Medium 好讀版點此。
在 Day 5 文章中,我們提到若不小心做錯,想退回去前面 commit 的狀態,可以用 git reset 或 git revert 指令,但事實上 git reset 又有 --soft、--mixed 與 --hard 三種模式,究竟這三者有什麼差別?git reset 三種模式與 git revert 對於 .git/ 資料夾又有哪些影響?讓我們再次直接做實驗觀察找答案。
首先,在一個新建的資料夾中,依序輸入以下指令
git init
echo "Hello, world!" > hello_world.txt
git add "hello_world.txt"
git commit -m "Initial commit"
上述指令是形成第一筆快照、產生第一個 commit。
接著我們把 hello_world.txt 內文中的驚嘆號拿掉,變成 Hello, world:
echo "Hello, world" > hello_world.txt
再重新依序輸入以下指令:
git add "hello_world.txt"
git commit -m "Remove exclamation mark"
這時形成了第二筆快照、產生第二個 commit。
此時 ./git 資料夾結構如下:
.git/
├── hooks/
├── info/
│
├── objects/
│ ├── 7f/
│ │ └── 647dbf56354cc71a5f5ff1274bb3778f5f19cf
│ ├── 55/
│ │ └── a0a031d13860599847a316c42433ea148735d5
│ ├── a5/
│ │ └── c19667710254f835085b99726e523457150e03
│ ├── af/
│ │ └── 5626b4a114abcb82d63db7c8082c3c4756e51b
│ ├── e5/
│ │ └── 9896eb1f48ef9c75e675692e23966e5ba7cdfb
│ ├── ee/
│ │ └── ee0e51db5bc89ee905864f50fc517c9e5272df
│ ├── info/
│ └── pack/
│
├── refs/
│ ├── heads/
│ │ └── main # 指向eeee0e51db5bc89ee905864f50fc517c9e5272df
│ └── tags/
│
├── logs/
│ └── ...
│
├── ...
└── index # 內容為100644 a5c19667710254f835085b99726e523457150e03 0 hello_world.txt
透過多次 git cat-file -p <SHA> 確認每個 git 物件內容,可得圖示如下: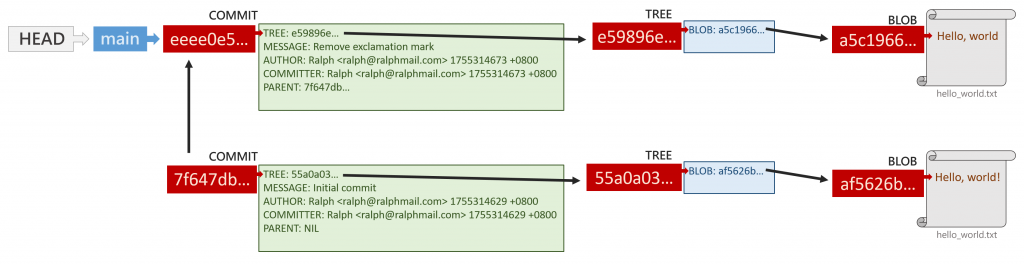
當我們發現某個步驟做錯了,想倒回去前面的 commit,這時可以用 git reset 處理。
但 git reset 有 --soft、--mixed 跟 --hard 三種模式,這三者差別在哪?讓我們實際做實驗比較。
首先我們嘗試最溫和的 git reset --soft,並以 HEAD~1 表示當前 HEAD 所指之 commit 的前一個:
git reset --soft HEAD~1
再以 git log 與 git status 在終端機觀察,發現變這樣: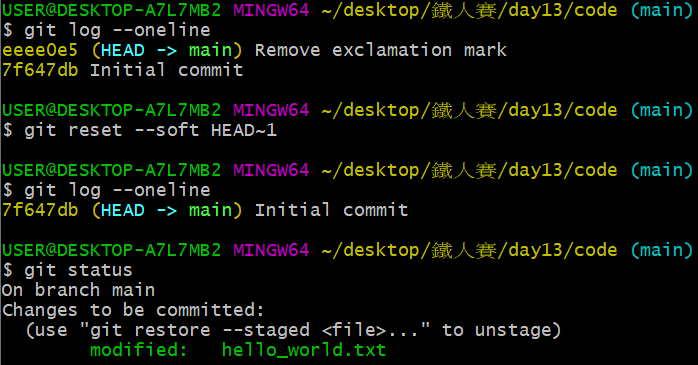
commit 少了一個、而剛剛修改過的 hello_world.txt 回到「進入預存區,但尚未 commit 的狀態」,透過 git ls-files --stage 觀察,也發現 index 檔案裡仍是 a5c1966... 這組雜湊碼:
打開 hello_world.txt 亦可發現仍是沒有驚嘆號版本(就是已經被改過)的內容: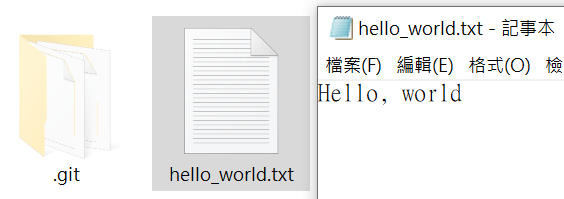
這表示經過 git reset --soft 之後,唯一改變的只有一件事情:
HEAD 指向的 commit其他的都不變,包含:
index 裡面存的東西(git add 的狀態仍在)hello_world.txt 檔案內容統整資料夾結構如下:
.git/
├── hooks/
├── info/
│
├── objects/ # 所有git物件都保持不變
│ ├── 7f/
│ │ └── 647dbf56354cc71a5f5ff1274bb3778f5f19cf
│ ├── 55/
│ │ └── a0a031d13860599847a316c42433ea148735d5
│ ├── a5/
│ │ └── c19667710254f835085b99726e523457150e03
│ ├── af/
│ │ └── 5626b4a114abcb82d63db7c8082c3c4756e51b
│ ├── e5/
│ │ └── 9896eb1f48ef9c75e675692e23966e5ba7cdfb
│ ├── ee/
│ │ └── ee0e51db5bc89ee905864f50fc517c9e5272df
│ ├── info/
│ └── pack/
│
├── refs/
│ ├── heads/
│ │ └── main # 指向7f647dbf56354cc71a5f5ff1274bb3778f5f19cf
│ └── tags/
│
├── logs/
│ └── ...
│
├── ...
└── index # 內容仍為100644 a5c19667710254f835085b99726e523457150e03 0 hello_world.txt
圖示如下:
現在我們改用 git reset --mixed 來看看會發生什麼改變?
以 git log 與 git status 指令會發現下列變化: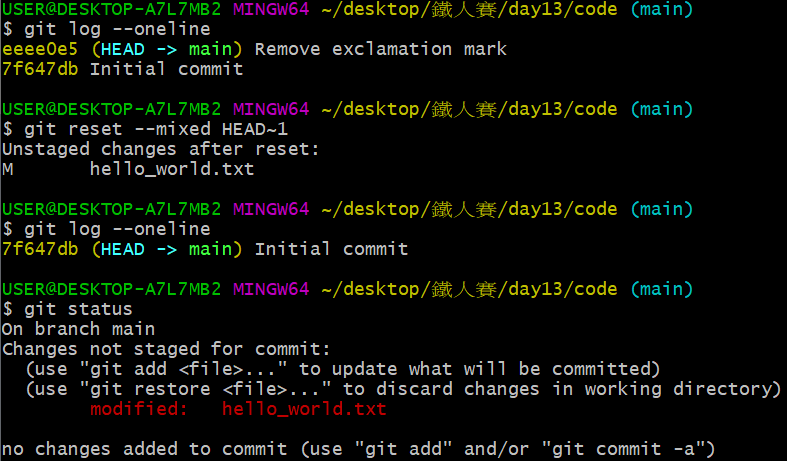
git log 的指令看起來跟剛剛 git reset --soft 的效果一樣,都是最新的 commit 消失,但 git status 後顯示的狀態是:修改過的 hello_world.txt 已經不再是經過 git add、放在預存區的狀態了。
那如果以 git ls-files --stage 檢視預存區 index 內的狀況呢?

變成 af5626b... 了!這表示更改過的檔案已經被移出預存區,怪不得在 git status 中, hello_world.txt 變成紅色、而不是綠色,完全退回 git add 之前的狀態。
打開 hello_world.txt 仍是沒有驚嘆號版本(就是已經被改過)的內容:
綜合上述觀察,我們知道經過 git reset --mixed 之後,改變的部分包含:
HEAD 指向的 commit(跟 git reset --soft 一樣)index 裡面存的東西變 reset 到之 commit 的內容(git add 狀態已消失)但下列還是不變:
hello_world.txt 檔案內容如果觀察 ./git 資料夾,可發現目前變成:
.git/
├── hooks/
├── info/
│
├── objects/ # 所有git物件都保持不變
│ ├── 7f/
│ │ └── 647dbf56354cc71a5f5ff1274bb3778f5f19cf
│ ├── 55/
│ │ └── a0a031d13860599847a316c42433ea148735d5
│ ├── a5/
│ │ └── c19667710254f835085b99726e523457150e03
│ ├── af/
│ │ └── 5626b4a114abcb82d63db7c8082c3c4756e51b
│ ├── e5/
│ │ └── 9896eb1f48ef9c75e675692e23966e5ba7cdfb
│ ├── ee/
│ │ └── ee0e51db5bc89ee905864f50fc517c9e5272df
│ ├── info/
│ └── pack/
│
├── refs/
│ ├── heads/
│ │ └── main # 跟--soft一樣改指向7f647dbf56354cc71a5f5ff1274bb3778f5f19cf
│ └── tags/
│
├── logs/
│ └── ...
│
├── ...
├── index # 變成100644 af5626b4a114abcb82d63db7c8082c3c4756e51b 0 hello_world.txt
└── ORIG_HEAD # 新增檔案,內容為eeee0e51db5bc89ee905864f50fc517c9e5272df
由資料夾結構可發現還多了一個 ORIG_HEAD 檔案,內容為 git reset --mixed 前指向的 commit,即 eeee0e5...。
經 git reset --mixed 後,發生的變化圖示如下: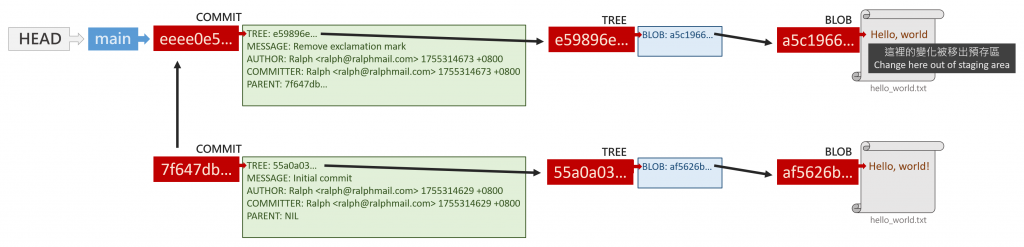
如果改用 git reset --hard,再以 git log 與 git status 指令觀察,變化如下: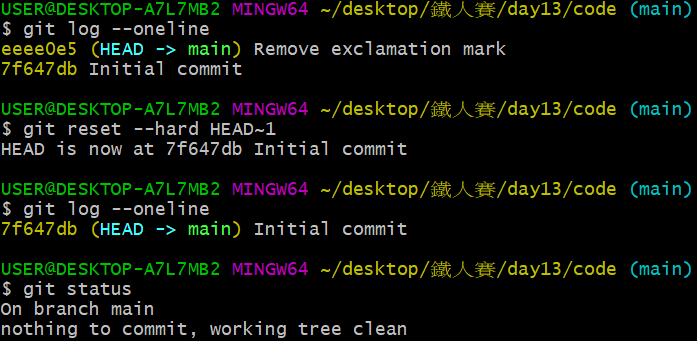
git log 的指令仍舊回到 7f647db... 這個 commit ,而 git status 已經沒有東西,彷彿修改檔案這件事沒發生過。
再以 git ls-files --stage 檢視預存區 index 內的狀況:
跟 git reset --mixed 一樣都變成 af5626b...,那如果實際打開 hello_world.txt 呢?
驚嘆號復活!變成檔案還沒修改過的狀態!
由以上實驗,我們可發現經 git reset --hard,以下全部發生改變:
HEAD 指向的 commit(跟 --soft 與 --mixed 一樣)index 裡面存的東西變 reset 到之 commit 的內容hello_world.txt 檔案內容(變成指定 commit 中的狀態)如果觀察 ./git 資料夾,則會發現目前變成:
.git/
├── hooks/
├── info/
│
├── objects/ # 所有git物件都保持不變
│ ├── 7f/
│ │ └── 647dbf56354cc71a5f5ff1274bb3778f5f19cf
│ ├── 55/
│ │ └── a0a031d13860599847a316c42433ea148735d5
│ ├── a5/
│ │ └── c19667710254f835085b99726e523457150e03
│ ├── af/
│ │ └── 5626b4a114abcb82d63db7c8082c3c4756e51b
│ ├── e5/
│ │ └── 9896eb1f48ef9c75e675692e23966e5ba7cdfb
│ ├── ee/
│ │ └── ee0e51db5bc89ee905864f50fc517c9e5272df
│ ├── info/
│ └── pack/
│
├── refs/
│ ├── heads/
│ │ └── main # 跟--soft與--mixed一樣改指向7f647dbf56354cc71a5f5ff1274bb3778f5f19cf
│ └── tags/
│
├── logs/
│ └── ...
│
├── ...
├── index # 100644 af5626b4a114abcb82d63db7c8082c3c4756e51b 0 hello_world.txt
└── ORIG_HEAD # eeee0e51db5bc89ee905864f50fc517c9e5272df
圖示如下: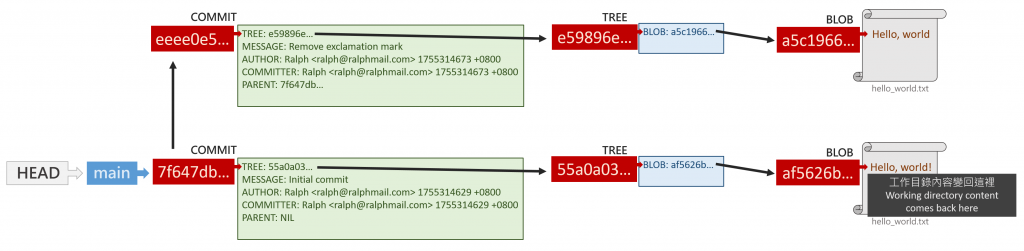
透過以上實驗,我們可以發現 --soft、--mixed 與 --hard 的差別如下:
--soft:只把 HEAD 改指到目標 commit 上,預存區與工作目錄都不影響;相當於退回 git commit 指令之前。--mixed:比 --soft 模式多影響到預存區,連放在預存區的檔案都拿掉,但工作目錄檔案內容仍不影響;相當於退回 git add 指令之前。--hard:連工作目錄都被影響,檔案內容變成指定 commit 上的樣子。比較表如下: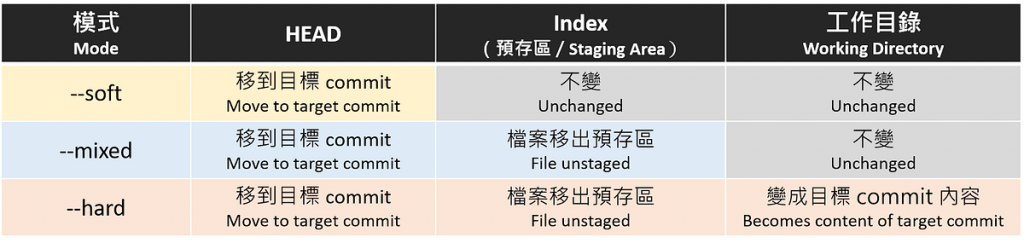
黃底、籃底與橙底表示該模式影響範圍
對應我們的實驗流程為:
hello_world.txt 的內容是 "Hello, world!",成為 commit A。"Hello, world",變成 commit B。三種模式的影響如下:
--soft:只把 HEAD 指回 commit A,但 hello_world.txt 內容仍為沒驚嘆號版本的 "Hello, world",且仍在預存區;相當於檔案改成無驚嘆號版本並做了 git add,但尚未 git commit。--mixed:HEAD 一樣指回 commit A,hello_world.txt 檔案內容雖仍為沒驚嘆號版本的 "Hello, world",但已被移出預存區;相當於檔案改成無驚嘆號版本後,連 git add 都還沒做。--hard:HEAD 一樣指回 commit A,hello_world.txt 檔案內容被改回 commit A 的有驚嘆號版本 "Hello, world!",也不在預存區。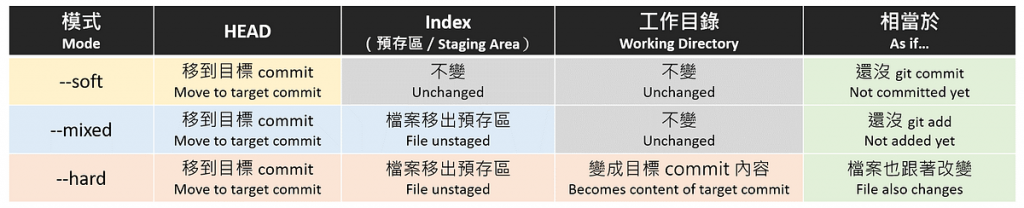
在 --mixed 與 --hard 兩種模式中,都會出現 ORIG_HEAD 這個新檔案,儲存發生 git reset 前,HEAD 指向的 commit。
如果在 git reset 後想要再 git reset 回去(如上述例子中,從 commit B 退回 commit A 後,想再反轉成 commit B),就可以使用 git reset --mixed ORIG_HEAD 或 git reset --hard ORIG_HEAD。
還有另外一種還原 commit 方法:git revert,我們一樣做個實驗比較。
先再次檢視當下 git log 狀態: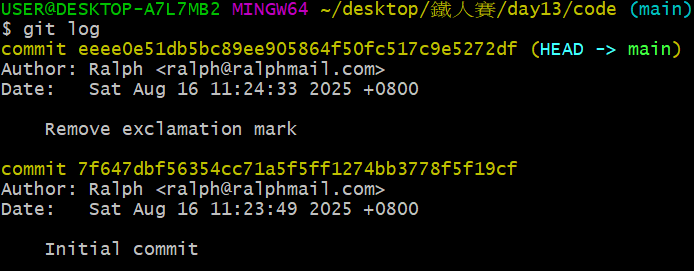
現在我們在 eeee0e5... 這個 commit,想要回到 7f647db... 這個 commit,就輸入以下指令:
git revert 7f647db
接著會跳出文字編輯器,內容如下:
Revert "Remove exclamation mark"
This reverts commit eeee0e51db5bc89ee905864f50fc517c9e5272df.
# Please enter the commit message for your changes. Lines starting
# with '#' will be ignored, and an empty message aborts the commit.
#
# On branch main
# Changes to be committed:
# modified: hello_world.txt
#
git revert 跟 git reset 的最大差別在於:git revert 是「做出一個新的 commit,其內容跟目標 commit 一模一樣」,而非如 git reset 會直接把 HEAD 往前移或改到更多檔案。
當 git revert 要做出新的 commit,便要有對應的 commit 訊息,而上面的文字編輯器就是讓我們編輯 commit 訊息的地方。
待編輯完 commit 訊息,再用 git log 指令觀察歷次 commit,就可以發現多了一個 commit,其雜湊碼為 d6dacfd...:
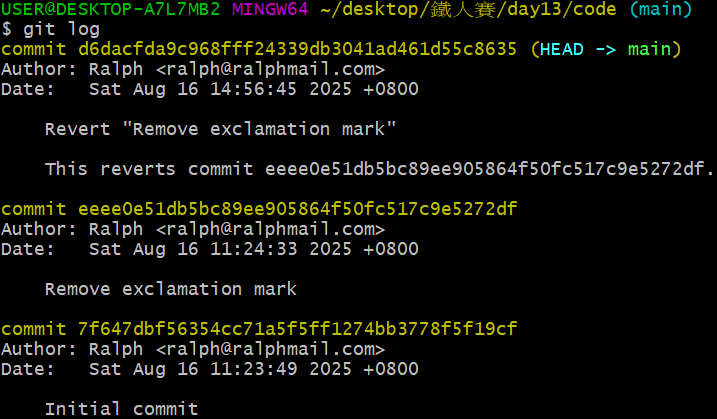
既然多了一個新 commit,那資料夾結構當然也跟著改變:
.git/
├── hooks/
│ └── ...
│
├── info/
│ └── exclude
│
├── objects/
│ ├── 7f/
│ │ └── 647dbf56354cc71a5f5ff1274bb3778f5f19cf
│ ├── 55/
│ │ └── a0a031d13860599847a316c42433ea148735d5
│ ├── a5/
│ │ └── c19667710254f835085b99726e523457150e03
│ ├── af/
│ │ └── 5626b4a114abcb82d63db7c8082c3c4756e51b
│ ├── d6 # 新的物件
│ │ └── dacfda9c968fff24339db3041ad461d55c8635
│ ├── e5/
│ │ └── 9896eb1f48ef9c75e675692e23966e5ba7cdfb
│ ├── ee/
│ │ └── ee0e51db5bc89ee905864f50fc517c9e5272df
│ ├── info/
│ └── pack/
│
├── refs/
│ ├── heads/
│ │ └── main # 變成最新的commit:d6dacfda9c968fff24339db3041ad461d55c8635
│ └── tags/
│
├── logs/
│ └── ...
│
├── ...
├── index # 仍為100644 af5626b4a114abcb82d63db7c8082c3c4756e51b 0 hello_world.txt
└── ORIG_HEAD # eeee0e51db5bc89ee905864f50fc517c9e5272df
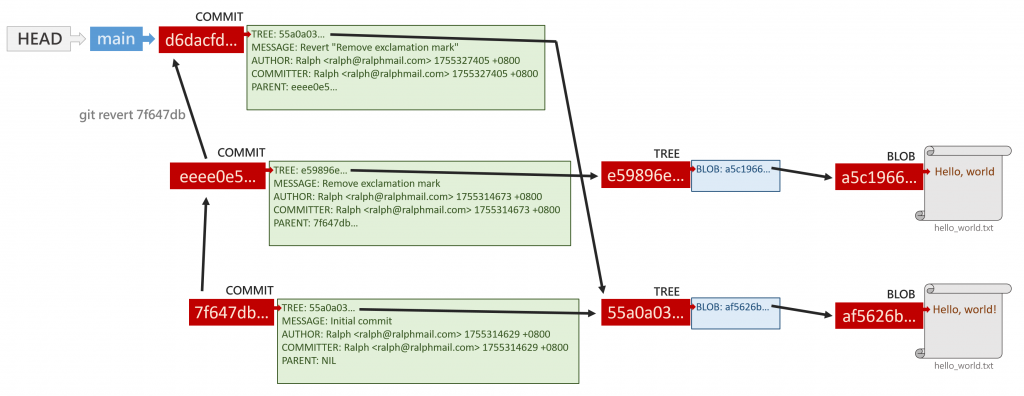
多了一個 git 物件,雜湊碼為 d6dacfd...,現在用 git cat-file -t d6dacfd 檢視其類別:
可知是一個 commit 物件,再用 git cat-file -p d6dacfd 來看這個 commit 跟其他物件的關係: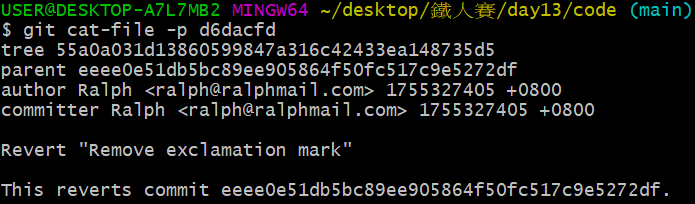
這個 commit 指向的 tree 物件為 55a0a03...,跟最開始的 commit 7f647db... 一模一樣;它的上代 commit 物件為 eeee0e5...,也就是移除驚嘆號時的 commit。
綜合以上觀察,我們可以圖解 git revert 7f647db 後的架構如下: