Vue 提供了監聽器,當資料變化時叫用函數,函數會有兩個傳入參數: 改變前的值、改變後的值,可以使用這個函數做跟此資料變化有關的處理。
監聽器在 Vue.js 中有兩種使用方式:
$watch : 實體上的函數,使用此函數註冊監聽器。watch : 實體上的屬性,此屬性設置的物件在實體建立時會叫用 $watch 註冊監聽器。$watch 是註冊監聽器的函數,而 watch 是為了開發者方便在實體上設置監聽器而提供的,其實 watch 本身也是使用 $watch 註冊監聽器。
接下來讓我們來看看如何使用這兩種方式設置監聽器。
unwatch = vm.$watch(expOrFn, callback, [options] )
$watch 的回傳值是註銷監聽器的函數,執行此函數可使監聽器失效。
expOrFn : 設定要監聽的目標,可以使用 JavaScript 表達式或是一個回傳監聽目標值的函數。callback : 當數值改變時要叫用的函數,此函數會有兩個傳入參數: callback(newVal, oldVal) 。
newVal : 改變後的資料值。oldVal : 改變前的資料值。[options] : 非必要參數,監聽器的設定。
deep : 監聽物件時,物件的下層屬性變化也會觸發監聽器。immediate : 在實體初始化設置監聽器的時候會馬上叫用 callback 函數。
expOrFn參數中使用的 JavaScript 表達式只能是以逗點分隔的物件路徑,像是a.b.c,如果需要監聽更複雜的表達式可以使用函數。
callback函數中如果要使用this,則不能使用 arrow funciton 。
var vm = new Vue({
...
data: {
a: 1,
newA: 0,
oldA: 0
}
});
vm.$watch('a', function(newA, oldA) {
this.newA = newA;
this.oldA = oldA;
});
<div id="app">
<button @click="a++">+</button>
<button @click="a--">--</button>
<div>a: {{a}}</div>
<div>changed: {{newA}}</div>
<div>before change: {{oldA}}</div>
</div>
按下 + / - 按紐時, $watch 會去更新 newA 及 oldA ,在畫面上會看到 {{newA}} 總會跟 a 相同,而 {{oldA}} 會是 a 改變之前的值。
var vm = new Vue({
...
data: {
...
b: {
c: {
d: 1
}
},
newD: 0,
oldD: 0,
}
});
...
vm.$watch('b.c.d', function(newD, oldD) {
this.newD = newD;
this.oldD = oldD;
});
跟前一個例子相同的功能,只是這次監聽的值在物件裡面,使用表達式 b.c.d 就可以監聽 d 屬性。
假設有個需求是只要物件下的其中一個屬性值改變,就要觸發監聽器,為此需要在 $watch 的第三個參數 [options] 加上 deep: true 的設定,讓監聽器知道要監聽下層的屬性。
var vm = new Vue({
...
data: {
...
b: {
c: {
d: 1,
e: 1,
}
},
newD: 0,
oldD: 0,
newB: {},
oldB: {},
}
});
...
vm.$watch('b', function(newB, oldB) {
this.newB = newB;
this.oldB = oldB;
}, {
deep: true
});
<div id="app">
...
<div>
<button @click="b.c.d++">+</button>
<button @click="b.c.d--">-</button>
<div>b.c.d: {{b.c.d}}</div>
<button @click="b.c.e++">+</button>
<button @click="b.c.e--">-</button>
<div>b.c.d: {{b.c.e}}</div>
<div>changed b: {{newB}}</div>
<div>before change b: {{oldB}}</div>
</div>
</div>
修改 b.c.d 或 b.c.e 時也會觸發 b 的監聽器去更新 newB 及 oldB 。
如果要監聽複雜的表達式,使用函數來設定目標。
var vm = new Vue({
...
data: {
...
f: 1,
g: 1,
fPlusg: 0
}
});
...
vm.$watch(function() {
return this.f + this.g;
}, function(fPlusg) {
this.fPlusg = fPlusg;
});
<div id="app">
...
<div>
<div>
f: {{f}}
<button @click="f++">+</button>
<button @click="f--">-</button>
</div>
<div>
g: {{g}}
<button @click="g++">+</button>
<button @click="g--">-</button>
</div>
<div>f + g: {{fPlusg}}</div>
</div>
</div>
上面的例子 f + g 的值不能用只有點分隔的表達式來表示,所以必須使用函數,函數回傳的值改變就會觸發監聽器。
常常會有一種情境是在實體初始化完成時要取得資料,而在資料改變時會使初始資料變化,這時我們也許向下面這樣設定:
var vm = new Vue({
...
data: {
...
n: 10,
zeroToNArr: []
},
created() {
this.zeroToNArr = Array.from(new Array(this.n + 1), (val, index) => index);
}
});
...
vm.$watch('n', function() {
this.zeroToNArr = Array.from(new Array(this.n + 1), (val, index) => index);
});
<div id="app">
<div>
<div>
n: {{n}}
<button @click="n++">+</button>
<button @click="n--">-</button>
</div>
zeroToNArr: {{zeroToNArr}}
</div>
</div>
在 created 鉤子我們設置 zeroToNArr 初始值,然後監聽 n 變化時重設 zeroToNArr ,這樣看起來有點嘮叨,讓我們使用監聽器的 immediate 選項來減化代碼:
var vm = new Vue({
...
// created() {
// // [0, 1, 2, 3..., n]
// this.zeroToNArr = Array.from(new Array(this.n + 1), (val, index) => index);
// }
});
...
vm.$watch('n', function() {
// [0, 1, 2, 3..., n]
this.zeroToNArr = Array.from(new Array(this.n + 1), (val, index) => index);
}, {
immediate: true
});
這樣不僅簡潔了許多,在初始實體時也會去設定 zeroToNArr 的初始值了。
使用 $watch 回傳的函數就可以註銷監聽器。
var vm = new Vue({
...
data: {
...
n: 10,
zeroToNArr: [],
unwatchNFunc: () => {}
}
});
...
vm.unwatchNFunc = vm.$watch('n', function() {
// [0, 1, 2, 3..., n]
this.zeroToNArr = Array.from(new Array(this.n + 1), (val, index) => index);
}, {
immediate: true
});
<div id="app">
<div>
<button @click="unwatchNFunc">unwatch n</button>
<div>
n: {{n}}
<button @click="n++">+</button>
<button @click="n--">-</button>
</div>
zeroToNArr: {{zeroToNArr}}
</div>
</div>
這裡將 $watch 的回傳值丟給 unwatchNFunc ,當按下 unwatch n 按鈕時觸發 unwatchNFunc 函數,註銷監聽器。
watch: {
key: value,
...
}
watch 為鍵值,下面定義的屬性都是欲監聽的資料來源。key : 監聽目標名稱,可以使用 JavaScript 表達式。value : callback 函數的設定,共有 string 、 Function 、 Object 及 Array 可以設定。
string : callback 函數名稱。Function : callback 函數。Object : 設定監聽物件,設定方式如下:
handler : callback 函數。deep: 布林值,是否監聽物件下層屬性。immediate: 布林值,是否在實體初始化時立即叫用 callback 函數。Array : 當有多個監聽器時,使用陣列帶入多個 callback 函數。
key的 JavaScript 表達式跟$watch相同,都只能設定以點為分隔的表達式。
value設定的callback函數跟$watch相同,有newVal及oldVal兩個傳入參數。
watch 的使用方式大部分跟 $watch 相似,這裡直接以範例說明相似的用法。
var vm = new Vue({
...
watch: {
// basic
a: function(newA, oldA) {
this.newA = newA;
this.oldA = oldA;
},
// string
a: 'aMethod',
// expression
'b.c.d': function(newD, oldD) {
this.newD = newD;
this.oldD = oldD;
},
// deep
b: {
handler: function(newB, oldB) {
this.newB = newB;
this.oldB = oldB;
},
deep: true
},
// immediate
n: {
handler: function() {
// [0, 1, 2, 3..., n]
this.zeroToNArr = Array.from(new Array(this.n + 1), (val, index) => index);
},
immediate: true
}
},
methods: {
aMethod(newA, oldA) {
this.newA = newA;
this.oldA = oldA;
}
}
});
可以使用把方法名稱字串設置為 value ,監聽器會去註冊此名稱的方法。
var vm = new Vue({
...
watch: {
a: 'aMethod',
},
methods: {
aMethod(newA, oldA) {
this.newA = newA;
this.oldA = oldA;
}
}
});
如果是複雜的表達式可以使用 computed 算出,再使用 watch 監聽此計算屬性。
var vm = new Vue({
data: {
f: 1,
g: 1,
fPlusg: 0,
},
computed: {
fPlusgComputed() {
return this.f + this.g;
}
},
watch: {
// function
fPlusgComputed: function(fPlusg) {
this.fPlusg = fPlusg;
},
}
});
var vm = new Vue({
...
data: {
...
z: 1,
zminus: 0,
zplus: 0
},
watch: {
...
z: [
{
handler: function(newVal) {
this.zminus = newVal - 1;
}
},
function(newVal) {
this.zplus = newVal + 1;
}
]
}
});
當 value 是陣列時, Vue 會註冊陣列中的每一個監聽器,可以使用不同的定義方式( string 、 Function 、 Object 及 Array )設定,本例使用 Object 及 Function 舉例。
使用 watch 無法註銷監聽器,如果要在選項中註銷監聽器可以在 created 中使用 $watch 。
var vm = new Vue({
data: {
n: 10,
zeroToNArr: [],
unwatchNFunc: () => {},
},
created() {
this.unwatchNFunc = this.$watch('n', function() {
// [0, 1, 2, 3..., n]
this.zeroToNArr = Array.from(new Array(this.n + 1), (val, index) => index);
}, {
immediate: true
});
}
});
監聽器是監看資料,如果有變化時觸發函數,監聽器有 $watch 及 watch 兩個的使用方式,本文以不同的範例說明它們如何設置,還有在使用上的差別。
下一章會將監聽器跟計算屬性這兩個極為相似的功能做比較,讓我們對它們的使用時機能夠掌握得更好。

請問大大為何實例中b.c.e變化時的newB & oldB 看起來是一樣的呢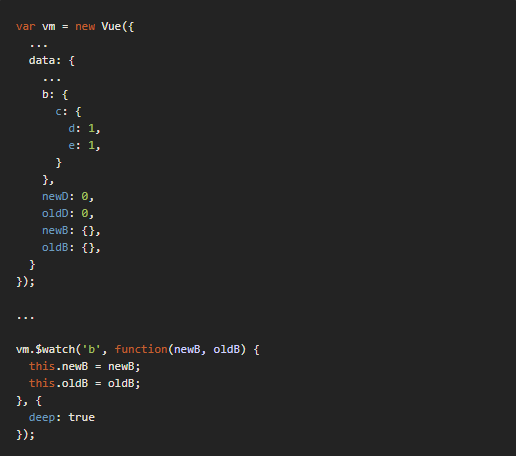
版主提供可運行的程式範例
你好~
我分為簡答跟詳答回覆你:
依照 Vue 官方文件 解釋:
Note: when mutating (rather than replacing) an Object or an Array, the old value will be the same as new value because they reference the same Object/Array. Vue doesn’t keep a copy of the pre-mutate value.
Vue 的操作會使 Object, Array 在新舊值中是對應到相同的記憶體位置,因此新舊值會相等
我建立了一個範例簡略模擬 Vue watcher 的流程:
https://codepen.io/peterhpchen/pen/bGEMwNB?editors=0012
可以試著將 b 由數值改為物件再跑一次,從中瞭解為什麼會相等
Vue 的 watcher 可以在代碼庫中找到:https://github.com/vuejs/vue/blob/dev/src/core/observer/watcher.js#L179
利用監聽計算屬性與 Object.assign 複製物件的方式避免等值問題,詳細可以看此 Github issue
謝謝版主抽空回應,簡答好像對我比較好理解XD
詳答的部分可能還需要再更熟悉javaScript知識才能理解= =
大大您好
想請問如果用watch監聽vue-router的變化
像這樣
watch: {
$route(nowRoute) {
let nowPage = nowRoute.name;
this.zoom(nowPage);
},
}
目前都是router一變化就會跑zoom了
是否有辦法等到transition結束之後再做呢
可以試試將 zoom 放在 transition 的 hook 中,可以參考 https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/transitions.html#JavaScript-Hooks