已經在Cloud Run 上架好了安全又方便的MCP ,那就來給 ADK Agent 使用吧 !
授予 Cloud Run 服務身分呼叫遠端 MCP 伺服器的權限
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
--member="serviceAccount:$SERVICE_ACCOUNT" \
--role="roles/run.invoker"
將MCP 伺服器網址儲存至環境變數
echo -e "\nMCP_SERVER_URL=https://zoo-mcp-server-${PROJECT_NUMBER}.europe-west1.run.app/mcp/" >> .env
使用公開 MCP 伺服器連結
echo -e "\nMCP_SERVER_URL=https://zoo-mcp-server-${PROJECT_NUMBER}.europe-west1.run.app/mcp/" >> .env
建立 init.py 檔案
cloudshell edit init.py
內容
from . import agent
cloudshell edit agent.py
agent.py的內容
import os
import logging
import google.cloud.logging
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from google.adk import Agent
from google.adk.agents import SequentialAgent
from google.adk.tools.mcp_tool.mcp_toolset import MCPToolset, StreamableHTTPConnectionParams
from google.adk.tools.tool_context import ToolContext
from google.adk.tools.langchain_tool import LangchainTool
from langchain_community.tools import WikipediaQueryRun
from langchain_community.utilities import WikipediaAPIWrapper
import google.auth
import google.auth.transport.requests
import google.oauth2.id_token
import collections.abc
# --- Setup Logging and Environment ---
cloud_logging_client = google.cloud.logging.Client()
cloud_logging_client.setup_logging()
load_dotenv()
model_name = os.getenv("MODEL")
# Greet user and save their prompt
def add_prompt_to_state(
tool_context: ToolContext, prompt: str
) -> dict[str, str]:
"""Saves the user's initial prompt to the state."""
tool_context.state["PROMPT"] = prompt
logging.info(f"[State updated] Added to PROMPT: {prompt}")
return {"status": "success"}
# Configuring the MCP Tool to connect to the Zoo MCP server
mcp_server_url = os.getenv("MCP_SERVER_URL")
if not mcp_server_url:
raise ValueError("The environment variable MCP_SERVER_URL is not set.")
def get_id_token():
"""Get an ID token to authenticate with the MCP server."""
target_url = os.getenv("MCP_SERVER_URL")
audience = target_url.split('/mcp/')[0]
request = google.auth.transport.requests.Request()
id_token = google.oauth2.id_token.fetch_id_token(request, audience)
return id_token
"""
# Use this code if you are using the public MCP Server and comment out the code below defining mcp_tools
mcp_tools = MCPToolset(
connection_params=StreamableHTTPConnectionParams(
url=mcp_server_url
)
)
"""
class _LazyAuthHeader(collections.abc.Mapping):
"""一個在需要時才動態獲取新 ID token 的類別,用於 Authorization 標頭。"""
def __getitem__(self, key):
if key == "Authorization":
logging.info("正在為 MCP 伺服器獲取新的 ID token。")
return f"Bearer {get_id_token()}"
raise KeyError(f"在延遲認證標頭中找不到 '{key}'。")
def __iter__(self):
yield "Authorization"
def __len__(self):
return 1
mcp_tools = MCPToolset(
connection_params=StreamableHTTPConnectionParams(
url=mcp_server_url,
headers=_LazyAuthHeader(),
),
)
# Configuring the Wikipedia Tool
wikipedia_tool = LangchainTool(
tool=WikipediaQueryRun(api_wrapper=WikipediaAPIWrapper())
)
# 1. Researcher Agent
comprehensive_researcher = Agent(
name="comprehensive_researcher",
model=model_name,
description="The primary researcher that can access both internal zoo data and external knowledge from Wikipedia.",
instruction="""
You are a helpful research assistant. Your goal is to fully answer the user's PROMPT.
You have access to two tools:
1. A tool for getting specific data about animals AT OUR ZOO (names, ages, locations).
2. A tool for searching Wikipedia for general knowledge (facts, lifespan, diet, habitat).
First, analyze the user's PROMPT.
- If the prompt can be answered by only one tool, use that tool.
- If the prompt is complex and requires information from both the zoo's database AND Wikipedia,
you MUST use both tools to gather all necessary information.
- Synthesize the results from the tool(s) you use into preliminary data outputs.
PROMPT:
{{ PROMPT }}
""",
tools=[
mcp_tools,
wikipedia_tool
],
output_key="research_data" # A key to store the combined findings
)
# 2. Response Formatter Agent
response_formatter = Agent(
name="response_formatter",
model=model_name,
description="Synthesizes all information into a friendly, readable response.",
instruction="""
You are the friendly voice of the Zoo Tour Guide. Your task is to take the
RESEARCH_DATA and present it to the user in a complete and helpful answer.
- First, present the specific information from the zoo (like names, ages, and where to find them).
- Then, add the interesting general facts from the research.
- If some information is missing, just present the information you have.
- Be conversational and engaging.
RESEARCH_DATA:
{{ research_data }}
"""
)
tour_guide_workflow = SequentialAgent(
name="tour_guide_workflow",
description="The main workflow for handling a user's request about an animal.",
sub_agents=[
comprehensive_researcher, # Step 1: Gather all data
response_formatter, # Step 2: Format the final response
]
)
root_agent = Agent(
name="greeter",
model=model_name,
description="The main entry point for the Zoo Tour Guide.",
instruction="""
- Let the user know you will help them learn about the animals we have in the zoo.
- When the user responds, use the 'add_prompt_to_state' tool to save their response.
After using the tool, transfer control to the 'tour_guide_workflow' agent.
""",
tools=[add_prompt_to_state],
sub_agents=[tour_guide_workflow]
)
source .env
# Grant the "Vertex AI User" role to your service account
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
--member="serviceAccount:$SERVICE_ACCOUNT" \
--role="roles/aiplatform.user"
# Run the deployment command
uvx --from google-adk \
adk deploy cloud_run \
--project=$PROJECT_ID \
--region=europe-west1 \
--service_name=zoo-tour-guide \
--with_ui \
. \
-- \
--labels=dev-tutorial=codelab-adk
提供已部署 Cloud Run 服務的網址。
https://zoo-tour-guide-58023433342.europe-west1.run.app/
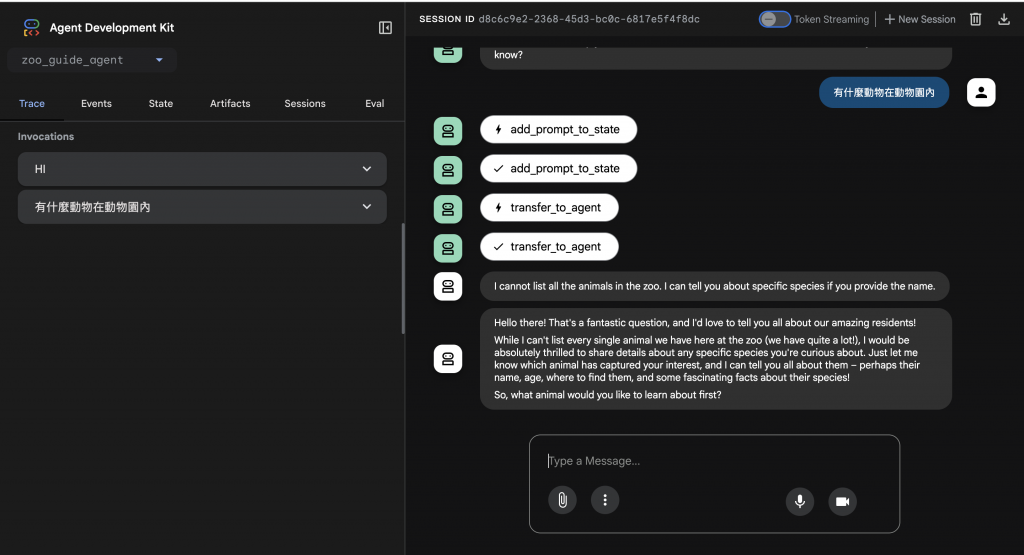
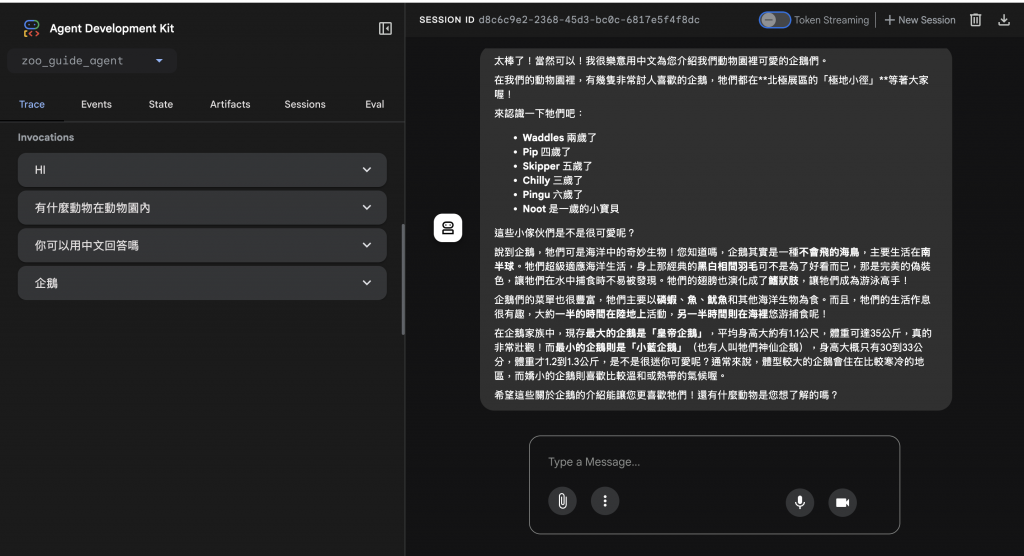
MCP、本地 MCP、Cloud Run MCP 的差異:
No MCP:整合困難、無法擴展、安全性差。
Local MCP:標準化了,但部署和擴展有限。
Cloud Run MCP:在整合、部署、自動伸縮、安全性、可重用性上都達到最佳。