3]] 換成
[ (1,2) ,(0,2,3), (1,0), (1) ]
代表 0 跟 1,2 這二點 有邊
1 跟 0,2,3 這三點 有邊
2 跟 1,0 這兩點 有邊
3 跟 1, 這一點 有邊
接著dfs 走訪 圖 ,先看每個變數是什麼意思:
ArrayList<Integer>[] graph : [ (1,2) (0,2,3) (1,0) (1) ] 代表圖
int currentNode : 現在的點
int parentNode : 上一個走過的點 ,像是A點 走到 B點 ,A點就是 parentNode , B點就是 currentNode
int[] times : 存每個點 是 第幾個走到的
int[] lowTimes : 如果這個點有Back edge:(所有指向ancestor()的edge)
,會更新lowTimes,讓lowTimes 跟 鄰居(祖先) 有一樣的lowTimes
boolean[] visitedNodes : 節點拜訪過了沒? True代表走過了
List<List<Integer>> ans : 最後的答案 ,代表有哪些邊是critical connection 。
參考:
Graph: Depth-First Search(DFS,深度優先搜尋)
0走到2在走到1,1又可以走到 0 。 1走到0 就叫做Back edge。
代表 有 2 這個點的邊 ,不會是 critical connection 。
因為拿掉2 ,1 和 0 還是可以連接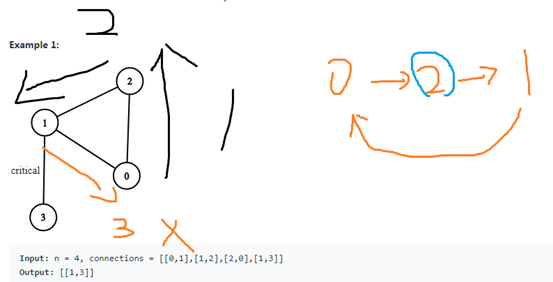
0 點 先 走到 1 點
1 點 是 (0,2,3) , 先走到0點 ,但是0 點是上一個走過的點 , 所以略過。
所以走到2點
2點 是 (1,0) ,所以走到1點 ,1點是上一個走過的點, 所以略過。
接著走到0 點 , 0拜訪過了 ,所以執行這段程式:
lowTimes[currentNode] = Math.min(lowTimes[currentNode], lowTimes[neighbourNode]);
也就是:
Math.min(lowTimes[2], lowTimes[0]) -- >
Math.min(2, 0) -- >
0
所以2 點 的lowTime 會被更新為0
Time 的意思 應該是 第幾個走到。
lowTimes 則是有考慮到backEdge的狀況 ,lowTimes要用來判斷是不是Critical Connections 。
所以現在2的 time為2 , lowTimes為0 。
不太懂,總之繼續執行程式 :
2 這個點就算完成遞迴了
所以我們退回1 這個點 , 1會執行dfs的下一行:
dfs(graph, neighbourNode, currentNode, times, lowTimes, visitedNodes, ans);
lowTimes[currentNode] = Math.min(lowTimes[currentNode], lowTimes[neighbourNode]);
if (times[currentNode] < lowTimes[neighbourNode]) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(currentNode, neighbourNode));
}
lowTimes[currentNode] = Math.min(lowTimes[currentNode], lowTimes[neighbourNode]);
也就是Math.min(lowTimes[1], lowTimes[2]);
也就是Math.min(1, 0);
也就是0
接著if (times[currentNode] < lowTimes[neighbourNode])
也就是 if (times[1] < lowTimes[2])
也就是 if (1 < 0)
接著繼續迴圈1走到3
3 沒有鄰居了,所以結束。
### 回到1 ,1繼續執行dfs 的下一行 :
lowTimes[currentNode] = Math.min(lowTimes[currentNode], lowTimes[neighbourNode]);
if (times[currentNode] < lowTimes[neighbourNode]) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(currentNode, neighbourNode));
}
lowTimes[currentNode] = Math.min(lowTimes[currentNode], lowTimes[neighbourNode]);
也就是 Math.min(lowTimes[1], lowTimes[3]);
也就是 Math.min(0, 3);
也就是 0
接著
if (times[currentNode] < lowTimes[neighbourNode]) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(currentNode, neighbourNode));
}
也就是if (times[1] < lowTimes[3])
也就是 if (1 < 3)
ans.add(1 和3 這個邊); 答案就是1到3
1 也跑完遞迴了 ,所以接著回到0, 0接著到2,2 走過了 ,在判斷 一下2,再判斷一下0,程式就結束了
流程大概懂了 ,但是沒有說很熟,就先到這吧
程式改成這樣 ,可以印出來測試:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
private static int currentTime = 0;
public static List<List<Integer>> criticalConnections(int n, List<List<Integer>> connections) {
{
int[] times = new int[n];
int[] lowTimes = new int[n];
boolean[] visitedNodes = new boolean[n];
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];
for(int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
for(List<Integer> connection: connections) {
graph[connection.get(0)].add(connection.get(1));
graph[connection.get(1)].add(connection.get(0));
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
visitedNodes[i] = false;
}
//看一下graph[i]的內容
//確定是[ (1,2) (0,2,3) (1,0) (1) ]
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println("graph[i]?"+graph[i]);
}
dfs(graph, 0, -1, times, lowTimes, visitedNodes, ans);
return ans;
}
}
private static void dfs(ArrayList<Integer>[] graph, int currentNode, int parentNode, int[] times, int[] lowTimes, boolean[] visitedNodes, List<List<Integer>> ans) {
System.out.println("currentNode?"+currentNode); // 0 1 2 3
visitedNodes[currentNode] = true;
times[currentNode] = lowTimes[currentNode] = currentTime++;
System.out.println(currentNode +" currentNode -- > " + (currentTime-1)); //因為前面++了,所以-1觀察
for (int neighbourNode : graph[currentNode]) {
if (neighbourNode == parentNode)
continue;
else if (!visitedNodes[neighbourNode]) {
dfs(graph, neighbourNode, currentNode, times, lowTimes, visitedNodes, ans);
lowTimes[currentNode] = Math.min(lowTimes[currentNode], lowTimes[neighbourNode]);
if (times[currentNode] < lowTimes[neighbourNode]) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(currentNode, neighbourNode));
}
} else {
System.out.println("lowTimes[currentNode]?"+lowTimes[currentNode]);
System.out.println("lowTimes[neighbourNode]?"+lowTimes[neighbourNode]);
lowTimes[currentNode] = Math.min(lowTimes[currentNode], lowTimes[neighbourNode]);
}
}
}
}
public class GraphTest {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
List<List<Integer>> connections = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> edge = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> edge1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> edge2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> edge3 = new ArrayList<>();
edge.add(0);
edge.add(1);
edge1.add(1);
edge1.add(2);
edge2.add(2);
edge2.add(0);
edge3.add(1);
edge3.add(3);
connections.add(edge);
connections.add(edge1);
connections.add(edge2);
connections.add(edge3);
System.out.println(connections); //[[0, 1], [1, 2], [2, 0], [1, 3]]
List<List<Integer>> ans = Solution.criticalConnections(4, connections);
System.out.println(ans); //[[1, 3]]
}
}
