http服務基於client與server二個端點的交互行為,client發出request,server收下request後進行對應邏輯處理,最後返回一個response給client
最基本的處理流程可以用下圖來表示
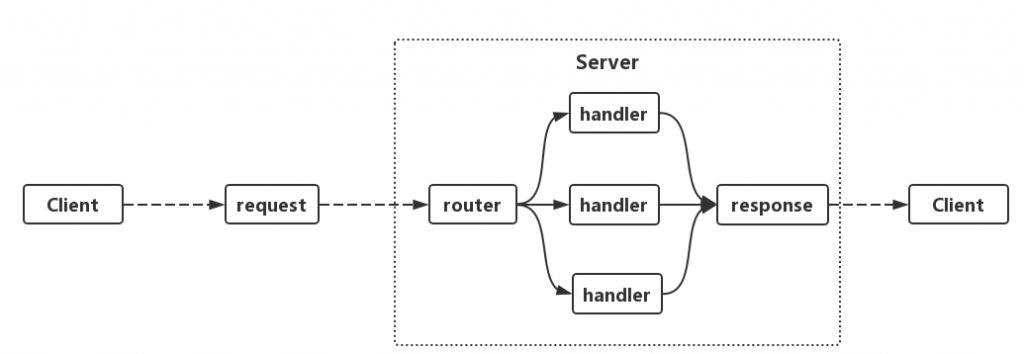
可以看到request進來,會經過router,根據對應的path對到相對應的handler,最後response出去。
以下我們來實作一個http server
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func ping(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf-8")
//fmt.Fprintf(w, "pong")
qq := map[string]string{
"data": "pong",
}
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(qq)
}
func mdfk(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf-8")
//fmt.Fprintf(w, "pong")
qq := map[string]string{
"year": "2020",
"message": "mdfk",
}
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(qq)
}
func main() {
//設定訪問的路由,HandleFunc接受2個參數,第一個是路由地址,第二個為處理方式。
//ex:如果打127.0.0.1:8787/ 這個url時,會進入"/" 對應的hanlder "ping"
//打127.0.0.1:8787/2020,會進入"/2020" 對應的hanlder "mdfk"
http.HandleFunc("/", ping)
http.HandleFunc("/2020", mdfk)
err := http.ListenAndServe(":8787", nil) //設定監聽的埠
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("ListenAndServe: ", err)
}
}
直接呼叫127.0.0.1:8787/2020看看否成功
curl --location --request GET '127.0.0.1:8787/2020'
有回傳值,表示server有收到request並回傳respose
{"message":"mdfk","year":"2020"}
除了上面的最基礎的寫法外,還可以自定義server的設定值
func main() {
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc("/", ping)
mux.HandleFunc("/bye", mdfk)
//定義一個http.Server struct
server := &http.Server{
//Addr填入host:port,如果是localhost就直接填入:port就好
Addr: ":8787",
//timeout設定
WriteTimeout: time.Second * 3,
ReadTimeout: time.Second * 30,
//ServeMux
Handler: mux,
}
log.Println("go http srever")
log.Fatal(server.ListenAndServe())
}
原生套件實作http server相對簡單,但是還是有一些不支援的功能
1.無法使用/customer/:customer_id
2.無法限制method(GET,POST,PUT,DELETE)
3.無法使用正則式
以下是除了原生套件外,星星數來說相對多的套件
github路徑:mux
只要把http.NewServeMux()換成mux.NewRouter()就好,handler都不用重構
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"net/http"
"github.com/gorilla/mux"
)
func main() {
//net/http原生寫法
//mux := http.NewServeMux()
//改呼叫mux.NewRouter,其他寫法跟原生的基本上一樣
mux := mux.NewRouter()
//普通路由
mux.HandleFunc("/", ping)
mux.HandleFunc("/2020", mdfk)
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", mux)
}
func ping(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf-8")
//fmt.Fprintf(w, "pong")
qq := map[string]string{
"data": "pong",
}
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(qq)
}
func mdfk(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf-8")
//fmt.Fprintf(w, "pong")
qq := map[string]string{
"year": "2020",
"message": "mdfk",
}
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(qq)
}
下面以path、query string跟正則match路徑,加上限制method為例
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/gorilla/mux"
)
func main() {
mux := mux.NewRouter()
//query string,限制使用post跟options
mux.HandleFunc("/list", queryStringGetList).Methods(http.MethodPost, http.MethodOptions)
//path parameter,限制使用get跟options
mux.HandleFunc("/list2/{id}/{level}", pathGetList).Methods(http.MethodGet, http.MethodOptions)
//正則路由parameter,id限制要輸入英文
mux.HandleFunc("/list3/{id:[a-z]+}", regexGetList)
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", mux)
}
func queryStringGetList(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
v := r.URL.Query()
id := v.Get("id")
level := v.Get("level")
fmt.Fprintln(w, "id: ", id, "level: ", level)
}
func pathGetList(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
vars := mux.Vars(r)
id := vars["id"]
level := vars["level"]
fmt.Fprintln(w, "id: ", id, "level: ", level)
}
func regexGetList(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
vars := mux.Vars(r)
id := vars["id"]
fmt.Fprintln(w, "id: ", id)
}
執行結果
//HTTP/1.1 405 Method Not Allowed,因為原本handler是限制使用post才行,所以確認有被限制住
curl '127.0.0.1:8080/list' -v
//HTTP/1.1 200 OK
curl --location --request POST '127.0.0.1:8080/list'
//使用path parameter,所以回傳值得到了id: aaa level: 3
curl --location --request GET '127.0.0.1:8080/list2/aaa/3'
//使用限制path字串,正則限制path要為英文,所以此path不合法,會得到404 page not found
curl --location --request GET '127.0.0.1:8080/list3/aaa44445'
//符合正則,得到回傳id: aaabbb
curl --location --request GET '127.0.0.1:8080/list3/aaabbb'
這功能很方便,如果需要不同路配搭不同middleware時,可以使用前綴來切割成多個子路由
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/gorilla/mux"
)
func main() {
mux := mux.NewRouter()
//設定前綴"/products/"並設成子路由
products := mux.PathPrefix("/products/").Subrouter()
products.HandleFunc("/list", queryStringGetList).Methods(http.MethodGet, http.MethodOptions)
//設定前綴"/customer/"並設成子路由
customer := mux.PathPrefix("/customer/").Subrouter()
customer.HandleFunc("/list", queryStringGetList).Methods(http.MethodGet, http.MethodOptions)
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", mux)
}
func queryStringGetList(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintln(w, "URL PATH:", r.URL.Path)
}
執行結果
//得到回傳值,URL PATH: /customer/list,與原本設定的子路由一致
curl --location --request GET '127.0.0.1:8080/customer/list'
//得到回傳值,URL PATH: /products/list,與原本設定的子路由一致
curl --location --request GET '127.0.0.1:8080/products/list'
middleware的詳細文章可以參考這篇 [鐵人賽Day04] - 淺談Middleware,簡單說事件介於request與response間,這樣子就不用每個handler都要寫相同的code(ex,log或是驗證權限)
範例使用剛剛的子路由設定,進行不同子路middleware的情境
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/gorilla/mux"
)
func main() {
mux := mux.NewRouter()
//設定前綴"/products/"並設成子路由
products := mux.PathPrefix("/products/").Subrouter()
products.HandleFunc("/list", queryStringGetList).Methods(http.MethodGet, http.MethodOptions)
//products 子路由使用loggingMiddleware
products.Use(loggingMiddleware)
//設定前綴"/customer/"並設成子路由
customer := mux.PathPrefix("/customer/").Subrouter()
customer.HandleFunc("/list", queryStringGetList).Methods(http.MethodGet, http.MethodOptions)
//customer 子路由使用checkTokenMiddleware
customer.Use(checkTokenMiddleware)
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", mux)
}
func queryStringGetList(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintln(w, "URL PATH:", r.URL.Path)
}
func loggingMiddleware(next http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
//Do stuff here
fmt.Fprintln(w, "use loggin middleware:", r.RequestURI)
// Call the next handler, which can be another middleware in the chain, or the final handler.
next.ServeHTTP(w, r)
})
}
func checkTokenMiddleware(next http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
token := r.Header.Get("Check-Token")
if token == "" {
http.Error(w, "Forbidden", http.StatusForbidden)
} else {
fmt.Println("request with token:\n", token)
// Pass down the request to the next middleware (or final handler)
next.ServeHTTP(w, r)
}
})
}
執行結果
//products子路由使用loggingMiddleware
//use loggin middleware: /products/list URL PATH: /products/list
curl --location --request GET '127.0.0.1:8080/products/list'
//customer子路由使用checkTokenMiddleware,會驗證header有沒有帶Check-Token
//有帶header:Check-Token ->URL PATH: /customer/list
//沒帶header:Check-Token ->Forbidden
curl --location --request GET '127.0.0.1:8080/customer/list' \
--header 'Check-Token: GG'
根據上面的執行結果來看,搭配使用mux套件建立的http server彈性與功能比原生net/http套件豐富,
可以視開發情境來選擇使用。
