描述
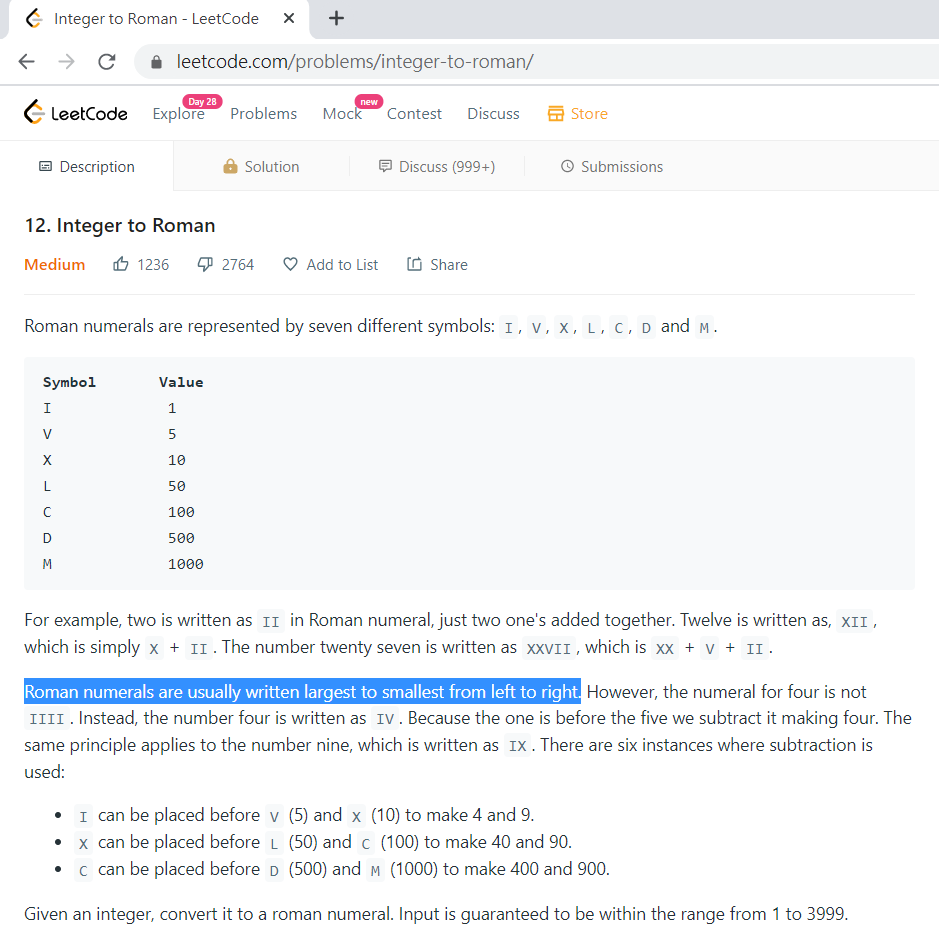
Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: I, V, X, L, C, D and M.
Symbol Value
I 1
V 5
X 10
L 50
C 100
D 500
M 1000
For example, two is written as II in Roman numeral, just two one's added together. Twelve is written as, XII, which is simply X + II. The number twenty seven is written as XXVII, which is XX + V + II.
Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not IIII. Instead, the number four is written as IV. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as IX. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
I can be placed before V (5) and X (10) to make 4 and 9.
X can be placed before L (50) and C (100) to make 40 and 90.
C can be placed before D (500) and M (1000) to make 400 and 900.
Given an integer, convert it to a roman numeral. Input is guaranteed to be within the range from 1 to 3999.
Input: 3
Output: "III"
Input: 4
Output: "IV"
Input: 9
Output: "IX"
Input: 58
Output: "LVIII"
Explanation: L = 50, V = 5, III = 3.
Example 5:
Input: 1994
Output: "MCMXCIV"
Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
階段狀態:處理1個位數
class Solution:
def intToRoman(self, num: int) -> str:
# know how many bits?
# print(len(num))
print(len(str(num)))
Romandict = {}
Romandict[1] = 'I'
Romandict[5] = 'V'
Romandict[10] = 'X'
Romandict[50] = 'L'
Romandict[100] = 'C'
Romandict[500] = 'D'
Romandict[1000] = 'M'
#print(type(Romandict.keys()))
dis = 4000
base = -1
for key in Romandict.keys():
#print(key)
if abs(key-num) < dis:
dis = abs(key-num)
base = key
print("base"+str(base))
''' Ex1
ans = ""
while num > 0 :
num = num - base
print(base)
ans+=Romandict[base]
print(ans)
return ans
'''
''' Ex2 3
leftCnt = 0
if num < base :
tmp = base
while num != base:
base -= 1
leftCnt+=1
ans = ""
for i in range(leftCnt):
ans+= Romandict[1]
ans+= Romandict[tmp]
print(ans)
return ans
'''
''' Ex value: 8
# 過 3 以大記 小/等3 以小記
tmplist = []
for i in Romandict.keys():
tmplist.append(i)
if i == base:
print(tmplist[len(tmplist)-2])
littleBase = tmplist[len(tmplist)-2]
if (num-littleBase)<=3:
base = littleBase
print(base)
dif = num - base
print("test:"+str(tmplist[tmplist.index(base) - 1]))
print("dif:"+str(dif))
if dif% tmplist[tmplist.index(base) - 1] == 0:
rightCnt = dif/ tmplist[tmplist.index(base) - 1]
ans = ""
ans += Romandict[base]
for i in range(int(rightCnt)):
ans+= Romandict[tmplist[tmplist.index(base) - 1]]
print("ans:"+ans)
return ans
'''
處理 兩個位數
class Solution:
def intToRoman(self, num: int) -> str:
# know how many bits?
# print(len(num))
print(len(str(num)))
Romandict = {}
Romandict[1] = 'I'
Romandict[5] = 'V'
Romandict[10] = 'X'
Romandict[50] = 'L'
Romandict[100] = 'C'
Romandict[500] = 'D'
Romandict[1000] = 'M'
#print(type(Romandict.keys()))
dis = 4000
base = -1
for key in Romandict.keys():
#print(key)
if abs(key-num) < dis:
dis = abs(key-num)
base = key
print("base"+str(base))
''' Ex1
ans = ""
while num > 0 :
num = num - base
print(base)
ans+=Romandict[base]
print(ans)
return ans
'''
''' Ex2 3
leftCnt = 0
if num < base :
tmp = base
while num != base:
base -= 1
leftCnt+=1
ans = ""
for i in range(leftCnt):
ans+= Romandict[1]
ans+= Romandict[tmp]
print(ans)
return ans
'''
''' Ex value: 8
# 過 3 以大記 小/等3 以小記
tmplist = []
for i in Romandict.keys():
tmplist.append(i)
if i == base:
print(tmplist[len(tmplist)-2])
littleBase = tmplist[len(tmplist)-2]
if (num-littleBase)<=3:
base = littleBase
print(base)
dif = num - base
print("test:"+str(tmplist[tmplist.index(base) - 1]))
print("dif:"+str(dif))
if dif% tmplist[tmplist.index(base) - 1] == 0:
rightCnt = dif/ tmplist[tmplist.index(base) - 1]
ans = ""
ans += Romandict[base]
for i in range(int(rightCnt)):
ans+= Romandict[tmplist[tmplist.index(base) - 1]]
print("ans:"+ans)
return ans
'''
'''
# 判斷 個 時 百 千
while num!=0:
rem = num%10
print("rem:"+str(rem))
num/=10
#print("num:"+str(num))
if int(num) == 0 :
print(num)
break
'''
ans=""
dif = num - base
print("dif"+str(dif))
ans+=Romandict[base]
return ans
思路 : 待整理
PS: 想法參考 Java版-49規則
正解
class Solution:
def intToRoman(self, num: int) -> str:
# 在 Symbol Value 中 + 4,9,40,90,400,900
# 49規則
'''
1994: 1000+900+90+4
1000: M
900 : CM
90 : XC
4 : IV
'''
rdict = {}
rdict[1] ='I'
rdict[4] ='IV'
rdict[5] ='V'
rdict[9] ='IX'
rdict[10]='X'
rdict[40]='XL'
rdict[50]='L'
rdict[90]='XC'
rdict[100]='C'
rdict[400]='CD'
rdict[500]='D'
rdict[900]='CM'
rdict[1000]='M'
ans=""
for i in reversed(rdict.keys()):
while num>=i:
num=num-i
ans+=rdict[i]
print("ans:"+ans)
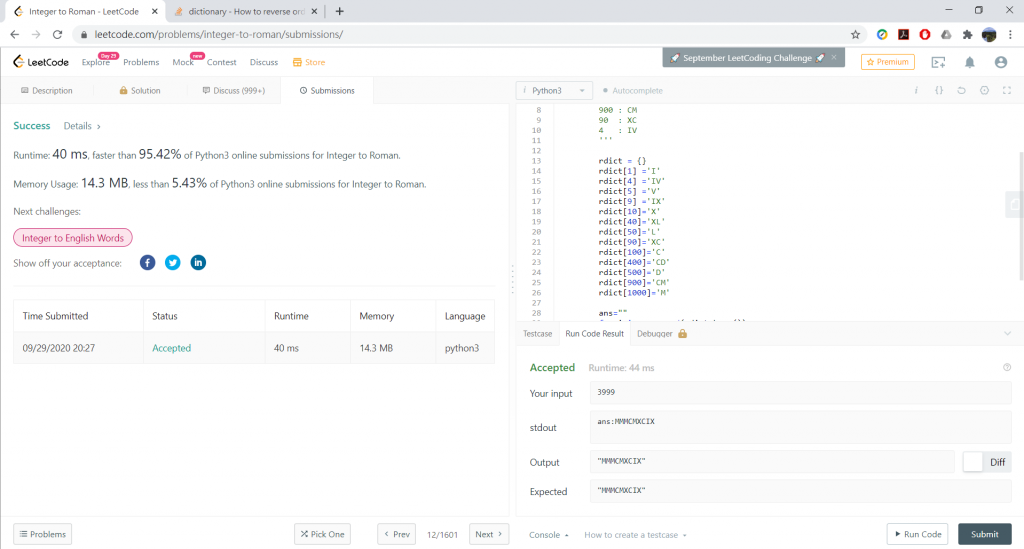
return ans
Result