嘗試腹腔鏡視頻與術前CT配准,還是得建立各自表面.目前mesh,surf,point cloud還是point cloud比較多資源,所以我先試用術前 CT/MRI,嘗試目前比較多的用deep learning直接medical register(ITK,simpleITK不用DL).
我的系統是Ubuntu 24.04,RTX 4060 8gb vram,CUDA 12.4
安裝monai沒有問題;voxelmorph用pip裝還好,不過這都要改寫程式,沒有CLI指令.DeepReg有CLI指令直接執行,但某次Ubuntu幫我更新到CUDA 12.4版,所以deepreg安裝又吃足苦頭, 所以記錄一下
conda deactivate
conda env remove -n deepreg_fallback
conda create -n deepreg_fallback python=3.9
conda activate deepreg_fallback
conda install -c conda-forge cudatoolkit=11.2 cudnn=8.1.0
mkdir -p $CONDA_PREFIX/etc/conda/activate.d
echo 'export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$CONDA_PREFIX/lib' > $CONDA_PREFIX/etc/conda/activate.d/env_vars.sh
conda deactivate
conda activate deepreg_fallback
pip install numpy==1.24.4 pandas==1.2.4 h5py==2.10.0 pyyaml==5.4.1 six==1.16.0 tensorboard==2.10.1 tensorflow-addons==0.14.0 matplotlib==3.4.1 nibabel==3.2.1 scikit-image==0.18.3 scipy==1.9.0 argparse==1.4.0 tabulate==0.8.9 tqdm==4.60.0 pydot==1.4.2 graphviz==0.20.1
pip install tensorflow-gpu==2.10.0
cd ~/2nd/DeepReg
pip install -e . --no-build-isolation --no-deps
檢查安裝
deepreg_train --help
python -c "import tensorflow as tf; print(tf.__version__); print(tf.test.is_built_with_cuda()); print(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'))"
以下可再安裝
pip black==21.5b1, flake8==3.9.0, GitPython==3.1.14, isort==5.8.0, m2r2==0.2.7, notebook==6.3.0, pre-commit==2.12.0, pydocstyle==6.0.0, pylint==2.8.1, pytest==6.2.3, pytest-cov==2.11.1, pytest-dependency==0.5.1, seed-isort-config==2.2.0, sphinx==3.5.3, sphinx-notfound-page==0.6, sphinx-rtd-theme==0.5.2, sphinx-tabs==3.0.0, testfixtures==6.17.1, tox==3.23.0
開發相關工具black, flake8, pylint, isort, seed-isort-config, pydocstyle, pre-commit:這些是程式碼格式檢查/風格整理工具。
測試工具pytest, pytest-cov, pytest-dependency, testfixtures:給 DeepReg 開發者或重構程式碼時進行自動測試用的。
文件產生工具sphinx, sphinx-tabs, sphinx-rtd-theme, sphinx-notfound-page, m2r2:用來生成線上文件(ReadTheDocs)。
環境管理與測試隔離(可跳過)tox: 多版本測試自動化工具。
Jupyter notebook(可依需求)notebook==6.3.0可略過。
GitPython:少部分功能會用到(如載入 git commit 資訊)。
修改/home/cmuh/2nd/DeepReg/demos/unpaired_ct_abdomen下3個.yaml
dataset:
train:
batch_size: 4 #4其實abdomen unpaired ct跑得動,但<==chest,prostate改成1
python demos/unpaired_ct_abdomen/demo_data.py
python demos/unpaired_ct_abdomen/demo_train.py --method unsup --full
另開視窗
watch -n 1 nvidia-smi
watch -n 1 free -g
htop
結果unpaired abdominal CT的batch可以到4,在8g vram跑半天;但batch=5以上不會跑,你會看到 GPU跟CPU都不到8%,而vRAM被佔了7G多,其實不夠用,都在vram跟ram切換,所以CPU,GPU只動到個位數使用.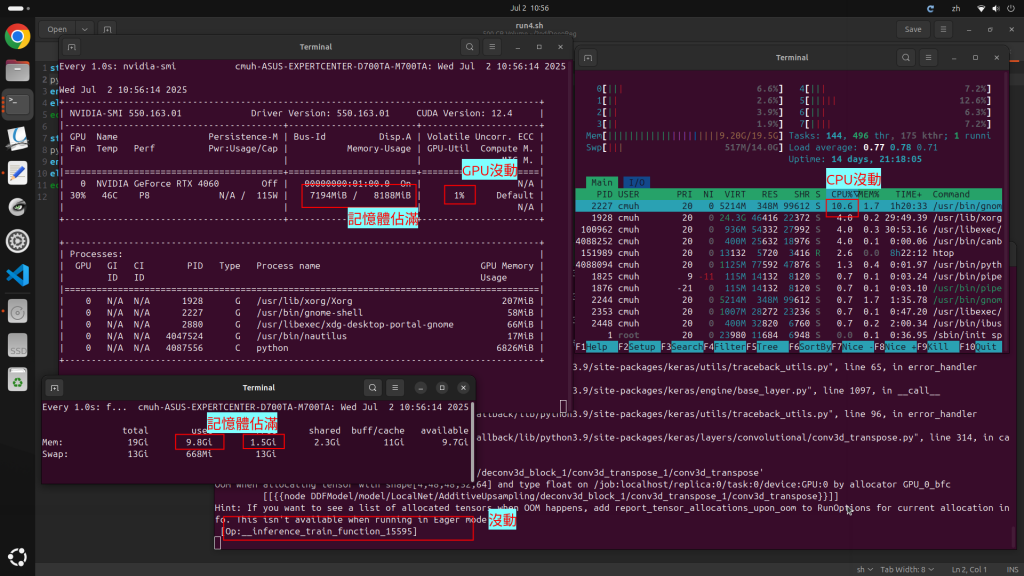
如果注意到這情形,嘗試batch設定小一點,可以看到vram約佔5~6g,ram約佔8g,CPU使用率約20~60%,GPU動則使用率近100%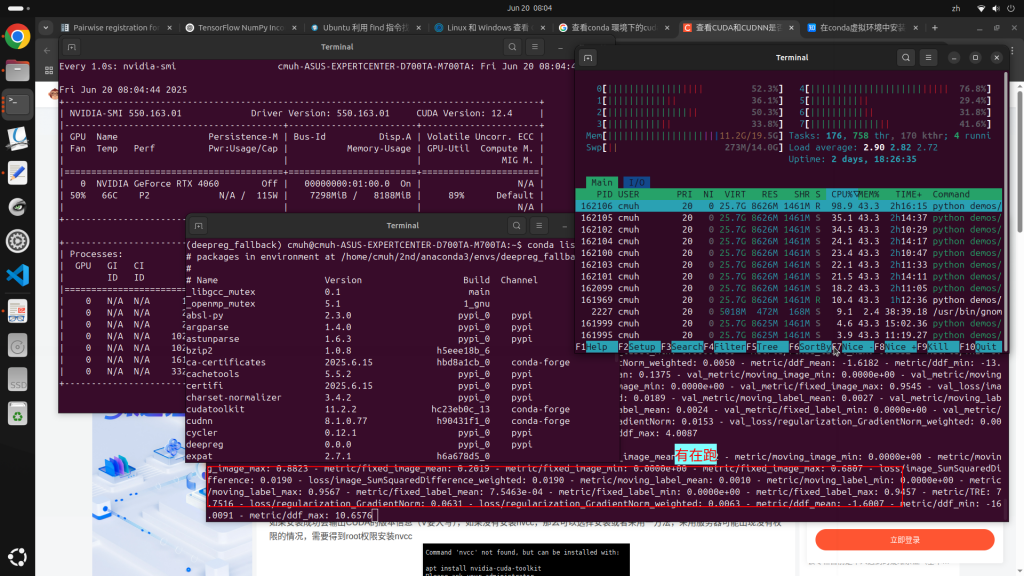
另外要注意的是自己跑的ckpt擋在哪裡,以免後續predict指令沒用.像我的這次是在~/DeepReg/demos/unpaired_ct_lung/logs_train/20250630-222341/save/下面,所以看圖前的predict指令是
deepreg_predict \
--gpu "0" \
--config_path demos/unpaired_ct_lung/logs_train/20250630-222341/config.yaml \
--ckpt_path demos/unpaired_ct_lung/logs_train/20250630-222341/save/ckpt-5000 \
--log_dir demos/unpaired_ct_lung \
--exp_name logs_predict \
--save_png \
--split test
再去demos/unpaired_ct_lung/logs_predict/test/看圖
或是
deepreg_vis -m 2 -i 'demos/unpaired_ct_lung/logs_predict/test/pair_2_0/moving_image.nii.gz, demos/unpaired_ct_lung/logs_predict/test/pair_2_0/pred_fixed_image.nii.gz, demos/unpaired_ct_lung/logs_predict/test/pair_2_0/fixed_image.nii.gz' --slice-inds '40,48,56' -s demos/unpaired_ct_lung/logs_predict
再去看~/DeepReg/demos/unpaired_ct_lung/logs_predict/visualisation.png
paired chest CT跟nonrigid prostate MRI的batch=1才可以跑,分別跑了300257s=3.5天跟210058s=2.4天
unpaired hippocampus MR, prostate ultrasound資料不能下載.
paired跟group其他,batch設定1也跑不動
Classical affine registration for head-and-neck CT images可跑
=======================
後記:voxelmorph照網頁就好
========================
monai跑IXI-tiny比voxelmorph還快,下面的是copy的程式,monai原本的3D brain register範例好像會動到voxelmorph,另外2個倒不會
下載IXI-tiny見這個
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#MONAI GPU 加速的 IXI 影像配準
#支援深度學習配準和傳統優化配準
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import nibabel as nib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pathlib import Path
import time
import os
#MONAI imports
from monai.transforms import (
Compose, LoadImaged, EnsureChannelFirstd, Orientationd,
Spacingd, ScaleIntensityRanged, CropForegroundd,
Resized, ToTensord, EnsureTyped
)
from monai.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from monai.networks.nets import GlobalNet
from monai.networks.blocks import Warp
from monai.losses import GlobalMutualInformationLoss, BendingEnergyLoss
from monai.utils import set_determinism
class IXIRegistration:
def __init__(self, device="cuda"):
#初始化 MONAI 配準器
self.device = torch.device(device if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"使用設備: {self.device}")
if self.device.type == "cuda":
print(f"GPU: {torch.cuda.get_device_name()}")
print(f"GPU 記憶體: {torch.cuda.get_device_properties(0).total_memory / 1e9:.1f} GB")
#設定隨機種子
set_determinism(seed=42)
#預處理管道
self.transforms = Compose([
LoadImaged(keys=["fixed", "moving"]),
EnsureChannelFirstd(keys=["fixed", "moving"]),
Orientationd(keys=["fixed", "moving"], axcodes="RAS"),
Spacingd(keys=["fixed", "moving"], pixdim=(2.0, 2.0, 2.0), mode=("bilinear", "bilinear")),
ScaleIntensityRanged(keys=["fixed", "moving"], a_min=0, a_max=1000, b_min=0.0, b_max=1.0, clip=True),
CropForegroundd(keys=["fixed", "moving"], source_key="fixed"),
Resized(keys=["fixed", "moving"], spatial_size=(128, 128, 128), mode="trilinear"),
EnsureTyped(keys=["fixed", "moving"], device=self.device)
])
def prepare_data(self, fixed_path, moving_path):
#準備配準資料
data_dict = {
"fixed": fixed_path,
"moving": moving_path
}
print("正在預處理影像...")
start_time = time.time()
#應用變換
transformed_data = self.transforms(data_dict)
fixed_tensor = transformed_data["fixed"]
moving_tensor = transformed_data["moving"]
print(f"預處理完成,耗時: {time.time() - start_time:.2f} 秒")
print(f"Fixed 影像尺寸: {fixed_tensor.shape}")
print(f"Moving 影像尺寸: {moving_tensor.shape}")
return fixed_tensor, moving_tensor
def visualize_images(self, fixed, moving, registered=None, slice_idx=None):
#視覺化影像
if slice_idx is None:
slice_idx = fixed.shape[-1] // 2
#轉換為 numpy
fixed_np = fixed.squeeze().cpu().numpy()[:, :, slice_idx]
moving_np = moving.squeeze().cpu().numpy()[:, :, slice_idx]
if registered is not None:
registered_np = registered.squeeze().cpu().numpy()[:, :, slice_idx]
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(12, 10))
axes[0, 0].imshow(fixed_np, cmap='gray')
axes[0, 0].set_title('Fixed Image')
axes[0, 0].axis('off')
axes[0, 1].imshow(moving_np, cmap='gray')
axes[0, 1].set_title('Moving Image')
axes[0, 1].axis('off')
axes[1, 0].imshow(registered_np, cmap='gray')
axes[1, 0].set_title('Registered Image')
axes[1, 0].axis('off')
diff = np.abs(fixed_np - registered_np)
axes[1, 1].imshow(diff, cmap='hot')
axes[1, 1].set_title('Difference')
axes[1, 1].axis('off')
else:
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 4))
axes[0].imshow(fixed_np, cmap='gray')
axes[0].set_title('Fixed Image')
axes[0].axis('off')
axes[1].imshow(moving_np, cmap='gray')
axes[1].set_title('Moving Image')
axes[1].axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
class OptimizationBasedRegistration:
#基於優化的傳統配準方法(GPU 加速)
def __init__(self, device="cuda"):
self.device = torch.device(device if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
def mutual_information_loss(self, fixed, moving):
#計算互資訊損失
#簡化的互資訊計算
fixed_flat = fixed.view(-1)
moving_flat = moving.view(-1)
#計算聯合直方圖
joint_hist = torch.histc(
torch.stack([fixed_flat, moving_flat]).T.contiguous().view(-1),
bins=64, min=0, max=1
)
#避免除零
joint_hist = joint_hist + 1e-10
joint_prob = joint_hist / joint_hist.sum()
#計算邊際機率
marginal_fixed = joint_prob.sum(dim=1)
marginal_moving = joint_prob.sum(dim=0)
#計算互資訊
mi = 0
for i in range(joint_prob.shape[0]):
for j in range(joint_prob.shape[1]):
if joint_prob[i, j] > 0:
mi += joint_prob[i, j] * torch.log(
joint_prob[i, j] / (marginal_fixed[i] * marginal_moving[j])
)
return -mi # 返回負值用於最小化
def affine_transform_3d(self, image, matrix):
#應用 3D 仿射變換
#建立採樣網格
N, C, D, H, W = image.shape
#建立標準網格
grid = F.affine_grid(matrix.unsqueeze(0), [N, C, D, H, W], align_corners=False)
#應用變換
warped = F.grid_sample(image, grid, mode='bilinear', padding_mode='border', align_corners=False)
return warped
def register_affine(self, fixed, moving, max_iterations=100, learning_rate=0.01):
#執行仿射配準
print("開始仿射配準...")
#初始化仿射變換矩陣 (3x4)
transform_matrix = torch.eye(3, 4, device=self.device, requires_grad=True)
#優化器
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([transform_matrix], lr=learning_rate)
best_loss = float('inf')
best_matrix = transform_matrix.clone()
losses = []
for iteration in range(max_iterations):
optimizer.zero_grad()
#應用變換
warped_moving = self.affine_transform_3d(moving, transform_matrix)
計算損失
loss = F.mse_loss(fixed, warped_moving)
反向傳播
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
losses.append(loss.item())
if loss.item() < best_loss:
best_loss = loss.item()
best_matrix = transform_matrix.clone()
if iteration % 10 == 0:
print(f"Iteration {iteration}, Loss: {loss.item():.6f}")
print(f"配準完成,最終損失: {best_loss:.6f}")
#應用最佳變換
with torch.no_grad():
registered = self.affine_transform_3d(moving, best_matrix)
return registered, best_matrix, losses
def main():
#主要執行函數
#檢查 GPU 可用性
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
print("警告: CUDA 不可用,將使用 CPU")
print("建議安裝 CUDA 版本的 PyTorch 以獲得最佳性能")
return
#初始化配準器
registrator = IXIRegistration()
optimizer_reg = OptimizationBasedRegistration()
#IXI 影像路徑
image_dir = Path("./image")
image_files = list(image_dir.glob("*_image.nii.gz"))
image_files.sort()
if len(image_files) < 2:
print("錯誤: 需要至少兩個影像檔案")
return
print(f"找到 {len(image_files)} 個影像檔案:")
for i, file in enumerate(image_files):
print(f" {i+1}. {file.name}")
#選擇配準對
fixed_path = str(image_files[0])
moving_path = str(image_files[1])
print(f"\nFixed 影像: {Path(fixed_path).name}")
print(f"Moving 影像: {Path(moving_path).name}")
#準備資料
try:
fixed_tensor, moving_tensor = registrator.prepare_data(fixed_path, moving_path)
except Exception as e:
print(f"資料準備失敗: {e}")
return
#顯示原始影像
print("\n=== 顯示原始影像 ===")
registrator.visualize_images(fixed_tensor, moving_tensor)
#執行優化配準
print("\n=== 執行 GPU 加速仿射配準 ===")
start_time = time.time()
try:
registered_tensor, transform_matrix, losses = optimizer_reg.register_affine(
fixed_tensor, moving_tensor, max_iterations=50
)
registration_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"配準完成,總耗時: {registration_time:.2f} 秒")
#顯示結果
print("\n=== 顯示配準結果 ===")
registrator.visualize_images(fixed_tensor, moving_tensor, registered_tensor)
#繪製損失曲線
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(losses)
plt.title('Registration Loss Over Iterations')
plt.xlabel('Iteration')
plt.ylabel('MSE Loss')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
#保存結果
print("\n=== 保存結果 ===")
save_registered_image(registered_tensor, "monai_registered_gpu.nii.gz")
#計算配準指標
print("\n=== 配準指標 ===")
calculate_registration_metrics(fixed_tensor, moving_tensor, registered_tensor)
except Exception as e:
print(f"配準失敗: {e}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
def save_registered_image(tensor, filename):
#保存配準結果為 NIfTI 檔案
try:
# 轉換為 numpy
array = tensor.squeeze().cpu().numpy()
#建立 NIfTI 影像
nii_img = nib.Nifti1Image(array, affine=np.eye(4))
#保存
nib.save(nii_img, filename)
print(f"已保存配準結果: {filename}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"保存失敗: {e}")
def calculate_registration_metrics(fixed, moving, registered):
#計算配準指標
#轉換為 numpy
fixed_np = fixed.squeeze().cpu().numpy()
moving_np = moving.squeeze().cpu().numpy()
registered_np = registered.squeeze().cpu().numpy()
#計算 MSE
mse_before = np.mean((fixed_np - moving_np) ** 2)
mse_after = np.mean((fixed_np - registered_np) ** 2)
#計算 SSIM (簡化版本)
def simple_ssim(img1, img2):
mu1, mu2 = img1.mean(), img2.mean()
sigma1, sigma2 = img1.std(), img2.std()
sigma12 = np.mean((img1 - mu1) * (img2 - mu2))
c1, c2 = 0.01**2, 0.03**2
ssim = ((2*mu1*mu2 + c1) * (2*sigma12 + c2)) / ((mu1**2 + mu2**2 + c1) * (sigma1**2 + sigma2**2 + c2))
return ssim
ssim_before = simple_ssim(fixed_np, moving_np)
ssim_after = simple_ssim(fixed_np, registered_np)
print(f"MSE (配準前): {mse_before:.6f}")
print(f"MSE (配準後): {mse_after:.6f}")
print(f"MSE 改善: {((mse_before - mse_after) / mse_before * 100):.2f}%")
print(f"SSIM (配準前): {ssim_before:.4f}")
print(f"SSIM (配準後): {ssim_after:.4f}")
def batch_registration():
#批次配準所有 IXI 影像
print("=== 批次 GPU 配準 ===")
registrator = IXIRegistration()
optimizer_reg = OptimizationBasedRegistration()
image_dir = Path("./image")
image_files = list(image_dir.glob("*_image.nii.gz"))
image_files.sort()
if len(image_files) < 2:
print("需要至少兩個影像進行批次配準")
return
reference_path = str(image_files[0])
print(f"使用參考影像: {Path(reference_path).name}")
#載入參考影像
reference_tensor, _ = registrator.prepare_data(reference_path, reference_path)
total_start_time = time.time()
for i, moving_path in enumerate(image_files[1:], 1):
print(f"\n配準影像 {i}/{len(image_files)-1}: {Path(moving_path).name}")
try:
#準備資料
_, moving_tensor = registrator.prepare_data(reference_path, str(moving_path))
#執行配準
registered_tensor, _, _ = optimizer_reg.register_affine(
reference_tensor, moving_tensor, max_iterations=30
)
#保存結果
output_filename = f"batch_registered_{i:03d}.nii.gz"
save_registered_image(registered_tensor, output_filename)
except Exception as e:
print(f"配準失敗: {e}")
total_time = time.time() - total_start_time
print(f"\n批次配準完成,總耗時: {total_time:.2f} 秒")
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("=== MONAI GPU 加速 IXI 影像配準 ===\n")
#檢查安裝
try:
import monai
print(f"MONAI 版本: {monai.__version__}")
except ImportError:
print("錯誤: MONAI 未安裝")
print("請執行: pip install monai[all]")
exit(1)
print("選擇執行模式:")
print("1. 單對影像配準")
print("2. 批次配準")
choice = input("請輸入選擇 (1 或 2): ").strip()
if choice == "1":
main()
elif choice == "2":
batch_registration()
else:
print("自動執行單對影像配準...")
main()
