
前面的文章已經有稍微介紹了介面(interface)的用法,介面能夠幫助我們定義物件應該有哪些屬性和方法,從而提供一種強型別的約束機制,讓開發者更容易組織代碼並進行程式設計。
介面可以用來定義類別應該實作哪些屬性和方法。這種方式能夠提供強型別的保證,並幫助類別遵循某種行為規範。介面是一種協議,它定義了類別的結構,但不提供具體實現。
interface AnimalInterface {
name: string;
makeSound(): void;
}
interface SuperpowerInterface {
usePower(): void;
}
// 使用 implements 關鍵字來實現介面,且可以實現多個介面
class DogInterface implements AnimalInterface, SuperpowerInterface {
constructor(public name: string, protected powerName?: string) {}
makeSound() {
console.log('汪!');
}
usePower() {
if (this.powerName) {
console.log(`使用${this.powerName}`)
} else {
console.log('沒有超能力')
}
}
}
const dog = new DogInterface('彭德', '預知未來');
dog.makeSound(); // 汪!
dog.usePower(); // 使用預知未來
介面不僅可以用來規範類別,還可以用來描述物件的形狀。這使得在 TypeScript 中操作物件時,可以強制檢查物件是否符合預期的結構。
interface Animal {
name: string;
makeSound(): void;
}
const usagi: Animal = {
name: '烏薩奇',
makeSound() {
console.log('嗚啦!');
}
}
usagi.makeSound(); // 嗚啦!
介面還可以用來定義函式的形狀,包含函式的參數類型與返回值,寫在同個 interface 也比較好管理函式重載。
// 利用函式重載的方式撰寫
interface GetDigitCount {
(x: string): number;
(x: number): number;
}
const getDigitCount: GetDigitCount = (x) => {
// 判斷數字的正則表達式
const regexp = /^-?(\d+)\.?\d*$/;
const match = x.toString().match(regexp);
if (!match) return 0;
return match[1].length;
}
console.log(getDigitCount(12345)); // 5
console.log(getDigitCount('-9876')); // 4
介面支持繼承,這使得我們可以將複雜的結構拆分為更小的部分,並且能夠讓新介面繼承已定義的屬性或方法。這一特性提高了代碼的重用性。
interface Shape {
color: string;
}
// 跟 class 一樣可以用 extends 關鍵字來繼承
interface Circle extends Shape {
radius: number;
}
const circle: Circle = {
color: 'red',
radius: 10
};
如果在同一作用域內定義了多個同名介面,TypeScript 會自動將這些介面合併成一個介面。這個特性稱為介面合併,它在處理大型系統中的不同模組時非常有用。
interface PersonInterface {
name: string;
}
interface PersonInterface {
age: number;
}
// 最終會自動合併介面,方便大型專案擴展型別
const person: PersonInterface = {
name: 'Johnson Mao',
age: 18
}
在實際使用中,type 和 interface 都有其優勢,選擇哪一個主要取決於具體需求和團隊偏好。
以我個人而言,如果需要定義物件的結構、擴展和合併的能力,我會選擇使用 interface 來定義,其餘都使用 type 的方式定義。
不過 type 在編輯器中會顯示結構還蠻方便的。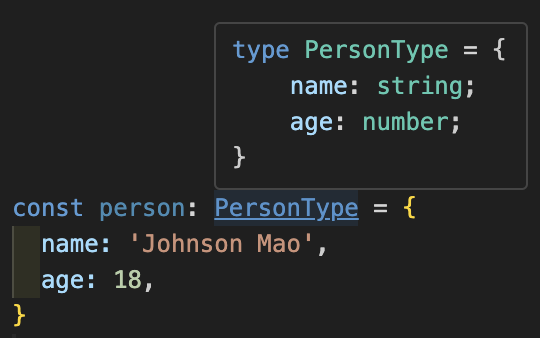
雖然 interface 和 type 都能用於定義型別,但它們還是有一些重要的區別。了解這些異同可以幫助你在不同情況下選擇最合適的工具來定義型別。
都可以定義物件結構
// 使用 interface 定義物件型別
interface PersonInterface {
name: string;
age?: number;
[key: string]: unknown;
}
// 使用 type 定義物件型別
type PersonType = {
name: string;
age?: number;
[key: string]: unknown;
};
都有擴展物件的方式
// 透過 extends 繼承另一個物件
interface EmployeeInterface extends PersonInterface {
position: string;
}
// 透過 & 融合不同物件
type EmployeeType = PersonType & {
position: string;
};
interface 只能定義物件型別。
type IdType = string | number;
// interface 就不能定義原始型別、元組、交集...等
interface 聲明同名會自動合併,type 不能聲明同名
interface 可以多次聲明同名,TypeScript 會自動合併這些聲明。
interface PersonInterface {
name: string;
}
interface PersonInterface {
age: number;
}
// 最終會自動合併介面,方便大型專案擴展型別
const person: PersonInterface = {
name: 'Johnson Mao',
age: 18
}
type 不能這樣重複聲明同名
// Error: 識別碼 'PersonType' 重複。
type PersonType = {
name: string;
}
// Error: 識別碼 'PersonType' 重複。
type PersonType = {
age: 18;
}
interface 繼承物件比 type 交集更嚴謹
interface 的繼承比較嚴謹
interface PersonInterface {
id: string
}
/**
* Error:
* 介面 'EmployeeInterface' 不正確地擴充介面 'PersonInterface'。
* 屬性 'id' 的類型不相容。
* 類型 'number' 不可指派給類型 'string'。
*/
interface EmployeeInterface extends PersonInterface {
id: number;
}
type 的交集則自動將屬性進行交集處理,不會提示屬性是否重複
type PersonType = {
id: string
}
// 並不會警告 id 因為 string 與 number 交集,變成了 never 的型別
type EmployeeType = PersonType & {
id: number;
}
介面和抽象類別都可以用來強制子類實作某些方法和屬性,但它們在概念和用途上存在一些明顯差異
只能描述物件的結構,不能有任何的程式碼方法實現,同時一個類別可以實現(implements)多個介面
可以有抽象方法,也可以實作具體方法,但是一個類別只能繼承一個抽象類別
