The relationship between classes and objects was shared earlier. When an object needs to be set with initial attributes, constructors can be used.
If the object itself in the class does not have a constructor, it will automatically generate a basic one (which will not appear in the code and do nothing). Usually, we use the constructor to set the initial content of the object, use it with the keyword “new”, and the constructor name must be the same as the class name: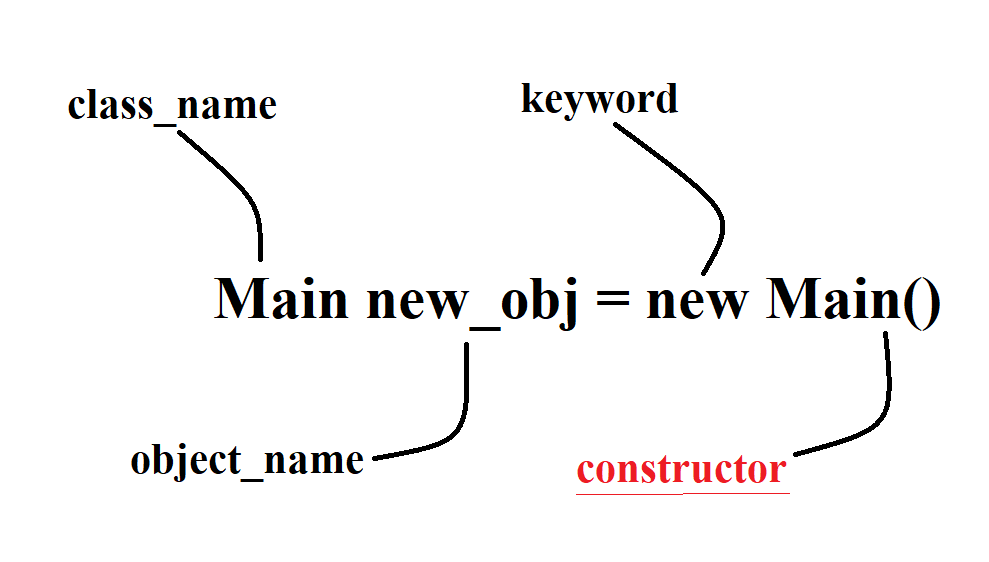
Like the settings we introduced earlier for objects, the last keyword is the constructor used to set the initial value, which we said was the class name. This can be further subdivided into two types, depending on whether or not there are any input arguments. In summary, there are three main types and four characteristics:
The following is a separate introduction to the concepts of constructors with and without parameter passing.
/*Default*/
public class Main{
String name;
int grade;
char gpa;
/*public Main(){ //系統預設
}*/
}
/*Constructor(NULL)*/
public class Main{
String name;
int grade;
char gpa;
public Main(){ //自行設定
}
}
The definition of the constructor will be:
(Modifier) class_name((argument)){
//Command
}
public class Main{
String name;
int grade;
char gpa;
public Main(){
name = "CHI";
grade = 82;
gpa = 'A';
}
void printout(){
System.out.println("Your personal information ");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Main newobj = new Main();
newobj.printout();
System.out.println("Student name : " + newobj.name);
System.out.println("Final test : " + newobj.grade);
System.out.println("GPA : " + newobj.gpa);
}
}
Next, we will change the above program to use the function input method and introduce the new keyword this.
public class Main{
String name;
int grade;
char gpa;
public Main(String name, int grade, char gpa){
this.name = name;
this.grade = grade;
this.gpa = gpa;
}
void printout(){
System.out.println("Your personal information");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Main newobj = new Main("Chi", 82, A);
newobj.printout();
System.out.println("Student name : " + newobj.name);
System.out.println("Final test : " + newobj.grade);
System.out.println("GPA : " + newobj.gpa);
}
}
Output: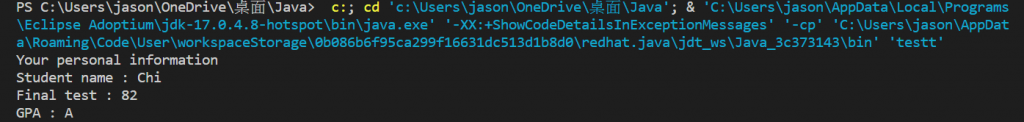
this refers to the nearest object, so when we use it, it refers to the name of the object created based on the constructor, and inherits the above-mentioned name results and other elements to this object.