主要異步框架提供了以下核心功能:
| 功能 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| 多線程池隔離 | 為不同類型的任務分配獨立資源,避免相互干擾 |
| 上下文傳遞 | 自動在異步任務中保留安全性與請求信息 |
| 通用反射執行 | 支援高度靈活的動態方法調用 |
| 標準化異常處理 | 統一的異常捕獲與日誌機制 |
| CompletableFuture 集成 | 豐富的組合 API 支援複雜異步流程 |
通過遵循本文檔中的最佳實踐,開發人員可以構建高效、可靠且易於維護的異步系統。
非同步執行配置(AsyncConfiguration)
提供兩個非同步執行配置,原因與建議使用方式:
快速任務使用專用線程池(asyncExecutor1),如需要低延遲的快速響應任務、API 調用、數據查詢等。
耗時任務使用專用線程池(asyncExecutor2) 批處理任務、郵件發送、文件導出等耗時作業。
配合兩個非同步執行配置,提供兩個包含SecurityContext以及RequestAttributes的配置(delegateTaskExecutor1、delegateTaskExecutor1)
系統架構圖
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ AsyncConfiguration │
│ (管理兩個線程池與上下文傳遞) │
├──────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ asyncExecutor1 & delegateTaskExecutor1 │
│ asyncExecutor2 & delegateTaskExecutor2 │
│ ContextCopyingTaskDecorator │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ AsyncGenericService (通用異步執行器) │
│ - genericAsyncExecutor1(代理執行) │
│ - genericAsyncExecutor2(代理執行) │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 異步工作者類別 │
│ - AsyncServiceWorkerSample (@Async 方法) │
│ - GenericClassForAsyncSample (代理執行用) │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
**新增AsyncConfiguration.java 於 tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async package(如package不存在,請新增)
package tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async;
import org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.task.TaskDecorator;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncConfigurer;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.task.DelegatingSecurityContextAsyncTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import tw.lewishome.webapp.base.utility.common.SystemEnvReader;
import tw.lewishome.webapp.base.utility.common.TypeConvert;
/**
* 非同步執行配置(AsyncConfiguration)。
*
* 本類別負責設定與初始化應用程式中使用的非同步執行緒池(ThreadPoolTaskExecutor),
* 並提供可供注入的命名 Bean(例如 {@code asyncExecutor1}、{@code asyncExecutor2})與
* 安全性委派執行器({@code delegateTaskExecutor1/2})。
*
*
* <h2>主要功能說明:</h2>
* <ul>
* <li>啟用 Spring 的異步方法支援({@code @EnableAsync})並提供多個命名的執行緒池。</li>
* <li>從外部設定(application.properties
* 或環境變數)讀取執行緒池參數:corePoolSize、maxPoolSize、queueCapacity 與
* threadNamePrefix。</li>
* <li>提供將安全性上下文(SecurityContext)委派給非同步任務的包裝執行器(DelegatingSecurityContextAsyncTaskExecutor)。</li>
* <li>提供自定義 TaskDecorator,用以在非同步任務中複製並還原安全性與請求上下文。</li>
* </ul>
*
* <h2>使用情境:</h2>
* <ul>
* <li>針對不同類型的非同步任務(例如快速回應任務與耗時背景任務)分配不同的執行緒池,以達到任務隔離與資源調度。</li>
* <li>需要在非同步任務中保留 Spring Security 或 Request 上下文時,使用 delegateTaskExecutor
* 包裝原始執行器。</li>
* <li>可透過 {@code @Async("asyncExecutor2")} 指定使用第二個執行緒池以實現隔離。</li>
* </ul>
*
* @author Lewis
* @since 2024
*/
// 在Spring Boot 中使用兩個 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 的好處主要在於分離和管理不同類型的併發任務,
// 例如一個用於處理用戶請求的快速響應任務,另一個用於執行後臺的耗時或異步任務。
// 這可以實現任務的隔離,避免高優先級任務被低優先級任務阻塞,
// 同時能夠爲不同任務定製不同的線程池配置(如核心線程數、隊列大小等),
// 從而優化系統性能和資源利用率,並提升整體系統的健壯性和響應速度。
// 兩個ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 的主要好處:
// 1. 任務類型隔離與優先級控制
// 2. 差異化資源配置
// 3. 提升系統穩定性和健壯
// 4. 簡化代碼維護與管理
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
@Slf4j
public class AsyncConfiguration implements AsyncConfigurer {
/**
* Fix for javadoc warning :
* use of default constructor, which does not provide a comment
* Constructs a new AsyncConfiguration instance.
* This is the default constructor, implicitly provided by the compiler
* if no other constructors are defined.
*/
public AsyncConfiguration() {
// Constructor body (can be empty)
}
@Autowired
private SystemEnvReader systemEnvReader;
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return (ex, method, params) -> log.error("Uncaught async exception in method: {} with params: {}",
method.getName(), params, ex);
}
/**
*
*
* 建立並返回一個異步執行緒池(執行緒名稱字首為 threadPool1-)。
*
* 此方法會根據設定的核心執行緒數、最大執行緒數、佇列容量及執行緒名稱前綴,
* 初始化一個 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 實例,並作為異步任務的執行器。
*
*
* 注意:此方法同時標註了 {@code @Bean("asyncExecutor1")} 及 {@code @Override},
* Spring 只會將此 bean 註冊為 {@code asyncExecutor1},且 {@code @Override} 會讓此 bean
* 成為預設的 async executor。
* 若需指定其他執行緒池,請於 {@code @Async} 註明 bean 名稱。
*
*
* @return a {@link java.util.concurrent.Executor} object
*/
@Bean("asyncExecutor1")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor asyncExecutor1() {
/** 執行緒池 1 維護執行緒的最少數量 */
String stringCorePoolSize1 = systemEnvReader.getProperty("async.corePoolSize1", "50");
Integer corePoolSize1 = TypeConvert.toInteger(stringCorePoolSize1, 50);
/** 執行緒池 1 維護執行緒的最大數量 */
String stringMaxPoolSize1 = systemEnvReader.getProperty("async.maxPoolSize1", "100");
Integer maxPoolSize1 = TypeConvert.toInteger(stringMaxPoolSize1, 100);
/** 執行緒池 1 緩衝佇列的大小 */
String stringQueueCapacity1 = systemEnvReader.getProperty("async.queueCapacity1", "500");
Integer queueCapacity1 = TypeConvert.toInteger(stringQueueCapacity1, 500);
/** 為每個執行緒名設定一個字首(1) */
String threadNamePrefix1 = systemEnvReader.getProperty("async.threadNamePrefix1", "threadPool1-");
// 執行緒池
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize1);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize1);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity1);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix(threadNamePrefix1);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setAllowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setTaskDecorator(new ContextCopyingTaskDecorator()); // Custom TaskDecorator
threadPoolTaskExecutor.initialize();
return threadPoolTaskExecutor;
}
/**
* 建立一個包裝指定 {@link ThreadPoolTaskExecutor} 的
* {@link DelegatingSecurityContextAsyncTaskExecutor} Bean。
* 此 Bean 會將安全性內容委派給異步任務執行器,確保在執行異步任務時能夠保留原有的安全性上下文。
*
* @param threadPoolTaskExecutor 被包裝的異步任務執行器
* @return 包裝後的 DelegatingSecurityContextAsyncTaskExecutor 實例
*/
@Bean("delegateTaskExecutor1")
public DelegatingSecurityContextAsyncTaskExecutor delegateTaskExecutor1(
@Qualifier("asyncExecutor1") ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor) {
return new DelegatingSecurityContextAsyncTaskExecutor(threadPoolTaskExecutor);
}
/**
* 建立並回傳次要的非同步執行緒池(執行緒名稱字首為 {@code threadPool2-})。
*
* 此方法會依據外部設定的 corePoolSize2、maxPoolSize2、queueCapacity2 與
* threadNamePrefix2 初始化 {@link ThreadPoolTaskExecutor},並回傳可注入使用的 Bean。
* 此執行緒池適合用於需要與主要執行緒池分離或接受高併發工作的場景。
*
*
* @return a {@link java.util.concurrent.Executor} instance 作為次要非同步執行器
*/
@Bean(name = "asyncExecutor2")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor asyncExecutor2() {
/** 執行緒池 2 維護執行緒的最少數量 */
String stringCorePoolSize2 = systemEnvReader.getProperty("async.corePoolSize2", "50");
Integer corePoolSize2 = TypeConvert.toInteger(stringCorePoolSize2, 50);
/** 執行緒池 2 維護執行緒的最大數量 */
String stringMaxPoolSize2 = systemEnvReader.getProperty("async.maxPoolSize2", "100");
Integer maxPoolSize2 = TypeConvert.toInteger(stringMaxPoolSize2, 100);
/** 執行緒池 2 緩衝佇列的大小 */
String stringQueueCapacity2 = systemEnvReader.getProperty("async.queueCapacity2", "500");
Integer queueCapacity2 = TypeConvert.toInteger(stringQueueCapacity2, 500);
/** 為每個執行緒名設定一個字首(2) */
String threadNamePrefix2 = systemEnvReader.getProperty("async.threadNamePrefix2", "threadPool2-");
// 執行緒池
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize2);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize2);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity2);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix(threadNamePrefix2);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
threadPoolTaskExecutor.setTaskDecorator(new ContextCopyingTaskDecorator()); // Custom TaskDecorator
threadPoolTaskExecutor.initialize();
return threadPoolTaskExecutor;
}
/**
* 建立一個包裝指定 {@link ThreadPoolTaskExecutor} 的
* {@link DelegatingSecurityContextAsyncTaskExecutor} Bean。
* 此 Bean 會將安全性內容委派給異步任務執行器,確保在執行異步任務時能夠保留原有的安全性上下文。
*
* @param threadPoolTaskExecutor 被包裝的異步任務執行器
* @return 包裝後的 DelegatingSecurityContextAsyncTaskExecutor 實例
*/
@Bean("delegateTaskExecutor2")
public DelegatingSecurityContextAsyncTaskExecutor delegateTaskExecutor2(
@Qualifier("asyncExecutor2") ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor) {
return new DelegatingSecurityContextAsyncTaskExecutor(threadPoolTaskExecutor);
}
// Custom TaskDecorator for copying SecurityContext and RequestContext
/**
* {@code ContextCopyingTaskDecorator}:複製與還原執行緒上下文的 {@link TaskDecorator} 實作。
*
* 此裝飾者會在非同步任務執行前,複製目前的 {@link SecurityContext} 與
* {@link RequestAttributes} 並設定到執行緒中,任務結束後則會清除並還原相關上下文,
* 以確保執行緒安全與避免上下文遺漏。
*
* @author Lewis
* @since 2024
*/
@SuppressWarnings("null")
static class ContextCopyingTaskDecorator implements TaskDecorator {
@Override
public Runnable decorate(Runnable runnable) {
SecurityContext securityContext = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
return () -> {
try {
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(securityContext); // Restore SecurityContext
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes); // Restore RequestContext
runnable.run();
} finally {
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext(); // Clear context after execution
RequestContextHolder.resetRequestAttributes(); // Reset RequestAttributes
}
};
}
}
}
2.提供通用的非同步執行機制與服務(AsyncGenericService)
1.一般沒有@Async 設定的Method,利用 Reflect方法提供通用的非同步執行機制與服務。
2.快速任務使用專用線程池(genericAsyncExecutor1),如需要低延遲的快速響應任務、API 調用、數據查詢等
3.耗時任務使用專用線程池(genericAsyncExecutor2) 批處理任務、郵件發送、文件導出等耗時作業。
**新增AsyncGenericService.java 於 tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async package。
package tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* 非同步通用服務類
*
* 提供通用的非同步執行機制,支援透過反射動態呼叫任意類別的方法。
* 本服務包含兩個獨立的線程池執行器,可根據不同需求選擇使用。
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class AsyncGenericService {
/**
* Fix for javadoc warning :
* use of default constructor, which does not provide a comment
* Constructs a new AsyncGenericService instance.
* This is the default constructor, implicitly provided by the compiler
* if no other constructors are defined.
*/
public AsyncGenericService() {
// Constructor body (can be empty)
}
/**
* 通用非同步執行器 1
*
* 使用 delegateTaskExecutor1 線程池執行非同步任務。
* 透過反射機制動態建立指定類別的實例,並呼叫指定的方法。
*
* @param class1 要執行方法的類別
* @param asyncMethod 要執行的方法物件
* @param cArg 方法的參數陣列
* @return CompletableFuture 包含方法執行結果的 Future 物件
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes" })
@Async("delegateTaskExecutor1")
public CompletableFuture<Object> genericAsyncExecutor1(Class class1, Method asyncMethod, Object... cArg) {
return doGenericAsyncJob(class1, asyncMethod, cArg);
}
/**
* 通用非同步執行器 2
*
* 使用 delegateTaskExecutor2 線程池執行非同步任務。
* 透過反射機制動態建立指定類別的實例,並呼叫指定的方法。
*
* @param class1 要執行方法的類別
* @param asyncMethod 要執行的方法物件
* @param cArg 方法的參數陣列
* @return CompletableFuture 包含方法執行結果的 Future 物件
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
@Async("delegateTaskExecutor2")
public CompletableFuture<Object> genericAsyncExecutor2(Class class1, Method asyncMethod, Object... cArg) {
return doGenericAsyncJob(class1, asyncMethod, cArg);
}
/**
* 執行通用非同步工作的核心方法
*
* 使用反射機制完成以下步驟:
* 1. 透過無參構造子建立指定類別的實例
* 2. 使用指定方法和參數呼叫該實例
* 3. 將結果包裝成 CompletableFuture 返回
*
* 執行過程中發生異常,會擷取原始異常原因並透過 failedFuture 返回。
* 若代理的方法拋出異常,會被包裝在 InvocationTargetException 中,
* 因此需要透過 getCause() 取得並回傳實際的異常。
*
* @param class1 要執行方法的類別
* @param asyncMethod 要執行的方法物件
* @param cArg 方法的參數陣列
* @return CompletableFuture 包含方法執行結果或異常的 Future 物件
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
private CompletableFuture<Object> doGenericAsyncJob(Class class1, Method asyncMethod, Object... cArg) {
try {
Constructor<?> constructor = class1.getConstructor();
Object instance = constructor.newInstance();
Object result = asyncMethod.invoke(instance, cArg);
// System.out.println("Result: " + result);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(result);
} catch (Exception ex) {
// 這裡會是 InvocationTargetException , 所以要 getCause 程式傳出的 Exception
return CompletableFuture.failedFuture(ex.getCause());
}
}
}
3.提供使用 Spring 的 @Async 支援的非同步任務執行範例(AsyncServiceWorkerSample)非同步任務執行範例
設計使用Loop非同步任務執行不同參數的相同@Async Method 範例(設定產生 Exception),並確認全部完成以及取得執行結果。
設計使用兩個不同@Async Method 範例,測試程式將兩個不同Method非同步任務執行,並確認完成以及取得執行結果。
設計使用有需要SecurityContext以及RequestAttributes的@Async Method 範例。
**新增AsyncServiceWorkerSample.java 於 tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async.worker package(如package不存在,請新增)
package tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async.worker;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* AsyncServiceWorkerExample 提供非同步任務執行範例,使用 Spring 的 @Async 支援。
*
* 本類別示範如何透過指定執行緒池 delegateTaskExecutor1 來非同步執行任務,
* 並以 CompletableFuture 回傳結果或例外。
*
*
* <ul>
* <li>當 seq 參數為 6 時,會拋出 RuntimeException。</li>
* <li>隨機睡眠 0 或 1 秒後,將隨機值附加至 message。</li>
* <li>所有執行過程皆有日誌記錄。</li>
* </ul>
*
* @author (your name or team)
* @since 1.0
*/
@Slf4j
@Service
public class AsyncServiceWorkerSample {
/**
* Fix for javadoc warning :
* use of default constructor, which does not provide a comment
* Constructs a new AsyncServiceWorkerSample instance.
* This is the default constructor, implicitly provided by the compiler
* if no other constructors are defined.
*/
public AsyncServiceWorkerSample() {
// Constructor body (can be empty)
}
// private final ThreadPoolExecutor executor = (ThreadPoolExecutor)
// Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
/**
* 非同步執行指定任務,使用 delegateTaskExecutor1 執行緒池。
*
* @param message 傳入訊息字串
* @param seq 序號
* @return CompletableFuture 包含處理結果的 CompletableFuture
* @throws java.lang.RuntimeException 當 seq 為 6 時拋出例外
*/
@Async("delegateTaskExecutor1")
public CompletableFuture<String> asyncFunction1(String message, int seq) {
try {
if (seq == 6) {
log.info("do something, exception {}", seq);
throw new RuntimeException("test failed for 6");
}
Random rand = new Random(); // instance of random class
int upperBound = 2;
int intRandom = rand.nextInt(upperBound);
Thread.sleep(1000 * intRandom);
message = message + "=" + Integer.toString(intRandom);
log.info("do something, message{}", seq);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(message);
} catch (Exception ex) {
return CompletableFuture.failedFuture(ex);
}
}
/**
* asyncFunction2
* @return CompletableFuture Integer
*/
@Async("delegateTaskExecutor1")
public CompletableFuture<Integer> asyncFunction2(int intNumber) {
// Access ThreadLocal values from the parent thread
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder
.getRequestAttributes();
if (requestAttributes != null) {
String requestId = requestAttributes.getRequest().getHeader("X-Request-ID");
System.out.println("Async thread - Request ID: " + requestId);
}
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication != null) {
System.out.println("Async thread - Authenticated user: " + authentication.getName());
}
// Simulate another long-running task
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return CompletableFuture.failedFuture(ex);
}
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(intNumber);
}
/**
* asyncFunction21
* @return CompletableFuture Object
*/
@Async("delegateTaskExecutor2")
public CompletableFuture<Object> asyncFunction21(String message) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return CompletableFuture.failedFuture(ex);
}
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(message);
}
/**
* asyncFunction21
* @return CompletableFuture Object
*/
@Async("delegateTaskExecutor1")
public CompletableFuture<Object> asyncFunction22(String message) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return CompletableFuture.failedFuture(ex);
}
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(message);
}
}
4.提供支援動態調用任意類別方法(沒有@Async 或一般專案外的Method)支援非同步任務執行範例的範例(GenericClassForAsyncSample)
設計一般沒有 Throw Exception的 Method 非同步執行範例,並確認全部完成以及取得執行結果。
設計一般回傳 Throw Exception的 Method 非同步執行範例,並確認全部完成以及取得執行結果。。
** 新增AsyncGenericClassSample.java 於 tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async.worker package(如package不存在,請新增)
package tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async.worker;
import java.util.Random;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* GenericClassForAsyncSample 是一個用於非同步操作範例的通用類別。
*
* 這個類別提供了兩個方法來演示不同的例外處理策略:
*
* 1. doNoThrowsMethod: Method 捕獲例外沒有 throws Exception
* 2. doThrowsMethod: Method 捕獲例外後 throws Exception
*
*/
@Slf4j
public class AsyncGenericClassSample {
/**
* Fix for javadoc warning :
* use of default constructor, which does not provide a comment
* Constructs a new AsyncServiceWorkerSample instance.
* This is the default constructor, implicitly provided by the compiler
* if no other constructors are defined.
*/
public AsyncGenericClassSample() {
// Constructor body (can be empty)
}
/**
* Method 捕獲例外沒有 throws Exception
*
* @param message test Message
* @param seq runseq
* @return a String Object
*/
public String doNoThrowsMethod(String message, int seq) {
try {
if (seq == 6) {
log.info("do something, exception {}", seq);
throw new RuntimeException("test failed for 6");
}
Random rand = new Random(); // instance of random class
int upperBound = 2;
int intRandom = rand.nextInt(upperBound);
Thread.sleep(1000 * intRandom);
message = message + "=" + Integer.toString(intRandom);
log.info("do something, message{}", seq);
return message;
} catch (Exception ex) {
return ex.toString();
}
}
/**
* Method 捕獲例外後 throws Exception
*
* @param message test Message
* @param seq runseq
* @return a String Object
* @throws RuntimeException RuntimeException
*/
public String doThrowsMethod(String message, int seq) throws RuntimeException {
try {
if (seq == 6) {
log.info("do something, exception {}", seq);
throw new RuntimeException("test failed for 6");
}
Random rand = new Random(); // instance of random class
int upperBound = 2;
int intRandom = rand.nextInt(upperBound);
Thread.sleep(1000 * intRandom);
message = message + "=" + Integer.toString(intRandom);
log.info("do something, message{}", seq);
return message;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("test failed for 6");
}
}
}
** 測試 Spring 的 @Async 支援的非同步任務執行範例.
**新增 .java 於單元測試目錄(src/test/java) tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async.worker 的 package
package tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async.worker;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.security.task.DelegatingSecurityContextAsyncTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.test.context.TestPropertySource;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.async.DeferredResult;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncTask;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
//啟動SpringBootTest
@SpringBootTest
// 指定適用Properties (這裡指定專案的properties 檔案,已可以另外指定 test專用的properties 檔案)
@TestPropertySource(locations = "classpath:application.properties")
public class AsyncServiceWorkerTest {
@Autowired
private AsyncServiceWorkerSample asyncServiceWorkerSample;
@Test
void testAsyncServiceWorker() {
List<String> callString = new ArrayList<>();
int count = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
callString.add("Msg" + i);
}
// 依據 service程序回傳的指定資料型別
ArrayList<CompletableFuture<String>> completableFutures = new ArrayList<>();
// submit service
for (int i = 0; i < callString.size(); i++) {
try {
completableFutures.add(asyncServiceWorkerSample.asyncFunction1(callString.get(i), i));
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 確認所有程序都返回 (但不表示全部正常結束)
CompletableFuture.allOf(completableFutures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0]))
// avoid throwing an exception in the join() call
.exceptionally(ex -> null)
.join();
// 收集return 值
// 指定 isCompletedExceptionally
// 所以 若程序有 Exception 的 result map 為 true;
// 所以 若程序沒有 Exception 的 result map 為 false;
Map<Boolean, List<CompletableFuture<String>>> result = completableFutures.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(CompletableFuture::isCompletedExceptionally));
result.forEach((k, clist) -> {
System.out.println("k = " + k);
for (CompletableFuture<String> rtnString : clist) {
System.out.println(rtnString);
}
});
// 依據 service程序回傳的指定資料型別
// for (Map.Entry<Boolean, List<CompletableFuture<RoomTypes.RoomType>>> entry :
// result.entrySet()) {
for (Map.Entry<Boolean, List<CompletableFuture<String>>> entry : result.entrySet()) {
// 沒有exception的是 false 的 map , 有exception 是 true 的 map
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
entry.getValue().forEach(x -> {
try {
System.out.println(x.get());
} catch (Exception ex) {
// ex.printStackTrace();
System.err.println("Caught exception: " + ex.getMessage());
}
});
}
}
@Test
void testMultipleAsyncFunctions() {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = asyncServiceWorkerSample.asyncFunction2(123);
CompletableFuture<Object> future2 = asyncServiceWorkerSample.asyncFunction21("Messages1");
try {
// Wait for both futures to complete
CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2).join();
Integer result1 = future1.get();
String result2 = (String) future2.get();
System.out.println("Combined Results: " + result1 + ", " + result2);
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Exceptional Future completed future1: " + future1.isCompletedExceptionally());
System.out.println("Exceptional Future completed future2: " + future2.isCompletedExceptionally());
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Total execution time: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
@Test
void testMultipleAsyncFunctions2() {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ArrayList<CompletableFuture<Object>> completableFutures = new ArrayList<>();
try {
completableFutures.add(asyncServiceWorkerSample.asyncFunction22("Messages22"));
completableFutures.add(asyncServiceWorkerSample.asyncFunction21("Messages21"));
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
// 確認所有程序都返回 (但不表示全部正常結束)
CompletableFuture.allOf(completableFutures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0]))
// avoid throwing an exception in the join() call
.exceptionally(ex -> null)
.join();
// 收集return 值 (需要反向思考, )
// 指定 isCompletedExceptionally
// 所以 若程序有 Exception 的 result map 為 true;
// 所以 若程序沒有 Exception 的 result map 為 false;
Map<Boolean, List<CompletableFuture<Object>>> result = completableFutures.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(CompletableFuture::isCompletedExceptionally));
result.forEach((k, clist) -> {
System.out.println("k = " + k);
for (CompletableFuture<Object> resultObject : clist) {
System.out.println(resultObject);
}
});
// 依據 service程序回傳的指定資料型別
// for (Map.Entry<Boolean, List<CompletableFuture<RoomTypes.RoomType>>> entry :
// result.entrySet()) {
for (Map.Entry<Boolean, List<CompletableFuture<Object>>> entry : result.entrySet()) {
// 沒有exception的是 false 的 map , 有exception 是 true 的 map
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
entry.getValue().forEach(x -> {
try {
System.out.println(x.get());
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Total execution time: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
@Autowired // 不指定@Qualifier 自動使用 asyncExecutor1
private @Qualifier("delegateTaskExecutor1") DelegatingSecurityContextAsyncTaskExecutor delegateTaskExecutor;
@Autowired // 不指定@Qualifier 自動使用 asyncExecutor1
private @Qualifier("asyncExecutor1") ThreadPoolTaskExecutor asyncExecutor1;
@Test
void logThreadPoolStatus() {
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = asyncServiceWorkerSample.asyncFunction1("message",1);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = asyncServiceWorkerSample.asyncFunction2(2);
try {
// Wait for both futures to complete
System.out.println("Active Threads: " + asyncExecutor1.getActiveCount());
System.out.println("Pool Size: " + asyncExecutor1.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("Core Pool Size: " + asyncExecutor1.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("Max Pool Size: " + asyncExecutor1.getMaxPoolSize());
System.out.println("Queue Size: " +
asyncExecutor1.getThreadPoolExecutor().getQueue().size());
System.out.println("Queue remainingCapacity: " +
asyncExecutor1.getThreadPoolExecutor().getQueue().remainingCapacity());
System.out.println("Available Threads: " + (asyncExecutor1.getMaxPoolSize() -
asyncExecutor1.getActiveCount()));
CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2).join();
String result1 = future1.get();
Integer result2 = future2.get();
System.out.println("Combined Results: " + result1 + ", " + result2);
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
// // https://www.51cto.com/article/797053.html
/**
* 使用 CompletableFuture 進行異步執行
*
* @return CompletableFuture<String> 異步執行的結果
* @throws InterruptedException 如果線程被中斷
*/
@Test
public void asyncTaskWithCompletableFuture() {
try {
int delay = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1000, 5000); // 隨機生成執行延遲時間
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(delay); // 模擬執行時間
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // 中斷狀態
}
return "使用 CompletableFuture 執行完成,耗時 " + delay + " 毫秒";
});
CompletableFuture.allOf(future1).join();
String result1 = future1.get();
System.out.println(result1);
System.out.println("end of method");
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 使用 WebFlux 進行異步執行
*
* @return Mono<String> 異步執行的結果
*/
@Test
public void asyncTaskWithWebFlux() {
try {
Mono<String> future1 = Mono.fromCallable(() -> {
int delay = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1000, 5000); // 隨機生成執行延遲時間
Thread.sleep(delay); // 模擬執行時間
return "使用 WebFlux 執行完成,耗時" + delay + " 毫秒";
}).delayElement(Duration.ofMillis(1000)) // 加入延遲以模擬執行
.doOnSuccess(i -> System.out.println("Success"));
Mono<String> future2 = Mono.fromCallable(() -> {
int delay = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1000, 5000); // 隨機生成執行延遲時間
Thread.sleep(delay); // 模擬執行時間
return "使用 WebFlux 執行完成,耗時" + delay + " 毫秒";
}).delayElement(Duration.ofMillis(1000)) // 加入延遲以模擬執行
.doOnSuccess(i -> System.out.println("Success"));
String result2 = future2.block(); // wait Mono.fromCallable completed
System.out.println("Received: " + result2);
String result = future1.block(); // wait Mono.fromCallable completed
System.out.println("Received: " + result);
// // Add a side-effect with doOnNext to process the emitted data
// future1.doOnNext(result1 -> {
// System.out.println("Processing result with doOnNext on thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// System.out.println("Received: " + result1);
// });
// future1.subscribe(
// value -> System.out.println("Received: " + value), // Consumer for the emitted value
// error -> System.err.println("Error: " + error.getMessage()), // Consumer for errors
// () -> System.out.println("Completion Signal") // Runnable for completion
// );
System.out.println("end of method");
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 使用 WebAsyncTask 進行異步執行
*
* @return WebAsyncTask<String> 異步執行的結果
*/
@Test
public void asyncTaskWithWebAsyncTask() {
try {
Callable<String> callable = () -> {
int delay = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1000, 5000); // 隨機生成執行延遲時間
Thread.sleep(delay); // 模擬執行時間
return "使用 WebAsyncTask 執行完成,耗時 " + delay + " 毫秒";
};
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = asyncExecutor1;
System.out.println("ThreadPoolTaskExecutor: " + executor);
// ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Future<String> future = executor.submit(callable);
String result = future.get(); // wait Callable completed
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
WebAsyncTask<String> future1 = new WebAsyncTask<>(callable); // 返回 WebAsyncTask
String result1 = (String) future1.getCallable().call(); // wait WebAsyncTask completed
System.out.println("Result: " + result1);
System.out.println("end of method");
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 使用 DeferredResult 進行異步執行
*
*
* @return DeferredResult<String> 異步執行的結果
*/
@SuppressWarnings("null")
@Test
public void asyncTaskWithDeferredResult() {
try {
DeferredResult<String> deferredResult = new DeferredResult<>();
asyncExecutor1.submit(() -> {
try {
int delay = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1000, 5000); // 隨機生成執行延遲時間
Thread.sleep(delay); // 模擬執行時間
deferredResult.setResult("使用 DeferredResult 執行完成,耗時 " + delay + " 毫秒");
String result1 = deferredResult.getResult().toString();
System.out.println(result1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // 中斷狀態
deferredResult.setErrorResult("發生錯誤"); // 回傳發生錯誤訊息
}
});
while (deferredResult.getResult() == null ){
Thread.sleep(100); // 等待結果完成
}
System.out.println("end of method");
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
** 測試 動態調用任意類別方法(沒有@Async 或一般專案外的Method)支援的非同步任務執行範例.
**新增 AsyncGenericClassTest.java 於單元測試目錄(src/test/java) tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async.worker 的 package
package tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async.worker;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.TestPropertySource;
import tw.lewishome.webapp.base.async.AsyncGenericService;
import tw.lewishome.webapp.base.utility.common.ReflectUtils;
@SpringBootTest
@TestPropertySource(locations = "classpath:application.properties")
public class AsyncGenericServiceTest {
@Autowired
AsyncGenericService asyncGenericService;
@Test
public void testAsyncGenericServiceNoThrows() {
// Test code for AsyncGenericService here for no exception throws method
try {
// 準備 非同步執行的 Class
AsyncGenericClassSample genericClassForAsync = new AsyncGenericClassSample();
// 準備 非同步執行的 Class Method
Method method = ReflectUtils.getAccessibleMethod(genericClassForAsync, "doNoThrowsMethod", String.class,int.class);
// return Type 也應該知道,如果程式需要也可以取得 Return Type
Type genericReturnType1 = method.getGenericReturnType();
System.out.println("Generic Return Type: " + genericReturnType1.getTypeName());
// 準備收集Async執行的結果,使用通用Object取得 Value
ArrayList<CompletableFuture<Object>> completableFutures = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Object[] callArg = new Object[2]; // 參數個數
callArg[0] = "TestMessage" + i; // 參數 1
callArg[1] = i; // 參數 2
completableFutures.add(asyncGenericService.genericAsyncExecutor2(genericClassForAsync.getClass(), method, callArg));
}
// 確認(等待)所有程序都返回 (但不表示全部正常結束)
CompletableFuture.allOf(completableFutures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0]))
// avoid throwing an exception in the join() call
.exceptionally(ex -> null)
.join();
// 收集return 值 , 指定 isCompletedExceptionally
// 因為 method 沒有 Throws Exception ,代理程式不會回傳 CompletableFuture.failedFuture
// 所以不會有 isCompletedExceptionally = true ( 沒有 Exceptuon)
System.out.println("Collecting results...");
Map<Boolean, List<CompletableFuture<Object>>> result = completableFutures.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(CompletableFuture::isCompletedExceptionally));
result.forEach((k, clist) -> {
System.out.println("k = " + k);
for (CompletableFuture<Object> rtnValue : clist) {
try {
System.out.println((String) rtnValue.get());
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
// 依據 service 程序回傳的指定資料型別 (No Exception Success)
List<CompletableFuture<Object>> listResultSuccess = result.get(false);
for (CompletableFuture<Object> resultSeccess : listResultSuccess) {
System.out.println(resultSeccess);
}
// 依據 service 程序回傳的指定資料型別 (throws Exception failed)
// 因為 method 沒有 Throws Exception ,代理程式不會回傳 CompletableFuture.failedFuture
// 所以不會有 isCompletedExceptionally = true ( 沒有 Exceptuon)
List<CompletableFuture<Object>> listResultFailed = result.get(true);
for (CompletableFuture<Object> resultFailed : listResultFailed) {
System.out.println(resultFailed);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void testAsyncGenericServiceThrows() {
// Test code for AsyncGenericService here for no exception throws method
try {
// 準備 非同步執行的 Class
AsyncGenericClassSample genericClassForAsync = new AsyncGenericClassSample();
// 準備 非同步執行的 Class Method
Method method = ReflectUtils.getAccessibleMethod(genericClassForAsync, "doThrowsMethod", String.class,int.class);
ArrayList<CompletableFuture<Object>> completableFutures = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Object[] cArg = new Object[2];
cArg[0] = "TestMessage" + i;
cArg[1] = i;
completableFutures.add(asyncGenericService.genericAsyncExecutor2(genericClassForAsync.getClass(), method, cArg));
}
// 確認所有程序都返回 (但不表示全部正常結束)
CompletableFuture.allOf(completableFutures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0]))
// avoid throwing an exception in the join() call
.exceptionally(ex -> null)
.join();
// 收集return 值
// 指定 isCompletedExceptionally
// 所以 若程序有 Exception 的 result map 為 true;
// 所以 若程序沒有 Exception 的 result map 為 false;
System.out.println("Collecting results...");
Map<Boolean, List<CompletableFuture<Object>>> result = completableFutures.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(CompletableFuture::isCompletedExceptionally));
result.forEach((k, clist) -> {
System.out.println("k = " + k);
for (CompletableFuture<Object> rtnValue : clist) {
try {
System.out.println((String) rtnValue.get());
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.err.println("Caught exception: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
**1. 因為非同步執行,沒有執行完成的順序會不一定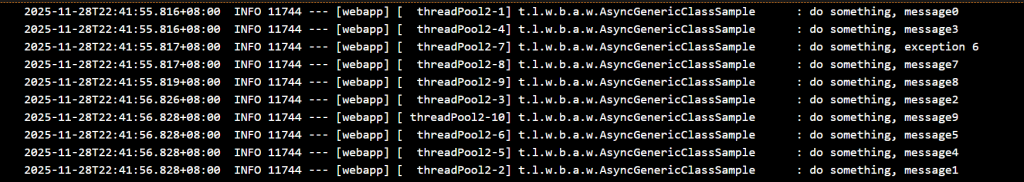
**2. 收集結果,可以查看9個執行完成成功,1 個執行完成失敗。