在程式設計中,「變數」就像一個容器,可以存放不同種類的資料。C# 作為一個強型別語言,每個變數在使用之前都需要先宣告其「資料型態」。今天,我們就來認識 C# 中的常見資料型態,以及如何在程式裡使用變數。
變數(Variable)就是一個具名的儲存空間,可以用來保存資料。例如:
在 C# 中,宣告變數的語法是:
型態 變數名稱 = 初始值;
宣告字串變數時,就直接用string來宣告此變數,由於是文字型態,所以要用""將內容包起來。
string firstFriend = "Maria";
string secondFriend = "Sage";
Console.WriteLine($"My friends are {firstFriend} and {secondFriend}");

字串不僅僅是字母的集合,可以使用 Length 來取得字串的長度。 Length 是字串的屬性,它會傳回該字串中的字元數:
Console.WriteLine($"The name {firstFriend} has {firstFriend.Length} letters.");
Console.WriteLine($"The name {secondFriend} has {secondFriend.Length} letters.");

假設今天有一段字串包含了不想顯示的前導空格或尾隨空格,需要從字串中修剪這些空格,可以使用 Trim 來達到此目的,其中 TrimStart 和 TrimEnd 分別就是消除前面空格以及後面空格的方法。
string greeting = " Hello World! ";
Console.WriteLine($"[{greeting}]");
string trimmedGreeting = greeting.TrimStart();
Console.WriteLine($"[{trimmedGreeting}]");
trimmedGreeting = greeting.TrimEnd();
Console.WriteLine($"[{trimmedGreeting}]");
trimmedGreeting = greeting.Trim();
Console.WriteLine($"[{trimmedGreeting}]");

接下來是 Replace 的功能,有就是我們日常會用到的「搜尋並取代」的功能。在 C# 裡的 Replace 方法就是做類似的事,它會幫你找到字串中的某個部分,然後換成你指定的新文字。這個方法需要兩個參數:第一個是要找的字串,第二個是要替換成的字串。
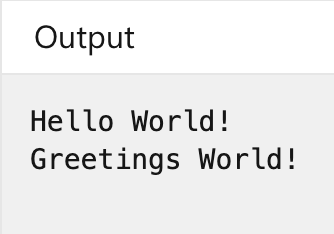
string sayHello = "Hello World!";
Console.WriteLine(sayHello);
sayHello = sayHello.Replace("Hello", "Greetings");
Console.WriteLine(sayHello);
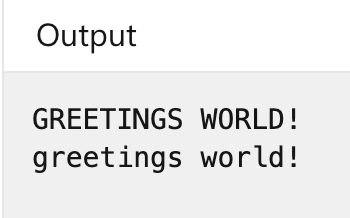
除此之外還有將字母全部轉成大寫跟小寫:
Console.WriteLine(sayHello.ToUpper());
Console.WriteLine(sayHello.ToLower());
最後是 Contains 這個方法,他是用來尋找字句裡是否有包含某個字詞,所以他回傳的是 true 跟 false 的布林值。
string songLyrics = "You say goodbye, and I say hello";
Console.WriteLine(songLyrics.Contains("goodbye"));
Console.WriteLine(songLyrics.Contains("greetings"));

先從最基礎的宣告整數變數以及最基本的加減乘除開始,宣告方式一樣,在最前面用 int 的方式來表示此變數為整是型態,接下來就可以進行一系列的運算並查看執行結果。會發現比較特別的現象是,即便答案是有小數點的,他還是會呈現為整數。
int a = 18;
int b = 6;
int c = a + b;
Console.WriteLine(c);
Output->24
int a = 5;
int b = 4;
int c = 2;
int d = a + b * c;
Console.WriteLine(d);
Output->13
d = (a + b) - 6 * c + (12 * 4) / 3 + 12;
Console.WriteLine(d);
Output->25
所以可以用%來呈現餘數:
int a = 7;
int b = 4;
int c = 3;
int d = (a + b) / c;
int e = (a + b) % c;
Console.WriteLine($"quotient: {d}");
Console.WriteLine($"remainder: {e}");

double 這個型別代表的是「雙精度浮點數」,其實它就是用來表示不是整數的數字,像是帶小數點的數,或者特別大、特別小的數值。至於「雙精度」的意思,就是電腦在儲存這種數字時,使用的二進位位數比「單精度」多一倍,所以精準度也更高。現在的電腦,大多數情況都會用雙精度 (double),而不是單精度 (float)。
double a = 5;
double b = 4;
double c = 2;
double d = (a + b) / c;
Console.WriteLine(d);
Output->4.5
double a = 19;
double b = 23;
double c = 8;
double d = (a + b) / c;
Console.WriteLine(d);
Output->5.25
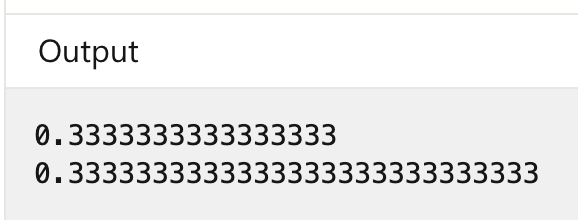
還有一種類型需要學習:十進制 (decimal) 類型,十進制類型的取值範圍比雙精度類型小,但精度更高。做個簡單的比較:
double a = 1.0;
double b = 3.0;
Console.WriteLine(a / b);
decimal c = 1.0M;
decimal d = 3.0M;
Console.WriteLine(c / d);
「Tuple(元組)」是一組固定長度、照順序排列的數值,裡面的每個元素都有自己的型別,而且可以選擇性地幫它取名字,可以透過以下範例來了解 Tuples:
var pt = (X: 1, Y: 2);
var slope = (double)pt.Y / (double)pt.X;
Console.WriteLine($"A line from the origin to the point {pt} has a slope of {slope}.");
可以看到結果如下: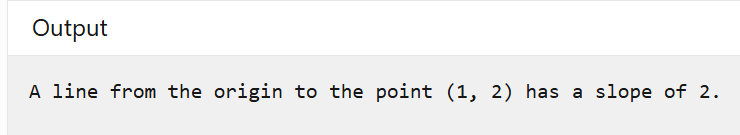
可以看到在定義 pt 這個變數時裡面同時包含了X、Y兩個int變數,並且可以用pt.X、pt.Y來調用參數。
我們可以重新定義 Tuples 中的任何成員,加上以下的程式碼可觀察差異:
pt.X = pt.X + 5;
Console.WriteLine($"The point is now at {pt}.");
結果: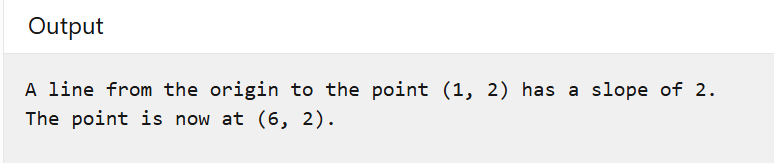
也可以使用 with 表達式建立一個新的元組,它是原始元組的修改副本。加入以下程式碼,可以看到執行結果的差異:
var pt2 = pt with { Y = 10 };
Console.WriteLine($"The point 'pt2' is at {pt2}.");
結果: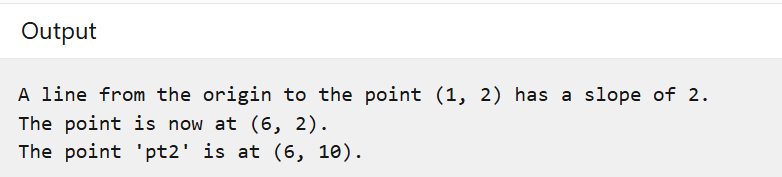
而在一個 Tuples 內不一定要是所有變數都是相同型態,例如:
var namedData = (Name: "Morning observation", Temp: 17, Wind: 4);
var person = (FirstName: "Lee", LastName: "Jessica");
var order = (Product: "guitar picks", style: "triangle", quantity: 500, UnitPrice: 0.10m);
Console.WriteLine($"My name is {person.LastName} {person.FirstName}. {namedData.Name} temp is {namedData.Temp} and wind is {namedData.Wind}.");
結果: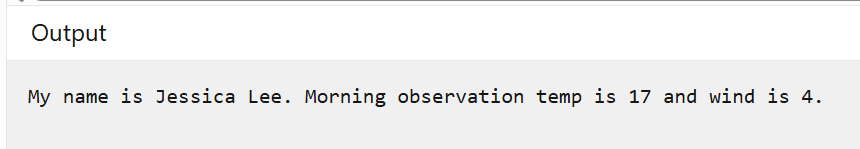
前面提到的 Tuple 很適合把多個值放在同一個結構裡的時候使用,它很輕量,而且可以在需要的地方直接宣告來用。不過,隨著程式越寫越多,可能會發現同樣的 tuple 型別在程式裡重複出現。像是如果你的應用程式需要處理 2D 座標,那代表點的 tuple 可能就會一直被用到。若遇到這種情況時,其實可以改用 record 型別 來存這些值,還能提供更多功能。下面這個程式碼範例就是用 Main 方法當作程式的進入點,並且在它前面宣告一個 record 型別。
public record Point(int X, int Y);
public static void Main()
{
Point pt = new Point(1, 1);
var pt2 = pt with { Y = 10 };
Console.WriteLine($"The two points are {pt} and {pt2}");
}
結果: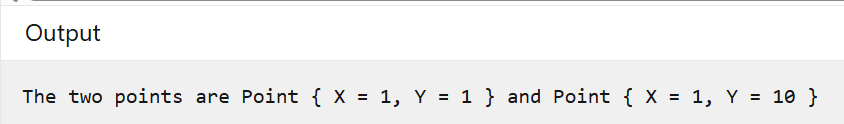
record 的宣告可以用一行程式碼就搞定,像這裡的 Point,它會把 X 和 Y 存在唯讀屬性裡。以後你只要用到這種型別,就直接寫 Point。有意義的名字(像 Point)能讓程式碼更好懂,也能看出用途。
在 Main 方法裡,你可以看到 with 的用法:它能複製一個既有的物件,然後只改想改的屬性。像 pt2 = pt with { Y = 10 } 這行,就表示「建立一個新的 pt2,裡面所有值跟 pt 一樣,只是 Y 改成 10」。而且 with 裡可以一次改好幾個屬性。
上面的 record 宣告只是一行程式碼,最後用 ; 結尾,就像一般的 C# 敘述一樣,也可以替 record 加更多功能,像是成員方法或更多資料欄位。
public record Point(int X, int Y)
{
public double Slope() => (double)Y / (double)X;
}
public static void Main()
{
Point pt = new Point(1, 1);
var pt2 = pt with { Y = 10 };
double slope = pt.Slope();
Console.WriteLine($"The slope of {pt} is {slope}");
Console.WriteLine($"The two points are {pt} and {pt2}");
}
結果: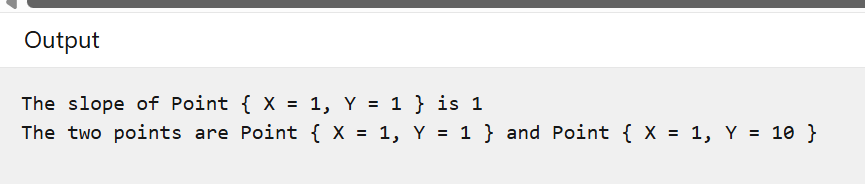
在 C# 裡,所有有名字的型別基本上都是 class 或 struct。
舉例來說:
實際差別是:
record 關鍵字會幫你自動產生一些常用的功能,例如比較相等性、指定、複製等等。如果你的型別主要就是用來存放一組相關資料,那用 record 會很方便。
如果你的型別除了存值,還需要更進階的行為,可以考慮直接用 struct 或 class,不用加 record。
另外還有 interface(介面型別),它可以定義一組「行為契約」,讓不同的 struct 或 class 去實作。這樣就能讓程式更有彈性。
參考資料:點擊以打開
