定義一個 Mediator 物件用來封裝一組物件的互動方式。Mediator 藉由避免物件間相互直接的引用,從而降低它們之間的耦合程度,並且可以讓我們獨立地改變這些物件間的互動方式。
在生活上有許多事情會有複雜的關係,例如一間軟體公司產品,需要開發團隊、設計團隊、行銷團隊、客服團隊等等才能有一個較完善的產品團隊。而開發跟設計可能需要協調產品頁面,行銷也要跟開發討論產品功能如何符合市場,客服也會跟設計反應哪些流程需要改善。如此一來團隊之間的關係就會非常的複雜,如下圖:
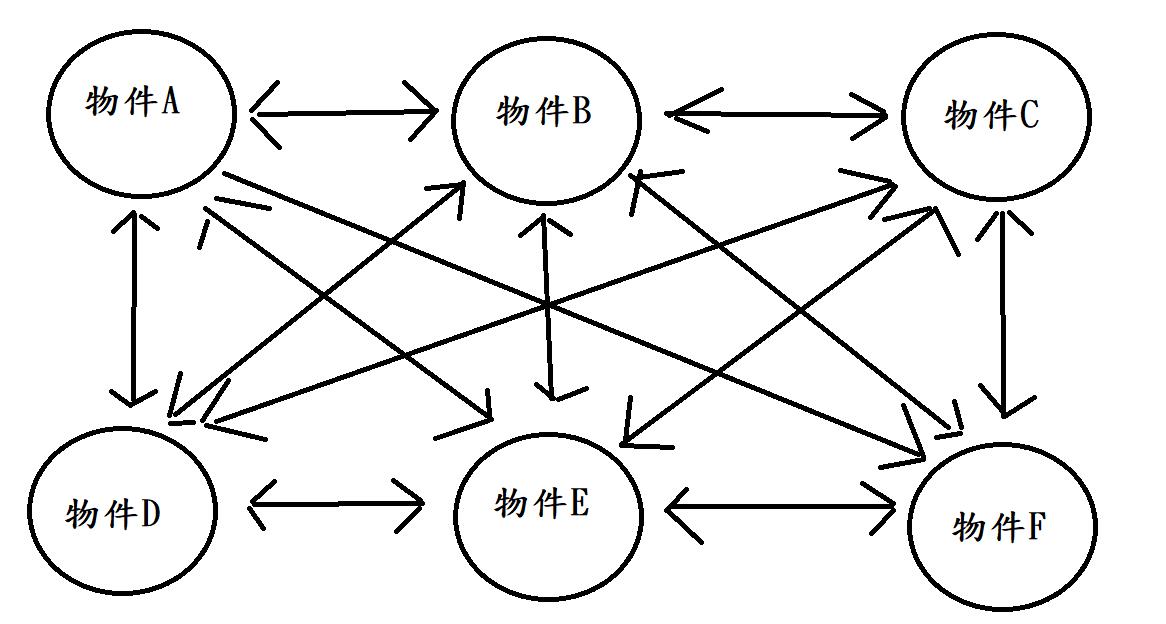
網狀結構
每個團隊自己去跟不同團隊有關係,我們稱這結構叫網狀結構。但很明顯這樣的一個結夠並不是很理想,所以產品需要一個產品經理,也就是中介者。由產品經理來處理所有團隊的,結構就會變成下圖:
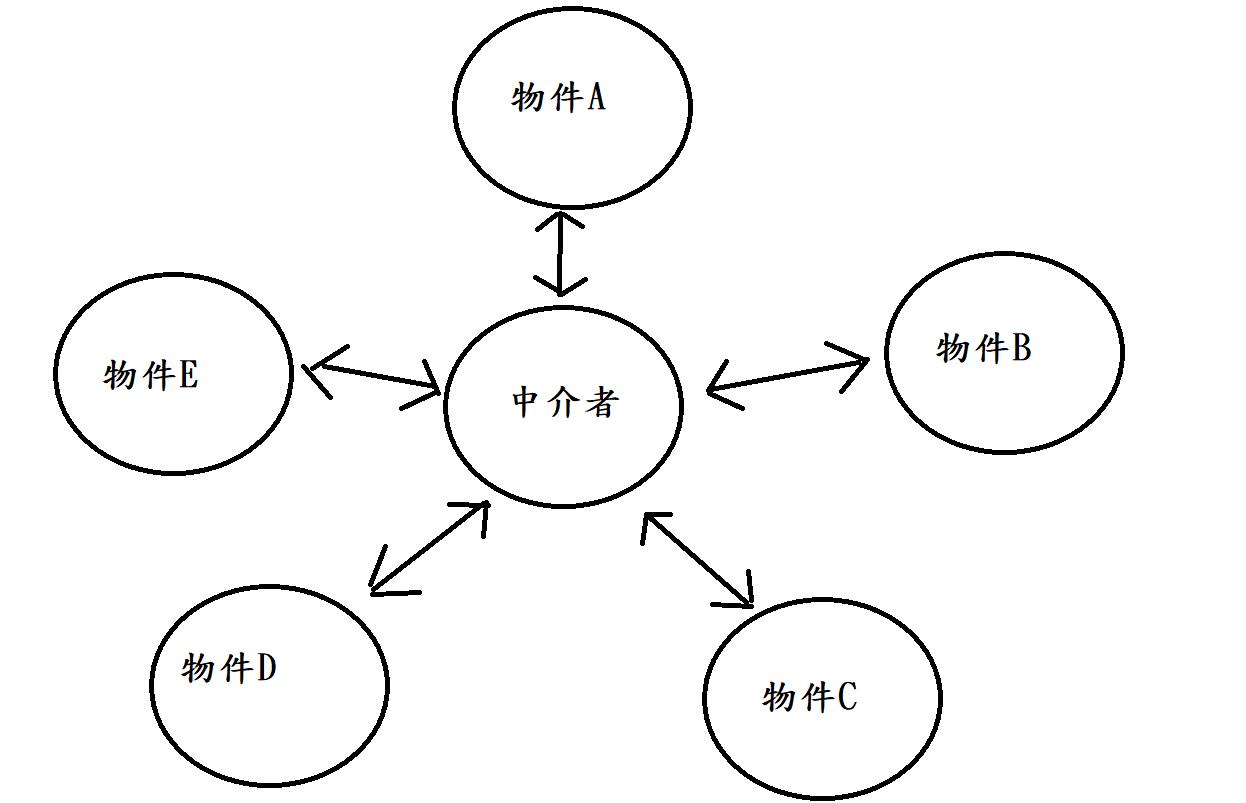
星狀結構
這種結構稱作星狀結構,現在每個團隊都經由產品經理去跟其他團隊溝通,團隊間的相依性就降低了許多。
| 成員 | 功用 |
|---|---|
| Mediator | 抽象中介者。主要為中介者接口,提供同事物件方法。 |
| ConcreteMediator | 實體中介者。實作抽象中介者,定義一個集合來管理同事物件,處理個同事間的關係,所以她依賴於同事。 |
| Colleague | 抽象同事類。定義同事類別的接口,保存中介者物件,提供同事物件抽象方法。 |
| ConcreteColleague | 實體同事類。實作抽象同事,當需要與其他同事物件工作時,需要由中介者物件負責後續的接洽。 |

剛剛有提到,一個產品需要工程、設計、客服、行銷團隊,而團隊之間的溝通則交由產品經理去做。所以我們首先要先定義抽象中介者給產品經理實作。
import java.util.*;
enum Type { // 建立一個列舉方便等等程式使用
ENGINEERING, DESIGN, SERVICE, MARKETING
}
//抽象中介者
abstract class Mediator {
public abstract void register(Type type, Colleague colleague);
public abstract void relay(Type type, String msg); //轉發
}
再來產品經理需要實作抽象中介者。
//實體中介者
class ProductManager extends Mediator {
private Map<Type, Colleague> colleagues = new HashMap<Type, Colleague>();
public void register(Type type, Colleague colleague) {
colleague.setMedium(this);
colleagues.put(type, colleague);
}
public void relay(Type type, String msg) {
Colleague toCl = colleagues.get(type);
toCl.receive(msg);
}
}
再來定義個團隊的抽象類別,有設定中介者的方法以及發送接收的抽象方法。
//抽象同事類
abstract class Colleague {
protected Mediator mediator;
public void setMedium(Mediator mediator) {
this.mediator = mediator;
}
public abstract void receive(String msg);
public abstract void send(Type type, String msg);
}
接著再依照不同的團隊,實作不同的邏輯在繼承的方法內。而在send最後會由中介者去轉發這個訊息到對應的同事類別內。
//實體同事類
class EngineeringTeam extends Colleague {
public void receive(String msg) {
System.out.println("工程團隊收到請求: " + msg + "。");
}
public void send(Type type, String msg) {
System.out.println("工程團隊發出請求: " + msg + "。");
mediator.relay(type, msg); //請中介者轉發
}
}
//實體同事類
class DesignTeam extends Colleague {
public void receive(String msg) {
System.out.println("設計團隊收到請求: " + msg + "。");
}
public void send(Type type, String msg) {
System.out.println("設計團隊發出請求: " + msg + "。");
mediator.relay(type, msg); //請中介者轉發
}
}
//實體同事類
class MarketingTeam extends Colleague {
public void receive(String msg) {
System.out.println("行銷團隊收到請求: " + msg + "。");
}
public void send(Type type, String msg) {
System.out.println("行銷團隊發出請求: " + msg + "。");
mediator.relay(type, msg); //請中介者轉發
}
}
//實體同事類
class CustomerService extends Colleague {
public void receive(String msg) {
System.out.println("客服團隊收到請求: " + msg + "。");
}
public void send(Type type, String msg) {
System.out.println("客服團隊發出請求: " + msg + "。");
mediator.relay(type, msg); //請中介者轉發
}
}
最後在Client端,先將各種團隊的物件建立起來,並都傳到中介者pm內。然後若某一個團隊有問題,只要將問題種類及問題發送出去,對應的團隊就會收到訊息。
public class MediatorPattern {
public static void main(String[] args){
ProductManager pm = new ProductManager();
Colleague c1, c2, c3, c4;
c1 = new DesignTeam();
c2 = new MarketingTeam();
c3 = new CustomerService();
c4 = new EngineeringTeam();
pm.register(Type.DESIGN, c1);
pm.register(Type.MARKETING, c2);
pm.register(Type.SERVICE, c3);
pm.register(Type.ENGINEERING, c4);
c1.send(Type.SERVICE, "設計有問題");
System.out.println("-------------");
c1.send(Type.ENGINEERING, "軟體設計有問題");
System.out.println("-------------");
}
}
output
設計團隊發出請求: 設計有問題。
客服團隊收到請求: 設計有問題。
-------------
設計團隊發出請求: 軟體設計有問題。
工程團隊收到請求: 軟體設計有問題。
-------------
而在開發中我們也可以簡化中介者模式:
1. 不定義中介者接口,將實體中介者物件創建成單例。
2. 同事物件不持有中介者,而是在需要的時候直接取得中介者物件並使用。
import java.util.*;
enum Type {
ENGINEERING, DESIGN, SERVICE, MARKETING
}
// 簡單單例中介者
class SimpleProductManager {
private static SimpleProductManager spm = new SimpleProductManager();
private Map<Type, SimpleColleague> colleagues = new HashMap<Type, SimpleColleague>();
private SimpleProductManager(){}
public static SimpleProductManager getMedium(){ // 讓同事物件取得中介者物件
return(spm);
}
public void register(Type type, SimpleColleague colleague) {
colleagues.put(type, colleague);
}
public void relay(Type type, String msg) {
SimpleColleague toCl = colleagues.get(type);
toCl.receive(msg);
}
}
interface SimpleColleague {
void receive(String msg);
void send(Type type, String msg);
}
// 實體同事類
class SimpleEngineeringTeam implements SimpleColleague {
SimpleEngineeringTeam(){
SimpleProductManager spm = SimpleProductManager.getMedium(); // 需要使用時直接取得
spm.register(Type.ENGINEERING, this); // 並使用
}
public void receive(String msg){
System.out.println("工程團隊收到請求: " + msg + "。");
}
public void send(Type type, String msg) {
SimpleProductManager spm = SimpleProductManager.getMedium();
System.out.println("工程團隊發出請求: " + msg + "。");
spm.relay(type, msg); // 中介者轉發
}
}
//實體同事類
class SimpleDesignTeam implements SimpleColleague {
SimpleDesignTeam(){
SimpleProductManager spm = SimpleProductManager.getMedium();
spm.register(Type.DESIGN, this);
}
public void receive(String msg) {
System.out.println("設計團隊收到請求: " + msg + "。");
}
public void send(Type type, String msg) {
SimpleProductManager spm = SimpleProductManager.getMedium();
System.out.println("設計團隊發出請求: " + msg + "。");
spm.relay(type, msg); // 中介者轉發
}
}
public class SimpleMediatorPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleColleague c1,c2;
c1 = new SimpleEngineeringTeam();
c2 = new SimpleDesignTeam();
c1.send(Type.DESIGN, "設計有問題");
System.out.println("-------------");
c1.send(Type.DESIGN, "UX設計有問題");
}
}
output
工程團隊發出請求: 設計有問題。
設計團隊收到請求: 設計有問題。
-------------
工程團隊發出請求: UX設計有問題。
設計團隊收到請求: UX設計有問題。
以上就是中介者模式以及中介者模式的簡化,藉由使用中介者模式,可以降低物件之間的耦合,也可增加物件的獨立性。
定義一個中介者物件來處理其餘物件的互動,藉此降低物件之間的耦合性。
Mediator:抽象中介者。主要為中介者接口,提供同事物件方法。
ConcreteMediator:實體中介者。實作抽象中介者,定義一個集合來管理同事物件,處理個同事間的關係,所以她依賴於同事。
Colleague:抽象同事類。定義同事類別的接口,保存中介者物件,提供同事物件抽象方法。
ConcreteColleague:實體同事類。實作抽象同事,當需要與其他同事物件工作時,需要由中介者物件負責後續的接洽。
優點
1. 降低物件之間的耦合性,讓物件容易重複使用。
2. 物件之間一對多的關聯性變成一對一,提高系統靈活性,也是整體容易維護及擴充。
缺點
1. 同事類別過多時,中介者責任很大,會使系統提升一定程度的複雜性,
1. 需要集合物件提供多種遍歷方法。
2. 需要遍歷不同的集合結構而提供統一的接口時。
中介者模式(详解版)
設計模式:中介者模式 (Mediator Pattern)
中介者模式 (Mediator Pattern)
