接下來是 100 天當中的第二部分 Python 語言進階。我也會分成好幾天做這階段的筆記。
算法:解決問題的方法和步驟
評價算法的好壞:漸近時間複雜度和漸近空間複雜度。
漸近時間複雜度的大 O (Big-o) 標記:
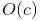 - 恆定時間複雜度 - 布隆過濾器 (Bloom Filter) / 雜湊表 (Hash table) 存儲
- 恆定時間複雜度 - 布隆過濾器 (Bloom Filter) / 雜湊表 (Hash table) 存儲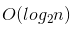 - 對數時間複雜度 - 二分搜尋 (Binary Search)
- 對數時間複雜度 - 二分搜尋 (Binary Search)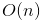 - 線性時間複雜度 - 循序搜尋 (Sequential Search) / 桶排序 (Bucket Sort)
- 線性時間複雜度 - 循序搜尋 (Sequential Search) / 桶排序 (Bucket Sort)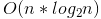 - 對數線性時間複雜度 - 高級排序算法(合併排序 (Merge sort)、快速排序 (Quick sort))
- 對數線性時間複雜度 - 高級排序算法(合併排序 (Merge sort)、快速排序 (Quick sort))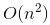 - 平方時間複雜度 - 簡單排序算法(選擇排序 (Selection sort)、插入排序(Insertion sort)、氣泡排序 (Bubble sort))
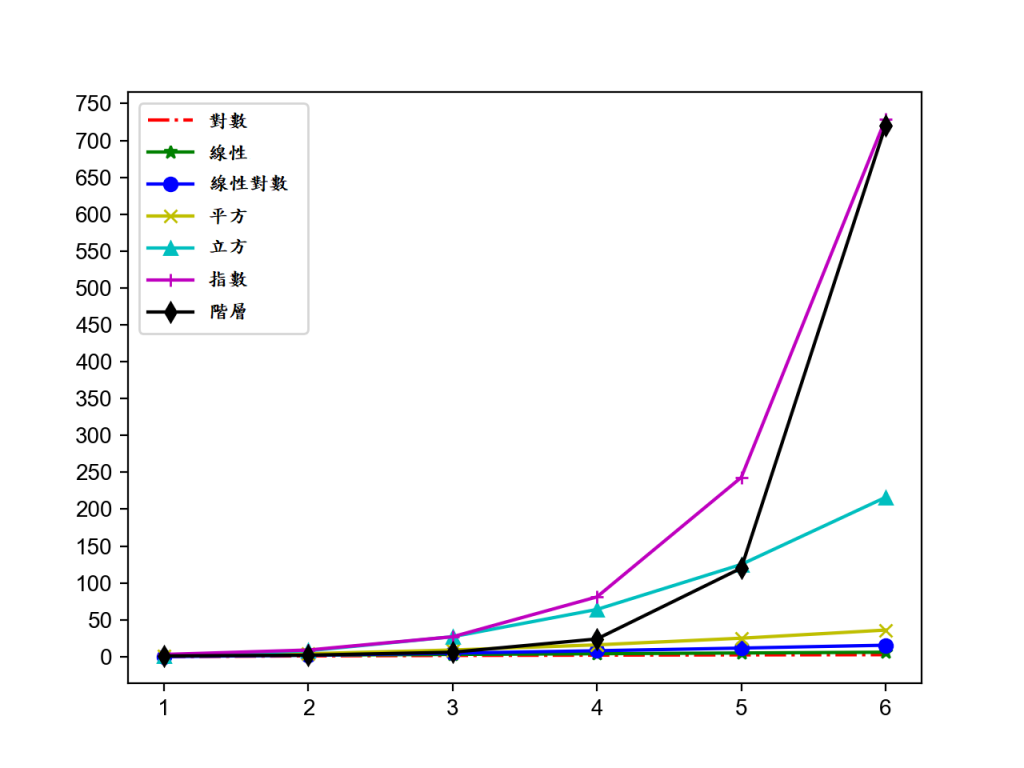
- 平方時間複雜度 - 簡單排序算法(選擇排序 (Selection sort)、插入排序(Insertion sort)、氣泡排序 (Bubble sort))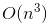 - 立方時間複雜度 - Floyd 算法 / 矩陣乘法運算
- 立方時間複雜度 - Floyd 算法 / 矩陣乘法運算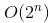 - 指數時間複雜度 - 河內塔
- 指數時間複雜度 - 河內塔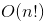 - 階乘時間複雜度 - 旅行推銷員問題 - NP
- 階乘時間複雜度 - 旅行推銷員問題 - NP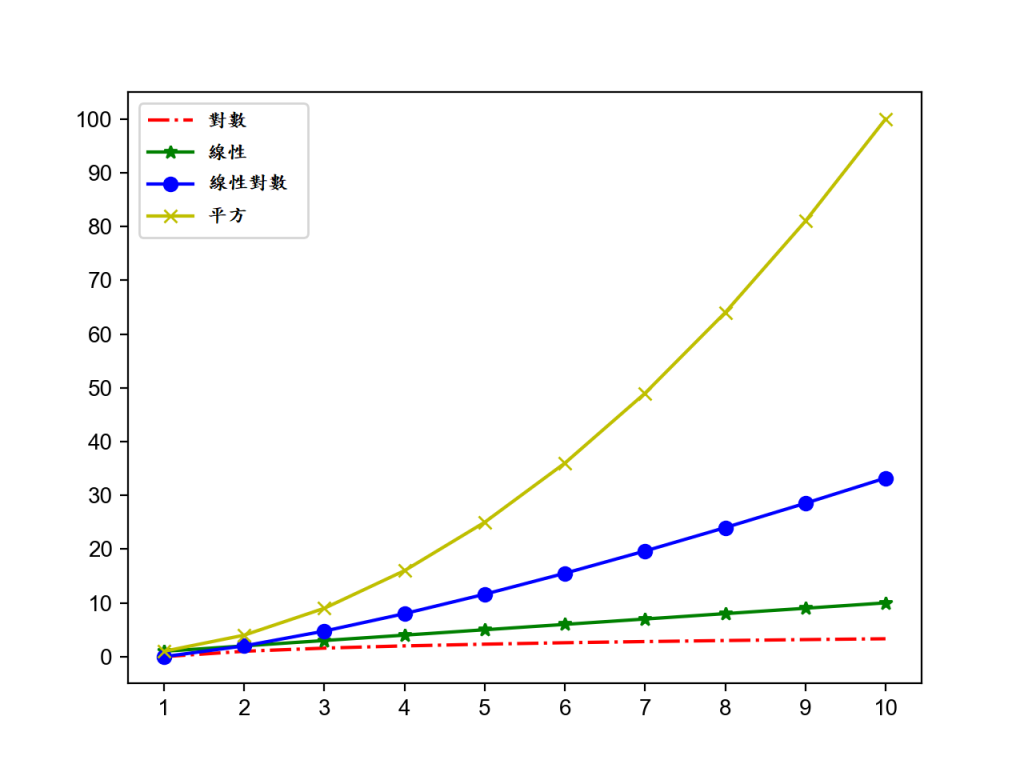
排序算法 - 選擇排序 (Selection sort)、氣泡排序 (Bubble sort)、合併排序 (Merge sort)
搜尋算法 - 二分搜尋 (Binary Search)、循序搜尋 (Sequential Search)
選擇排序 (Selection sort)
def select_sort(origin_items, comp = lambda x, y: x < y):
items = origin_items[:]
for i in range (len(items) - 1):
min_index = i
for j in range(i + 1, len(items)):
if comp(items[j], items[min_index]):
min_index = j
items[i], items[min_index] = items[min_index], items[i]
return items
origin_items = [1,300,123,44,156,12]
print(select_sort(origin_items))
氣泡排序 (Bubble sort)
def bubble_sort(origin_items, comp = lambda x, y: x > y):
items = origin_items[:]
for i in range(len(items) - 1):
swapped = False
for j in range(i, len(items) - 1 - i):
if comp(items[j], items[j + 1]):
items[j], items[j + 1] = items[j + 1], items[j]
swapped = True
if swapped:
swapped = False
for j in range (len(items) - 2 - i, i, -1):
if comp (items[j - 1], items[j]):
items[j], items[j - 1] = items[j - 1], items[j]
swapped = True
if not swapped:
break
return items
origin_items = [1,300,123,44,156,12]
print(bubble_sort(origin_items))
合併排序 (Merge sort)
def merge_sort(items, comp = lambda x, y: x <= y):
if len(items) < 2:
return items[:]
mid = len(items) // 2
left = merge_sort(items[:mid], comp)
right = merge_sort(items[mid:], comp)
return merge(left, right, comp)
def merge(items1, items2, comp):
items = []
index1, index2 = 0, 0
while index1 < len(items1) and index2 < len(items2):
if comp(items1[index1], items2[index2]):
items.append(items1[index1])
index1 += 1
else:
items.append(items2[index2])
index2 += 1
items += items1[index1:]
items += items2[index2:]
return items
items = [1,300,123,44,156,12]
print(merge_sort(items))
以上三種皆會印出此結果
二分搜尋 (Binary Search)
def binary_search(items, key):
start, end = 0, len(items) - 1
while start <= end:
mid = (start + end) // 2
if key > items[mid]:
start = mid + 1
elif key < items[mid]:
end = mid - 1
else:
return mid
return -1
items = [1,300,123,44,156,12]
print(binary_search(items,100))
print(binary_search(items,123))
循序搜尋 (Sequential Search)
def sequential_search(items, key):
for index, item in enumerate(items):
if item == key:
return index
return -1
items = [1,300,123,44,156,12]
print(sequential_search(items,100))
print(sequential_search(items,123))
以上兩種皆會印出此結果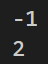
推導式語法 - 可以用來生成列表、集合和字典。
prices = {
'AAPL': 191.88,
'GOOG': 1186.96,
'IBM': 149.24,
'ORCL': 48.44,
'ACN': 166.89,
'FB': 208.09,
'SYMC': 21.29
}
# 用股票價格 > 100元的股票構成一個新的字典
prices2 = {key: value for key, value in prices.items() if value > 100}
print(prices2)

嵌套的列表
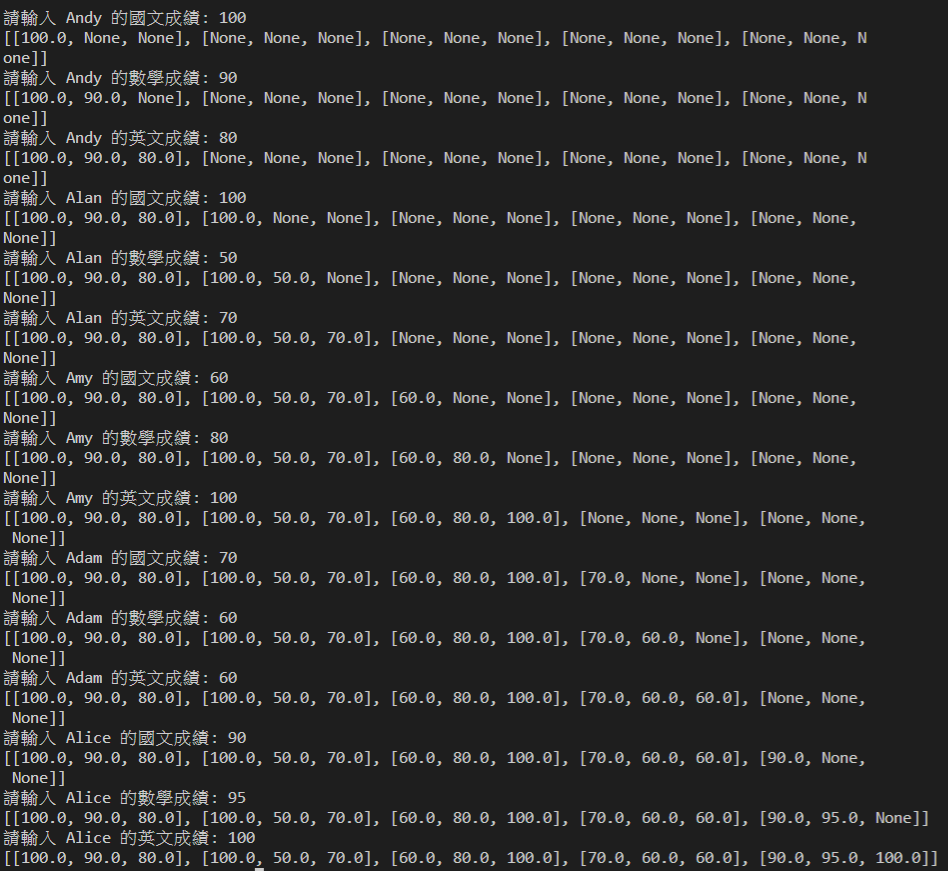
names = ['Andy', 'Alan', 'Amy', 'Adam', 'Alice']
courses = ['國文', '數學', '英文']
# 輸入五個學生三門課的成績
scores = [[None] * len(courses) for _ in range(len(names))]
for row, name in enumerate(names):
for col, course in enumerate(courses):
scores[row][col] = float(input(f'請輸入 {name} 的{course}成績: '))
print(scores)
heapq、itertools 等的用法
從列表中找出最大的或最小的 N 個元素
import heapq
list1 = [34, 25, 12, 99, 87, 63, 58, 78, 88, 92]
list2 = [
{'name': 'IBM', 'shares': 100, 'price': 91.1},
{'name': 'AAPL', 'shares': 50, 'price': 543.22},
{'name': 'FB', 'shares': 200, 'price': 21.09},
{'name': 'HPQ', 'shares': 35, 'price': 31.75},
{'name': 'YHOO', 'shares': 45, 'price': 16.35},
{'name': 'ACME', 'shares': 75, 'price': 115.65}
]
print(heapq.nlargest(3, list1)) # 最大的三個
print(heapq.nsmallest(3, list1)) # 最小的三個
print(heapq.nlargest(2, list2, key = lambda x: x['price'])) # price 最大的兩個
print(heapq.nlargest(2, list2, key = lambda x: x['shares'])) # shares 最大的兩個

迭代工具 - 排列 / 组合 / 笛卡兒積
import itertools
# ABCD 的所有排列情況
print(list(itertools.permutations('ABCD')))
# ABCDE 3 個一組的組合
print('----------------------------')
print(list(itertools.combinations('ABCDE', 3)))
# ABCD 和 123 的組合
print('----------------------------')
print(list(itertools.product('ABCD', '123')))

collections 模組的工具
找出列表中出現次數最多的元素
from collections import Counter
words = [
'look', 'into', 'my', 'eyes', 'look', 'into', 'my', 'eyes',
'the', 'eyes', 'the', 'eyes', 'the', 'eyes', 'not', 'around',
'the', 'eyes', "don't", 'look', 'around', 'the', 'eyes',
'look', 'into', 'my', 'eyes', "you're", 'under'
]
counter = Counter(words)
print(counter.most_common(3))

