我們掌握了 spec-kit 規格驅動開發,並且也學習 Playwright Agents 的三位一體,今天我們將試著將整個系列的所有武功融會貫通,透過 spec-kit 和 Playwright Agents 撰寫測試腳本。
我們學會 spec-kit 從需求到藍圖和 Playwright Agents 從藍圖到程式碼,我們會試著將其打造一個能更自動產出高品質且可維護性高的測試程式碼。
我們的核心策略是:
memory/test-constitution.md - 這份文件是根據前幾天的文件草稿,由 AI Agent 重構,其實內容可以適度刪減,除了成本考量、也可以讓他漸漸調整成為自己的風格,或是建立新的規範。適度刪減內容,可以減低 Token 的成本消耗。
# 測試規範憲章 (Test Constitution)
> **版本**: 1.0.0
> **最後更新**: 2025-10-13
> **適用範圍**: 所有 Playwright 測試程式碼
## 📋 目錄
1. [核心原則](#核心原則)
2. [自訂 Fixture](#1-自訂-fixture)
3. [Page Object Model](#2-page-object-model)
4. [Page Factory Pattern](#3-page-factory-pattern)
5. [Loadable Component Pattern](#4-loadable-component-pattern)
6. [Fluent Pattern](#5-fluent-pattern)
7. [完整範例](#完整範例)
8. [驗證清單](#驗證清單)
---
## 核心原則
所有產生的測試程式碼**必須**遵循以下原則:
- ✅ 使用 TypeScript 撰寫測試
- ✅ 遵循 Page Object Model 設計模式
- ✅ 實作 Loadable Component 確保頁面載入
- ✅ 採用 Fluent Pattern 提升可讀性
- ✅ 使用自訂 Fixture 管理測試資料
- ✅ 清晰的註解說明測試意圖
---
## 1. 自訂 Fixture
### 📖 說明
自訂 Fixture 讓多個測試案例可以共用初始化邏輯和測試資料。通常用於:
- 建立測試帳號
- 準備測試資料
- 設定測試環境
- 管理資源生命週期
### ✅ 正確範例
`typescript
import { test as base, expect } from '@playwright/test';
// 定義 Fixture 型別
type TestFixtures = {
testData: {
email: string;
password: string;
};
};
// 擴展 base test 加入自訂 fixture
const test = base.extend<TestFixtures>({
testData: async ({}, use) => {
// Setup: 建立測試資料
const data = {
email: "test@example.com",
password: "SecurePass123!"
};
// 將資料傳遞給測試
await use(data);
// Teardown: 清理邏輯(如果需要)
// await cleanup();
}
});
// 使用自訂 fixture
test("Should login with test user", async ({ page, testData }) => {
await page.goto("https://example.com/login");
// 使用 fixture 提供的測試資料
await page.getByRole("textbox", { name: "Email" }).fill(testData.email);
await page.getByRole("textbox", { name: "Password" }).fill(testData.password);
await page.getByRole("button", { name: "Login" }).click();
// 驗證登入成功
await expect(page).toHaveURL(/home/);
});
`
### ❌ 錯誤範例
`typescript
// ❌ 語法錯誤、缺少型別定義
onst test = base.extend(
testData: async {} use => { // 語法錯誤
const data = {
email: "@example.com", // 不完整的 email
password: "123456" // 弱密碼
}
await use(data)
})
}
`
### 💡 最佳實踐
- 使用 TypeScript 型別定義 Fixture
- Setup 和 Teardown 邏輯清晰分離
- 使用有意義的測試資料
- 考慮資料清理以避免測試間干擾
---
## 2. Page Object Model
### 📖 說明
Page Object Model (POM) 將頁面元素和操作封裝在類別中,提供以下優勢:
- 提高程式碼可維護性
- 減少重複程式碼
- 元素變更時只需修改一處
- 測試程式碼更接近業務語言
### ✅ 正確範例
#### Page Object 定義
`typescript
// pages/LoginPage.ts
import { Page, Locator, expect } from '@playwright/test';
/**
* 登入頁面的 Page Object
* 封裝所有與登入頁面相關的元素和操作
*/
export class LoginPage {
readonly page: Page;
readonly usernameInput: Locator;
readonly passwordInput: Locator;
readonly submitButton: Locator;
readonly errorMessage: Locator;
constructor(page: Page) {
this.page = page;
// 使用語義化的 locator
this.usernameInput = page.getByRole('textbox', { name: /username|email/i });
this.passwordInput = page.getByRole('textbox', { name: /password/i });
this.submitButton = page.getByRole('button', { name: /login|sign in/i });
this.errorMessage = page.getByRole('alert');
}
/**
* 導航到登入頁面
*/
async goto(): Promise<void> {
await this.page.goto('https://your-app.example.com/login');
}
/**
* 執行登入操作
* @param username - 使用者名稱或 email
* @param password - 密碼
*/
async login(username: string, password: string): Promise<void> {
await this.usernameInput.fill(username);
await this.passwordInput.fill(password);
await this.submitButton.click();
}
/**
* 驗證錯誤訊息
* @param expectedMessage - 預期的錯誤訊息
*/
async verifyErrorMessage(expectedMessage: string): Promise<void> {
await expect(this.errorMessage).toContainText(expectedMessage);
}
}
`
#### 測試檔案使用
`typescript
// tests/login.spec.ts
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
import { LoginPage } from '../pages/LoginPage';
test.describe('登入功能測試', () => {
test('使用者可以成功登入', async ({ page }) => {
const loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
await loginPage.goto();
await loginPage.login('user01', 'SecurePass123!');
// 驗證登入成功
await expect(page).toHaveURL(/home|dashboard/);
});
test('使用無效憑證登入應顯示錯誤', async ({ page }) => {
const loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
await loginPage.goto();
await loginPage.login('invalid', 'wrongpass');
// 驗證錯誤訊息
await loginPage.verifyErrorMessage('Invalid credentials');
});
});
`
### 💡 最佳實踐
- 使用 `readonly` 標記不可變屬性
- 為每個公開方法添加 JSDoc 註解
- 使用語義化的 locator (getByRole, getByLabel 等)
- 方法名稱清楚描述其行為
- 避免在 Page Object 中包含斷言(驗證方法除外)
---
## 3. Page Factory Pattern
### 📖 說明
Page Factory 統一管理所有 Page Object 的建立,提供以下優勢:
- 集中管理 Page Object 建立邏輯
- 確保所有 Page Object 使用相同的 page 實例
- 方便擴展新的 Page Object
- 減少測試中的重複程式碼
### ✅ 正確範例
#### Page Factory 定義
`typescript
// pages/PageFactory.ts
import { Page } from '@playwright/test';
import { LoginPage } from './LoginPage';
import { HomePage } from './HomePage';
import { DashboardPage } from './DashboardPage';
import { ProfilePage } from './ProfilePage';
/**
* Page Factory - 統一管理所有 Page Object 的建立
*
* @example
* const factory = new PageFactory(page);
* const loginPage = factory.loginPage();
*/
export class PageFactory {
constructor(private readonly page: Page) {}
/**
* 取得登入頁面物件
* @returns {LoginPage} 登入頁面實例
*/
loginPage(): LoginPage {
return new LoginPage(this.page);
}
/**
* 取得首頁物件
* @returns {HomePage} 首頁實例
*/
homePage(): HomePage {
return new HomePage(this.page);
}
/**
* 取得儀表板頁面物件
* @returns {DashboardPage} 儀表板頁面實例
*/
dashboardPage(): DashboardPage {
return new DashboardPage(this.page);
}
/**
* 取得個人資料頁面物件
* @returns {ProfilePage} 個人資料頁面實例
*/
profilePage(): ProfilePage {
return new ProfilePage(this.page);
}
}
`
#### 測試檔案使用
`typescript
// tests/login-flow.spec.ts
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
import { PageFactory } from '../pages/PageFactory';
test.describe('完整登入流程測試', () => {
test('使用者可以成功登入並進入首頁', async ({ page }) => {
const factory = new PageFactory(page);
// 使用 Factory 建立頁面物件
const loginPage = factory.loginPage();
await loginPage.goto();
await loginPage.login('user01', 'SecurePass123!');
// 驗證登入後跳轉到首頁
const homePage = factory.homePage();
await homePage.waitUntilLoaded();
expect(await homePage.isLoaded()).toBeTruthy();
});
test('使用者可以從首頁導航至個人資料', async ({ page }) => {
const factory = new PageFactory(page);
// 先登入
const loginPage = factory.loginPage();
await loginPage.goto();
await loginPage.login('user01', 'SecurePass123!');
// 從首頁導航
const homePage = factory.homePage();
await homePage.clickProfileLink();
// 驗證個人資料頁面載入
const profilePage = factory.profilePage();
await profilePage.waitUntilLoaded();
expect(await profilePage.isLoaded()).toBeTruthy();
});
});
`
### 💡 最佳實踐
- 使用 `readonly` 確保 page 實例不被修改
- 為每個工廠方法添加 JSDoc 註解
- 保持工廠方法命名一致性 (如: `xxxPage()`)
- 可選:加入快取機制避免重複建立相同頁面物件
---
## 4. Loadable Component Pattern
### 📖 說明
Loadable Component 確保頁面完全載入後才執行後續操作,避免因為:
- DOM 元素尚未載入
- 非同步資料尚未取得
- 頁面轉場動畫尚未完成
導致的測試不穩定問題。
### ✅ 正確範例
#### Page Object 實作 Loadable Component
`typescript
// pages/LoginPage.ts
import { Page, Locator, expect } from '@playwright/test';
export class LoginPage {
readonly page: Page;
readonly pageTitle: Locator;
readonly usernameInput: Locator;
readonly passwordInput: Locator;
readonly submitButton: Locator;
constructor(page: Page) {
this.page = page;
this.pageTitle = page.getByRole('heading', { name: /login/i });
this.usernameInput = page.getByRole('textbox', { name: /username/i });
this.passwordInput = page.getByRole('textbox', { name: /password/i });
this.submitButton = page.getByRole('button', { name: /login/i });
}
/**
* 導航到登入頁面
*/
async goto(): Promise<void> {
await this.page.goto('https://your-app.example.com/login');
// 導航後自動等待頁面載入
await this.waitUntilLoaded();
}
/**
* Loadable Component 核心方法
* 等待頁面關鍵元素載入完成
*/
async waitUntilLoaded(): Promise<void> {
// 等待頁面標題出現
await expect(this.pageTitle).toBeVisible();
// 等待關鍵表單元素出現
await expect(this.usernameInput).toBeVisible();
await expect(this.submitButton).toBeEnabled();
}
/**
* 驗證頁面是否已載入
* @returns {Promise<boolean>} 頁面是否已載入
*/
async isLoaded(): Promise<boolean> {
try {
await expect(this.pageTitle).toBeVisible({ timeout: 5000 });
return true;
} catch {
return false;
}
}
/**
* 執行登入操作
*/
async login(username: string, password: string): Promise<void> {
await this.usernameInput.fill(username);
await this.passwordInput.fill(password);
await this.submitButton.click();
}
}
`
#### 測試檔案使用
`typescript
// tests/login.spec.ts
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
import { LoginPage } from '../pages/LoginPage';
import { HomePage } from '../pages/HomePage';
test('使用有效憑證登入', async ({ page }) => {
const loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
// goto() 內部已包含 waitUntilLoaded()
await loginPage.goto();
// 確認頁面已載入後才執行登入
await loginPage.login('user01', 'SecurePass123!');
// 等待導航到首頁並確認載入完成
const homePage = new HomePage(page);
await homePage.waitUntilLoaded();
// 驗證登入成功
await expect(page).toHaveURL(/home|dashboard/);
});
test('頁面載入驗證', async ({ page }) => {
const loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
await page.goto('https://your-app.example.com/login');
// 明確等待頁面載入
await loginPage.waitUntilLoaded();
// 或使用 isLoaded() 進行條件判斷
const loaded = await loginPage.isLoaded();
expect(loaded).toBeTruthy();
});
`
### 💡 最佳實踐
- 每個 Page Object 都應實作 `waitUntilLoaded()` 方法
- 在 `goto()` 方法中自動呼叫 `waitUntilLoaded()`
- 等待關鍵元素而非固定時間延遲
- 可選實作 `isLoaded()` 方法用於條件判斷
- 考慮頁面的主要載入狀態指標(如 loading spinner 消失)
---
## 5. Fluent Pattern
### 📖 說明
Fluent Pattern (流暢介面) 讓方法可以鏈式調用,使程式碼更簡潔易讀,接近自然語言描述。
**核心概念**: 每個方法返回 `this` 或 `Promise<this>`
### ✅ 正確範例
#### Page Object 實作 Fluent Pattern
`typescript
// pages/LoginPage.ts
import { Page, Locator, expect } from '@playwright/test';
export class LoginPage {
readonly page: Page;
readonly usernameInput: Locator;
readonly passwordInput: Locator;
readonly submitButton: Locator;
constructor(page: Page) {
this.page = page;
this.usernameInput = page.getByRole('textbox', { name: /username/i });
this.passwordInput = page.getByRole('textbox', { name: /password/i });
this.submitButton = page.getByRole('button', { name: /login/i });
}
/**
* 導航到登入頁面
* @returns {Promise<LoginPage>} 返回自身支援鏈式調用
*/
async goto(): Promise<LoginPage> {
await this.page.goto('https://your-app.example.com/login');
await this.waitUntilLoaded();
return this;
}
/**
* 等待頁面載入
* @returns {Promise<LoginPage>} 返回自身支援鏈式調用
*/
async waitUntilLoaded(): Promise<LoginPage> {
await expect(this.usernameInput).toBeVisible();
return this;
}
/**
* 輸入使用者名稱
* @param username - 使用者名稱
* @returns {Promise<LoginPage>} 返回自身支援鏈式調用
*/
async enterUsername(username: string): Promise<LoginPage> {
await this.usernameInput.fill(username);
return this;
}
/**
* 輸入密碼
* @param password - 密碼
* @returns {Promise<LoginPage>} 返回自身支援鏈式調用
*/
async enterPassword(password: string): Promise<LoginPage> {
await this.passwordInput.fill(password);
return this;
}
/**
* 點擊登入按鈕
* @returns {Promise<LoginPage>} 返回自身支援鏈式調用
*/
async clickLoginButton(): Promise<LoginPage> {
await this.submitButton.click();
return this;
}
/**
* 驗證導航到首頁
* @returns {Promise<LoginPage>} 返回自身支援鏈式調用
*/
async shouldSeeHomePage(): Promise<LoginPage> {
await expect(this.page).toHaveURL(/home|dashboard/);
return this;
}
/**
* 組合方法:完整登入流程
* @param username - 使用者名稱
* @param password - 密碼
* @returns {Promise<LoginPage>} 返回自身支援鏈式調用
*/
async loginWith(username: string, password: string): Promise<LoginPage> {
await this.enterUsername(username);
await this.enterPassword(password);
await this.clickLoginButton();
return this;
}
}
`
#### 測試檔案使用 Fluent Pattern
`typescript
// tests/login.spec.ts
import { test } from '@playwright/test';
import { LoginPage } from '../pages/LoginPage';
test.describe('登入功能 - Fluent Pattern', () => {
test('使用 Fluent API 登入成功', async ({ page }) => {
const loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
// 鏈式調用,清晰表達測試流程
await loginPage
.goto()
.then(p => p.enterUsername('user01'))
.then(p => p.enterPassword('SecurePass123!'))
.then(p => p.clickLoginButton())
.then(p => p.shouldSeeHomePage());
});
test('使用組合方法登入', async ({ page }) => {
const loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
// 使用組合方法簡化流程
await loginPage
.goto()
.then(p => p.loginWith('user01', 'SecurePass123!'))
.then(p => p.shouldSeeHomePage());
});
test('多步驟操作展示', async ({ page }) => {
const loginPage = new LoginPage(page);
// 複雜流程的清晰表達
await loginPage
.goto()
.then(p => p.waitUntilLoaded())
.then(p => p.enterUsername('user01'))
.then(p => p.enterPassword('SecurePass123!'))
.then(p => p.clickLoginButton())
.then(p => p.shouldSeeHomePage());
});
});
`
### 🎯 Fluent Pattern 的優勢
1. **可讀性**: 程式碼讀起來像自然語言
2. **簡潔性**: 減少中間變數
3. **維護性**: 方法職責單一,易於修改
4. **擴展性**: 容易添加新的鏈式方法
### 💡 最佳實踐
- 所有操作方法都返回 `Promise<this>`
- 使用 `.then()` 進行鏈式調用
- 保持每個方法職責單一
- 提供組合方法處理常見流程
- 驗證方法也返回 `this` 以支援繼續操作
---
## 完整範例
### 完整的 Page Object 實作
結合所有模式的完整範例:
`typescript
// pages/LoginPage.ts
import { Page, Locator, expect } from '@playwright/test';
/**
* 登入頁面 - 完整實作範例
* 整合: Page Object Model + Loadable Component + Fluent Pattern
*/
export class LoginPage {
readonly page: Page;
readonly pageTitle: Locator;
readonly usernameInput: Locator;
readonly passwordInput: Locator;
readonly submitButton: Locator;
readonly errorMessage: Locator;
constructor(page: Page) {
this.page = page;
this.pageTitle = page.getByRole('heading', { name: /login/i });
this.usernameInput = page.getByRole('textbox', { name: /username/i });
this.passwordInput = page.getByRole('textbox', { name: /password/i });
this.submitButton = page.getByRole('button', { name: /login/i });
this.errorMessage = page.getByRole('alert');
}
// Loadable Component
async waitUntilLoaded(): Promise<LoginPage> {
await expect(this.pageTitle).toBeVisible();
await expect(this.usernameInput).toBeVisible();
return this;
}
async isLoaded(): Promise<boolean> {
try {
await expect(this.pageTitle).toBeVisible({ timeout: 5000 });
return true;
} catch {
return false;
}
}
// Fluent Pattern - 導航
async goto(): Promise<LoginPage> {
await this.page.goto('https://your-app.example.com/login');
return this.waitUntilLoaded();
}
// Fluent Pattern - 操作方法
async enterUsername(username: string): Promise<LoginPage> {
await this.usernameInput.fill(username);
return this;
}
async enterPassword(password: string): Promise<LoginPage> {
await this.passwordInput.fill(password);
return this;
}
async clickSubmit(): Promise<LoginPage> {
await this.submitButton.click();
return this;
}
// 組合方法
async loginWith(username: string, password: string): Promise<LoginPage> {
await this.enterUsername(username);
await this.enterPassword(password);
await this.clickSubmit();
return this;
}
// Fluent Pattern - 驗證方法
async shouldSeeHomePage(): Promise<LoginPage> {
await expect(this.page).toHaveURL(/home|dashboard/);
return this;
}
async shouldSeeError(message: string): Promise<LoginPage> {
await expect(this.errorMessage).toContainText(message);
return this;
}
}
`
### 完整的測試範例
`typescript
// tests/login-complete.spec.ts
import { test as base, expect } from '@playwright/test';
import { PageFactory } from '../pages/PageFactory';
// 自訂 Fixture
type TestFixtures = {
pageFactory: PageFactory;
validUser: { username: string; password: string };
};
const test = base.extend<TestFixtures>({
pageFactory: async ({ page }, use) => {
const factory = new PageFactory(page);
await use(factory);
},
validUser: async ({}, use) => {
const user = {
username: 'testuser@example.com',
password: 'SecurePass123!'
};
await use(user);
// Teardown: 清理使用者資料(如果需要)
}
});
test.describe('完整登入流程測試', () => {
test('成功登入流程', async ({ pageFactory, validUser }) => {
const loginPage = pageFactory.loginPage();
// 使用 Fluent Pattern 執行完整流程
await loginPage
.goto()
.then(p => p.loginWith(validUser.username, validUser.password))
.then(p => p.shouldSeeHomePage());
// 驗證首頁載入
const homePage = pageFactory.homePage();
expect(await homePage.isLoaded()).toBeTruthy();
});
test('無效憑證登入失敗', async ({ pageFactory }) => {
const loginPage = pageFactory.loginPage();
await loginPage
.goto()
.then(p => p.loginWith('invalid', 'wrongpass'))
.then(p => p.shouldSeeError('Invalid credentials'));
});
});
`
---
## 驗證清單
使用此清單確保您的測試程式碼符合所有規範:
### ✅ 基本要求
- [ ] 使用 TypeScript 撰寫
- [ ] 所有 Page Object 檔案放在 `pages/` 目錄
- [ ] 所有測試檔案放在 `tests/` 目錄
- [ ] 使用有意義的檔案和類別命名
### ✅ Page Object Model
- [ ] 頁面元素定義為 `readonly` Locator
- [ ] 使用語義化的 locator (getByRole, getByLabel 等)
- [ ] 每個 Page Object 有清楚的 JSDoc 註解
- [ ] 避免在 Page Object 中硬編碼測試資料
### ✅ Loadable Component
- [ ] 每個 Page Object 實作 `waitUntilLoaded()` 方法
- [ ] `goto()` 方法內部呼叫 `waitUntilLoaded()`
- [ ] 可選實作 `isLoaded()` 方法
- [ ] 等待關鍵元素而非使用固定延遲
### ✅ Fluent Pattern
- [ ] 所有操作方法返回 `Promise<this>`
- [ ] 支援鏈式調用
- [ ] 驗證方法也返回 `this`
- [ ] 提供組合方法處理常見流程
### ✅ 自訂 Fixture
- [ ] 使用 TypeScript 定義 Fixture 型別
- [ ] Setup 和 Teardown 邏輯清晰
- [ ] 避免 Fixture 間的相依性
- [ ] 使用有意義的 Fixture 名稱
### ✅ Page Factory
- [ ] 統一通過 Factory 建立 Page Object
- [ ] Factory 方法有清楚的命名
- [ ] 確保所有 Page Object 使用相同 page 實例
### ✅ 測試品質
- [ ] 測試有清楚的描述
- [ ] 使用 `test.describe` 組織相關測試
- [ ] 每個測試保持獨立性
- [ ] 使用有意義的斷言訊息
- [ ] 避免測試間的相依性
---
## 附錄
### 目錄結構建議
`
project-root/
├── pages/ # 所有 Page Object
│ ├── PageFactory.ts # Page Factory
│ ├── LoginPage.ts
│ ├── HomePage.ts
│ └── DashboardPage.ts
├── tests/ # 所有測試檔案
│ ├── login.spec.ts
│ ├── dashboard.spec.ts
│ └── user-profile.spec.ts
├── fixtures/ # 自訂 Fixture (可選)
│ └── testData.ts
└── playwright.config.ts # Playwright 設定
`
### 命名規範
- **Page Object**: `XxxPage.ts` (如 `LoginPage.ts`)
- **測試檔案**: `xxx.spec.ts` (如 `login.spec.ts`)
- **方法命名**: 使用動詞開頭 (如 `clickButton`, `enterText`, `verifyTitle`)
- **Locator 命名**: 描述元素用途 (如 `submitButton`, `emailInput`)
### 參考資源
- [Playwright 官方文檔](https://playwright.dev/)
- [Page Object Model 設計模式](https://playwright.dev/docs/pom)
- [Playwright Best Practices](https://playwright.dev/docs/best-practices)
---
**版本歷史**:
- v1.0.0 (2025-10-13): 初始版本,整合所有測試規範
tests/seed.spec.ts - 當撰寫測試案例的程式碼時,AI 會以這份文件當作基本的程式碼,所以共同初始化的程式碼都可以撰寫在這裡,除此之外,AI Agent 也能透過這份程式碼的風格,撰寫出來類似的風格。
// Seed file for Playwright Website Testing
// 此檔案提供基礎的頁面載入測試,確保測試環境正常運作
// 遵循 test-constitution.md 規範:
// - Page Object Model
// - Loadable Component
// - Fluent Pattern
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
import { PlaywrightHomePage } from '../pages/PlaywrightHomePage';
import { PlaywrightInstallationPage } from '../pages/PlaywrightInstallationPage';
import { PageFactory } from '../pages/PageFactory';
test.describe('Seed Tests - Playwright Website', () => {
test('應該能夠載入 Playwright 首頁', async ({ page }) => {
// 使用 Page Object 導航到首頁
const homePage = new PlaywrightHomePage(page);
await homePage.goto();
// 驗證頁面成功載入 - 檢查關鍵元素可見
await expect(homePage.mainHeading).toBeVisible();
await expect(homePage.getStartedButton).toBeVisible();
// 驗證 URL 正確
expect(page.url()).toBe('https://playwright.dev/');
});
test('應該能夠從首頁導航至安裝頁面', async ({ page }) => {
// 使用 Page Factory
const factory = new PageFactory(page);
// 導航到首頁
const homePage = factory.homePage();
await homePage.goto();
// 點擊 Get Started 按鈕
await homePage.clickGetStartedButton();
// 驗證安裝頁面載入
const installationPage = factory.installationPage();
await installationPage.waitUntilLoaded();
// 驗證頁面元素
await expect(installationPage.installationHeading).toBeVisible();
await expect(page).toHaveURL(/docs\/intro/);
});
test('驗證 Page Factory 正常運作', async ({ page }) => {
const factory = new PageFactory(page);
// 驗證可以建立首頁物件
const homePage = factory.homePage();
expect(homePage).toBeDefined();
expect(homePage.page).toBe(page);
expect(homePage.baseURL).toBe('https://playwright.dev/');
// 驗證可以建立安裝頁面物件
const installationPage = factory.installationPage();
expect(installationPage).toBeDefined();
expect(installationPage.page).toBe(page);
});
test('驗證 Fluent Pattern 鏈式調用', async ({ page }) => {
const homePage = new PlaywrightHomePage(page);
// 測試鏈式調用
await homePage
.goto()
.then(p => p.verifyGetStartedButtonVisible())
.then(p => p.verifyGetStartedButtonEnabled());
// 驗證最終狀態
await expect(homePage.getStartedButton).toBeVisible();
await expect(homePage.getStartedButton).toBeEnabled();
});
test('驗證 Loadable Component 模式', async ({ page }) => {
const homePage = new PlaywrightHomePage(page);
// 導航(內部會呼叫 waitUntilLoaded)
await homePage.goto();
// 驗證頁面已完全載入
await expect(homePage.mainHeading).toBeVisible();
// 測試獨立的 waitUntilLoaded 方法
await homePage.waitUntilLoaded();
// 再次驗證
await expect(homePage.mainHeading).toBeVisible();
});
});
藉著你可以使用前面幾天學習的 AI Agent 幫忙產生測試程式碼,AI Agent 會閱讀 test-plan.md 和 memory/test-constitution.md 和 seed.spec.ts 的規範和風格撰寫程式碼,根據這樣的方式就可以產生可維護的程式碼。
可以參考下列的執行畫面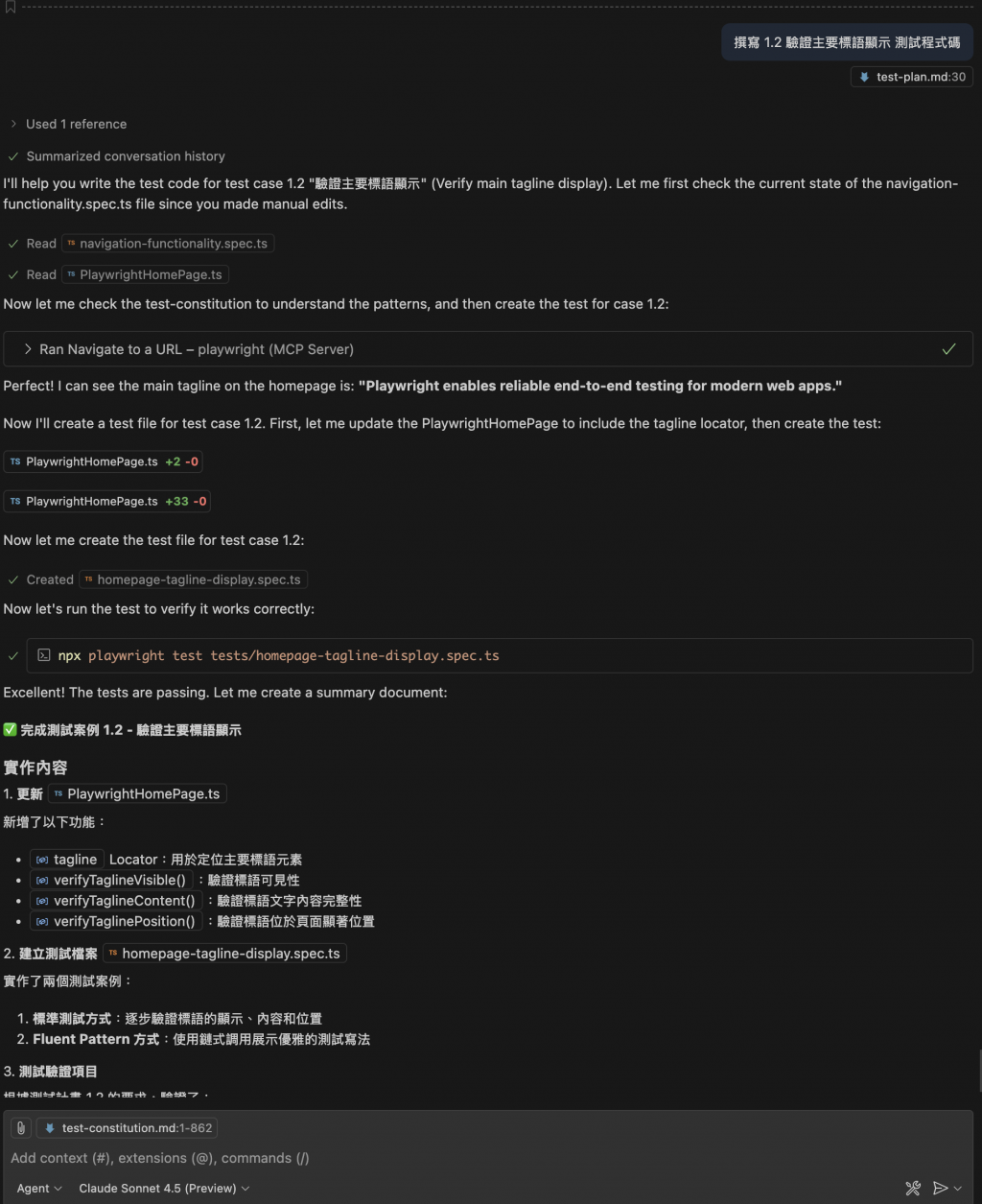
這個框架是可以很容易擴充的。我們可以輕鬆地引入更多「心法」:
今天,我們完成了這趟旅程的終極目標。我們將 spec-kit 的規格驅動能力、獨孤九劍 的設計模式智慧,以及 Playwright Agents 的自動化執行力,成功地融合為一個無縫、高效、且具備自我修復能力的 AI 驅動開發平台。在這個平台中,您的角色已經徹底昇華:您不再是日夜編碼的執行者,而是定義規則、描述意圖、監督成果的「架構師」與「指揮官」 。
整個系統會根據你的規範產生測試程式碼,而這個就是第一天說的 AI 時代的「唯快不破」,也是您在這近三十天修煉中,達到的「無招勝有招」的最高境界。
