這幾天我們來介紹一些工具,在之後實作專案時會很常用到
我們的app 常常需要一些來自後臺的資料,像是與Web 伺服器進行通信來傳遞資訊,而這些數據傳輸方式基本都是用JSON,JSON是我們開發中最常使用的一種資料格式,官方文件
我們通常會將需要發送的數據序列化為JSON格式的字串流結構化資料進行傳輸,而反序列化則是將從獲得的JSON格式字串流結構化資料進行反序列化,重建我們所要的資料結構數據
手動序列化數據
規模較小的專案可以使用手動序列化
使用Flutter 內建的dart:convert的庫,這個library 包含了一個簡單的JSON編碼器和解碼器
例如:
import 'dart:convert';
void main() {
String jsonString = ''' {
"name": "John Smith",
"email": "john@example.com"
} ''';
manualDecode(jsonString);
}
void manualDecode(String jsonString) {
Map<String, dynamic> user = jsonDecode(jsonString);
print('Howdy, ${user['name']}!'); //印出 Howdy, John Smith!
print('We sent the verification link to ${user['email']}.'); //印出 We sent the verification link to john@example.com.
}
然而,jsonDecode()返回一個Map<String, dynamic>,也就是說直到執行時我們才知道值的類型,代表使用這個方法,我們就失去了大部分的靜態類型語言特性:類型安全,自動補全以及最重要的編譯時異常,例如,當我們要存取name欄位,但是名稱卻打錯了,此時編譯器在編譯時不會幫忙報錯
解決方法:在Model 類別中序列化JSON
通過事先定義與Json結構對應的Model類,然後在請求到數據後再動態根據數據創建出Model類的實例
例如:
建立一個與上述範例Json 對應的Model 類別,User:
User.fromJson建構函數,用於從map 結構資料中構造出一個新的User實例toJson方法,將User實例轉化為一個map 結構化資料class User {
final String name;
final String email;
User(this.name, this.email);
User.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json)
: name = json['name'],
email = json['email'];
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() =>
{
'name': name,
'email': email,
};
}
通過這種方法可以擁有類型安全, name和email字段的自動補全字段以及編譯時異常(檢測),如果你發生了筆誤或者把String類型的字段看成了int類型,app在編譯時就不會通過,而不是在執行時拋出異常
解碼序列化邏輯現在移動到了模型內部,通過此方法可以很容易地解碼/反序列化一個 user
import 'dart:convert';
void main() {
String jsonString = ''' {
"name": "John Smith",
"email": "john@example.com"
} ''';
Map userMap = json.decode(jsonString);
var user = new User.fromJson(userMap);
print('Howdy, ${user.name}!');
print('We sent the verification link to ${user.email}.');
}
class User {
final String name;
final String email;
User(this.name, this.email);
User.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json)
: name = json['name'],
email = json['email'];
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => {
'name': name,
'email': email,
};
}
要編碼/序列化 user,將User實例傳到jsonEncode()函數中,你不需要調用toJson()方法,因為jsonEncode()已經幫你做了這件事
String json = jsonEncode(user);
通過這種方法,被調用的代碼根本不需要擔心序列化JSON數據的問題,然而,模型Model 類別仍然是必須的。在一個生產環境下的App,你可能希望確保序列化數據能正確奏效。所以User.fromJson()和 User.toJson()方法都需要單元測試以便驗證正確的行為
然而,現實場景通常不是那麼簡單,有時候響應的JSON API 會更加複雜,例如它可能會包含一些相鄰的JSON 對象,而這些對象同樣需要使用它的model 類進行解析,此時我們就需要使用代碼來自動生成庫序列化JSON 數據
利用代碼自動生成序列化數據
儘管有其它的library 可以使用,我們來介紹官方推薦的函式庫json_serializable,由於序列化數據不再需要手動編寫或者維護,你可以將序列化JSON 數據在運行時的異常風險降到最低
添加依賴:
...
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
cupertino_icons: ^1.0.0
json_annotation: ^3.1.0 #當前版本
dev_dependencies:
flutter_test:
sdk: flutter
build_runner: ^1.10.3 #當前版本
json_serializable: ^3.5.0 #當前版本
...
以 json_serializable 的方式創建model類
user.dart:
import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart';
/// This allows the `User` class to access private members in
/// the generated file. The value for this is *.g.dart, where
/// the star denotes the source file name.
part 'user.g.dart';
/// An annotation for the code generator to know that this class needs the
/// JSON serialization logic to be generated.
@JsonSerializable()
class User {
User(this.name, this.email);
String name;
String email;
/// A necessary factory constructor for creating a new User instance
/// from a map. Pass the map to the generated `_$UserFromJson()` constructor.
/// The constructor is named after the source class, in this case, User.
factory User.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$UserFromJson(json);
/// `toJson` is the convention for a class to declare support for serialization
/// to JSON. The implementation simply calls the private, generated
/// helper method `_$UserToJson`.
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => _$UserToJson(this);
}
有了這些設置,程式碼生成器就會生成用於從JSON中編碼和解碼name和email這兩個欄位的程式碼
如果需要,自定義命名策略也很容易。例如,如果我們正在使用的API返回帶有snake_case的對象,但我們想在我們的模型中使用lowerCamelCase,那麼我們可以使用@JsonKey標註:
/// Tell json_serializable that "registration_date_millis" should be
/// mapped to this property.
@JsonKey(name: 'registration_date_millis')
final int registrationDateMillis;
當你首次創建json_serializable類時,你會得到類似下圖的錯誤
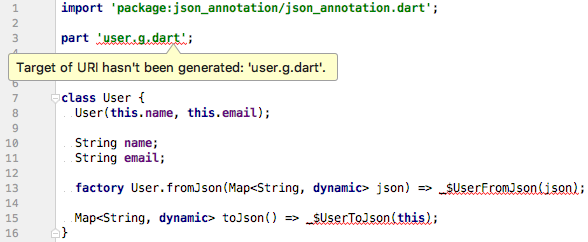
這些錯誤是完全正常的,這是因為Model類的生成代碼還不存在。為了解決這個問題,我們必須運行代碼生成器來為我們生成序列化模板。有兩種運行代碼生成器的方法:
透過在專案的根目錄下執行flutter packages pub run build_runner build,這觸發了一次性構建,我們可以在需要時為我們的Model生成json序列化代碼,它通過我們的源文件,找出需要生成Model類的源文件(包含@JsonSerializable標註的)來生成對應的.g.dart文件。一個好的建議是將所有Model 類放在一個單獨的目錄下,然後在該目錄下執行命令
雖然這非常方便,但如果我們不需要每次在Model類中進行更改時都要手動運行構建命令的話會更好
使用watcher可以使我們的源代碼生成的過程更加方便。它會監視我們項目中文件的變化,並在需要時自動構建必要的文件,我們可以通過flutter packages pub run build_runner watch在項目根目錄下運行來啟動watcher。只需啟動一次觀察器,然後它就會在後台運行,這是安全的
使用json_serializable,在User類中你可以忘記所有手動序列化的JSON數據。源代碼生成器會創建一個名為user.g.dart的文件,它包含了所有必須的序列化數據邏輯。你不必再編寫自動化測試來確保序列化數據奏效。現在由庫來負責確保序列化數據能正確地奏效
你可能在代碼中用了嵌套類,在你把類別作為參數傳遞給一些服務(比如Firebase)的時候,你可能會遇到Invalid argument錯誤
比如下面的這個Address類:
import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart';
part 'address.g.dart';
@JsonSerializable()
class Address {
String street;
String city;
Address(this.street, this.city);
factory Address.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$AddressFromJson(json);
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => _$AddressToJson(this);
}
一個Address類被嵌套在User類中使用:
import 'address.dart';
import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart';
part 'user.g.dart';
@JsonSerializable()
class User {
String firstName;
Address address;
User(this.firstName, this.address);
factory User.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$UserFromJson(json);
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => _$UserToJson(this);
}
在終端機中運行flutter pub run build_runner build創建* .g.dart文件,但私有函數如_ $ UserToJson()會看起來像下面這樣
user.g.dart:
(
Map<String, dynamic> _$UserToJson(User instance) => <String, dynamic>{
'firstName': instance.firstName,
'address': instance.address,
};
看起來沒有什麼問題,但如果print User 實例時:
import 'package:json_tutorial/user.dart';
import 'address.dart';
void main() {
Address address = Address("My st.", "New York");
User user = User("John", address);
print(user.toJson()); // 印出 {firstName: John, address: Instance of 'Address'}
//不是我們要的結果:{name: John, address: {street: My st., city: New York}}
}
為了得到正常的輸出,你需要在類別聲明之前為@JsonSerializable方法加入explicitToJson: true參數
user.dart:
import 'address.dart';
import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart';
part 'user.g.dart';
@JsonSerializable(explicitToJson: true)
class User {
String firstName;
Address address;
User(this.firstName, this.address);
factory User.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$UserFromJson(json);
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => _$UserToJson(this);
}
main.dart:
import 'package:json_tutorial/user.dart';
import 'address.dart';
void main() {
Address address = Address("My st.", "New York");
User user = User("John", address);
print(user.toJson()); // 印出 {firstName: John, address: {street: My st., city: New York}}
}
