前一章談到了 Mustache 標籤: 可以把實體的資料響應在頁面上的 {{}} ,這次來看看另一個語法 Directives 。
Directive 使用起來像是 HTML 的 Attributes ,相較於 Mustache 標籤只是單純的取代頁面上的區塊, Directives 的設定會影響 DOM 本身,使 DOM 元素因響應造成 Attributes 或是渲染上的變化。
Directives 的配置會像是 DOM 元素標籤中的 name 、 id 、 class ... 等,跟 {{}} 放在 DOM 元素下層的方式不同, Directives 是放在元素中:
<div id="app">
{{a}} <!-- under the #app -->
<button v-on:click="a++">+</button> <!-- inside of the button tag -->
</div>
上面的例子中 v-on 就是個 Directives , v-on 的功能是可以把 Vue 實體中的 Methods 或是 JavaScript 陳述式使用在某個事件上。
{{a}} : 直接在 <div id="app"> 中,當作 <div id="app"> innerHTML 的一部分。v-on:click="a++" : 在 <button> 內,當作 <button> 的 Attributes 。Directives 的名稱為了跟一般的 Attribues 作區別,都會以 v- 為前綴字,上節的 v-on 或是前一篇文章說到的 v-once 都是 Directives 。
Directives 的數值跟 Mustache 相同是一個 JavaScript 的陳述式( v-for 的語法較為特別,之後的章節會介紹),同樣可以用 return [expression] 的方式驗證正確性。
Directives 可以使頁面渲染的方式依照相關的設置改變,像是 v-if 決定是否渲染元素、 v-for 重複渲染相同元素...等,也可以當作 Attributes 的值,像是 v-bind 、v-on 綁定屬性及事件,接下來會簡介幾個不同功能的 Directives ,從中介紹相關的特性。
v-html 會將資料當作 HTML 做渲染:
var vm = new Vue({
...
data: {
...
html: '<h1>I am header</h1>'
}
});
<div id="app">
...
<div>{{html}}</div>
<div v-html="html"></div>
</div>
{{html}} : Mustache 標籤會將 html 資料當作字串輸出。v-html="html" : 它會將 html 資料設置給此元素( <div> )的 innerHTML,所以渲染完成的頁面會是 <div><h1>I am header</h1></div> 。
v-html中設置的 HTML 是直接設置在 HTML 上,不會經過編譯器,所以不能設置 Vue 的模板語法。
Vue 其實不鼓勵直接改變 HTML ,如果使用到 v-html 可以想想是否可以包成 Components 。
可以使用 v-if 來決定是否要渲染元素:
<div id="app">
...
<div v-if="condition">render</div>
<div v-if="!condition">never render</div>
</div>
condtion 為 true 的情況下,渲染結果如下:
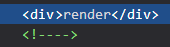
v-if 為 false 的元素會變為 而不會渲染出來。
假設要依照資料綁定到 DOM 的 Attributes 上,學過上一章的 Mustache 標籤,大家可能會想要像下面這樣寫:
<div id="app">
...
<div id="{{id}}">Mustache</div>
</div>
這其實是錯誤的,它會被當作一般的字串渲染出來(像是這樣: <div id="{{id}}">Mustache</div> ),這是因為只要不是 Vue 的 Directives ,其他的都會被 Vue 所忽略,所以要綁定像是 name 、 id 等的元素 Attributes ,需要使用 v-bind :
<div id="app">
...
<div v-bind:id="id">Bind Directives</div>
</div>
看到 v-bind , Vue 就會知道這個 Attribute 要抓取實體上的 id 做渲染。
這裡要注意的是如果綁定的值是布林值的話,如果是 null 、 undefined 或是 false 的話,此 Attribute 就不會被渲染出來,如下的例子:
<div id="app">
...
<button v-bind:disabled='isDisabled'>I am disabled</button>
</div>
如果 isDisabled 是 false 的話,按鈕會被渲染成:
<button>I am disabled</button>
當要在 <button> 或是其他元素上綁定事件時,我們會使用 v-on 來綁定,看一個常見的例子:
var vm = new Vue({
...
data: {
b: 10000,
...
},
methods: {
click() {
this.b--;
}
}
});
<div id="app">
...
<div>
<span>{{b}}</span>
<button v-on:click.once='click'>b--</button>
</div>
</div>
這裡 v-on:click.once 綁定了實體中的 click 方法,所以按下按鈕後, b 會減一,但是後面加了 once 這個修飾符,代表這個事件只能被叫用一次,所以減了一次之後就不會在叫用此事件了。
上面的例子中我們看到了幾個不同的配置方式:
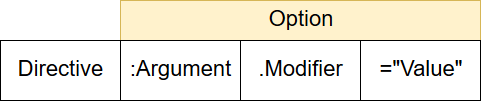
每個 Directives 的配置會有所不同,從最簡單只有 Directive 本身到加上 Argument 及 Modifier 的 Directive:Argument.Modifier="Value" 都有,下面會一一介紹。
將此 Directive 作用在元素上,像是 v-once 是將只渲染一次的效果作用在元素上。
依照 Value 將此 Directive 的效果作用在元素上,像是 v-html="html" 是將 html 的值寫入 innerHTML 。
依照 Value 將此 Directive 作用在 Argument 上,例如 v-bind:id="id" 是將 id 的值綁定到 id Attribute 上。
依照 Value 將此 Directive 依照 Modifier 設定的特殊方式作用在 Argument 上,像是 v-on:click.once="click" 是將實體中的 click 事件依照只作用一次的條件綁定到元素的 click 事件上。
在撰寫模板的時候,我們會需要大量的使用 v-bind 及 v-on 來綁定 Attribute 及事件,因此 Vue 給這兩個 Directives 縮寫,以減少開發上要寫的代碼數量。
<!-- 一般寫法 -->
<button v-bind:disabled='isDisabled'>I am disabled</button>
<!-- 簡寫 -->
<button :disabled='isDisabled'>I am disabled</button>
v-bind 使用 : 當作簡寫。
<!-- 一般寫法 -->
<button v-on:click.once='click'>b--</button>
<!-- 簡寫 -->
<button @click.once='click'>b--</button>
v-on 使用 @ 當作簡寫。
這一章剛開始先介紹 Directives 它的功用以及如何設置,再來用不同的範例演示在不同情況下要使用的 Directives 有哪些,接著在統整出它的配置方式,使我們對 Directives 有個通盤的了解,最後介紹 Vue 為了開發者方便而釋出的縮寫方法。
從昨天介紹的 Mustache 到今天的 Directive ,模板語法跳脫不了這兩個東西,可是 Directives 的種類繁多,在這兩章我們學會配置後,後面的篇章會以不同功用的語法分章節做細部的講解。
