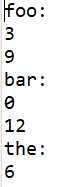我在寫一個演算法題目 其中我自己寫了個class用來封裝資料
且覆寫了比較的方法,卻不太明白問題出在哪裡
因為我直接實驗在main方法中是可以成功的
class StringIndexAndLen
{
public int index=-1;
public int len=-1;
public StringIndexAndLen(int i,int l)
{
index=i;
len=l;
}
}
其中 我希望依照index的值給陣列排序大小
這個程式我有寫成遞迴,但是 我通過打印出來確定陣列的值是正確的
但當一排序後就會有未知的數字
Arrays.sort(infoArray,(n1,n2)->n1.index-n2.index);
int count=0;
System.out.print("start:");
for(;count<infoArray.length;count++)
{
System.out.print(infoArray[count].index+" ");
}
System.out.print("end\n");
排序前:
ex1:start:3 0 6 end
ex2:start:3 12 6 end
排序後
ex1:start:0 3 6 end
ex2:start:0 6 12 end
若你希望實驗看看
public class SubstringwithConcatenationofAllWords {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution sol=new Solution();
String s = "barfoothefoobarman";
String[]words = new String[]{"foo","bar","the"};
sol.findSubstring(s, words);
}
}
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findSubstring(String s, String[] words) {
List<Integer>ans=new ArrayList<Integer>();
indexRecur(0,new StringIndexAndLen[words.length],ans,s,words);
return ans;
}
void indexRecur(int index,StringIndexAndLen[]infoArray,List<Integer>ans,String s, String[] words)
{
if(index==words.length)
{
//Arrays.sort(infoArray,(n1,n2)->n1.index-n2.index);
System.out.print("start:");
for(int count=0;count<infoArray.length;count++)
{
System.out.print(infoArray[count].index+" ");
}
System.out.print("end\n");
}
else
{
//CAN HELP
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
{
i=s.indexOf(words[index],i);
if(i==-1)
break;
infoArray[index]=new StringIndexAndLen(i,words[index].length());
indexRecur(index+1,infoArray,ans,s,words);
}
}
}
}
class StringIndexAndLen
{
public int index=-1;
public int len=-1;
public StringIndexAndLen(int i,int l)
{
index=i;
len=l;
}
}

日安, 可以理解成你想要的Print的產出是這樣嗎
start:0 3 6 end
start:3 6 12 end
start:0 6 9 end
start:6 9 12 end
如果是的話 問題不在排序上, 而是排序後的流程, 因為排序完之後你的infoArray還會被拿來做後續的行為, 造成結果從第二組開始就不是你想要的結果
你可以試著在Sort之前把infoArray先Copy出來, 再做Sort, 並比較第二組start的運作狀態
如果還是有疑問, 思考看看index在sort前後的的改變跟他代表的意義, 或是先把單詞改成2,3,4這種不同長度的字串再看看infoArray呼叫時的變化
一、編碼風格混亂
Java 的括號是
method() {
}
而非
method()
{
}
都一致也罷
你的程式居然有兩套風格
看了非常頭疼
二、debug 能力不足
你說
但當一排序後就會有未知的數字
可是測出來並非排序的問題
簡單打印就知道
System.out.print("before: ");
for (StringIndexAndLen a : infoArray) {
System.out.print(a.index + " ");
}
System.out.println();
Arrays.sort(infoArray,(n1,n2)->n1.index-n2.index);
System.out.print("after: ");
for (StringIndexAndLen a : infoArray) {
System.out.print(a.index + " ");
}
System.out.println();
解 bug 的第一步要正確鎖定 bug 在哪!
三、未說明意圖
導致我們即使看了你整段程式碼,仍不懂你想要幹嘛
目前看到
這裡會出現矛盾,多對多怎麼知道誰是誰?
更不用說你排序了,這串 index 基本上無意義
因此說明目的非常重要
因為新手往往一開始就想錯了
後面就一路歪下去
你這個情況需要貼出題目
以及你的思路、步驟等
而不是只有說「排序」
四、改良實作
這是假設你要查出一組字詞各自在字串中的 index
public class SubstringwithConcatenationofAllWords {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution sol = new Solution();
String s = "barfoothefoobarman";
String[] words = new String[] { "foo", "bar", "the" };
// sol.findSubstring(s, words);
Test test = new Test();
Map<String, List<Integer>> result = test.findSubstring(s, words);
for (String word : words) {
System.out.println(word + ":");
List<Integer> indexList = result.get(word);
for (Integer index : indexList) {
System.out.println(index);
}
}
}
}
class Test {
public Map<String, List<Integer>> findSubstring(String string, String[] words) {
Map<String, List<Integer>> result = new HashMap<String, List<Integer>>();
for (String word : words) {
List<Integer> indexList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int index = string.indexOf(word);
while (index >= 0) {
indexList.add(index);
index = string.indexOf(word, index + 1);
}
Collections.sort(indexList);
result.put(word, indexList);
}
return result;
}
}
結果: