名詞定義:
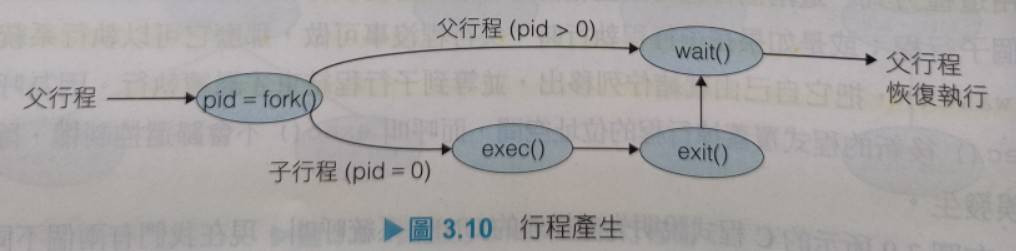
當一個行程產生一個新的行程時,在執行作法上有兩種:
以下程式介紹第2種,父行程等著它的所有子行程中止後才繼續執行:
newproc-posix.c
/**
* This program forks a separate process using the fork()/exec() system calls.
*
* Figure 3.09
*
* @author Silberschatz, Galvin, and Gagne
* Operating System Concepts - Ninth Edition
* Copyright John Wiley & Sons - 2013
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
/* fork a child process */
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) { /* error occurred */
fprintf(stderr, "Fork Failed\n");
return 1;
}
else if (pid == 0) { /* child process */
printf("I am the child %d\n",pid);
execlp("/bin/ls","ls",NULL);
}
else { /* parent process */
/* parent will wait for the child to complete */
printf("I am the parent %d\n",pid);
wait(NULL);
printf("Child Complete\n");
}
return 0;
}
Terminal
編譯並執行
gcc -o newproc-posix newproc-posix.c
./newproc-posix
結果:
我的解釋:
pid = fork();
else { /* parent process */
/* parent will wait for the child to complete */
printf("I am the parent %d\n",pid);
wait(NULL);
接著說明看不懂的 execlp 這行:
else if (pid == 0) { /* child process */
printf("I am the child %d\n",pid);
execlp("/bin/ls","ls",NULL); /* 同 ls */
}
printf("Child Complete\n");
}
參考:greggagne/OSC9e/ch3/newproc-posix.c
