窮舉法
百錢百雞
公雞 5 元一隻,母雞 3 元一隻,小雞 1 元三隻,用 100 元買 100 隻雞,公雞/母雞/小雞各多少隻。
sum = 0
for i in range (0,20):
for j in range (0,33):
if 5 * i + 3 * j + (100 - i - j) / 3 == 100:
print("公雞 %d 隻,母雞 %d 隻,小雞 %d 隻 " % (i,j,(100 - i - j)))

五人分魚
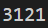
A、B、C、D、E 五人在某天夜裡合夥捕魚最後疲憊不堪各自睡覺。
第二天 A 第一個醒來他將魚分為 5 份,扔掉多餘的 1 條拿走自己的一份。B 第二個醒來也將魚分為 5 份,扔掉多餘的 1 條拿走自己的一份。然後 C、D、E 依次醒來也按同樣的方式分魚問他們至少捕了多少條魚
fish = 6
while True:
total = fish
enough = True
for _ in range(5):
if (total - 1) % 5 == 0:
total = (total - 1) // 5 * 4
else:
enough = False
break
if enough:
print(fish)
break
fish += 5
貪婪法
有一個背包,最多能裝 20 公斤,如下表所示的物品。
他不能把所有物品都裝進背包,所以必須確定拿走哪些物品,留下哪些物品。
| 名稱 | 價錢 | 重量 |
|---|---|---|
| 電腦 | 200 | 20 |
| 收音機 | 20 | 4 |
| 時鐘 | 175 | 10 |
| 花瓶 | 50 | 2 |
| 書 | 10 | 1 |
| 油畫 | 90 | 9 |
class Thing(object): # 物品
def __init__(self, name, price, weight):
self.name = name
self.price = price
self.weight = weight
@property
def value(self): # 價格重量比
return self.price / self.weight
def input_thing(): # 輸入名字 價錢 重量 (以空格分開)
name_str, price_str, weight_str = input().split()
return name_str, int(price_str), int(weight_str)
def main():
# 輸入承受重量 物品數量(以空格分開)
max_weight, num_of_things = map(int, input().split())
all_things = []
for _ in range(num_of_things):
all_things.append(Thing(*input_thing()))
# 將物品依價格重量比排序
all_things.sort(key = lambda x: x.value, reverse = True)
total_weight = 0
total_price = 0
for thing in all_things:
if total_weight + thing.weight <= max_weight:
print(f'拿走{thing.name}')
total_weight += thing.weight
total_price += thing.price
print(f'總價值: {total_price} ')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()

分治法
快速排序 (Quick sort)
從數列中挑出一個元素為基準,重新排序數列,所有比基準值小的元素擺放在基準前面,所有比基準值大的元素擺在基準後面,分割結束之後,遞迴排序地將小於基準值元素的子序列和大於基準值元素的子序列排序。
def quick_sort(origin_items, comp = lambda x, y: x <= y):
items = origin_items[:]
_quick_sort(items, 0, len(items) - 1, comp)
return items
def _quick_sort(items, start, end, comp):
if start < end:
pos = _partition(items, start, end, comp)
_quick_sort(items, start, pos - 1, comp)
_quick_sort(items, pos + 1, end, comp)
def _partition(items, start, end, comp):
pivot = items[end]
i = start - 1
for j in range(start, end):
if comp(items[j], pivot):
i += 1
items[i], items[j] = items[j], items[i]
items[i + 1], items[end] = items[end], items[i + 1]
return i + 1
items = [1,300,123,44,156,12]
print(quick_sort(items))

回溯法
騎士巡邏 (Knight's tour) 是指在按照國際象棋中騎士的規定走法走遍整個棋盤的每一個方格,而且每個網格只能夠經過一次。
import sys
import time
SIZE = 5
total = 0
def print_board(board): # 印出的棋盤
for row in board:
for col in row:
print(str(col).center(4), end = '')
print()
def patrol(board, row, col, step=1):
if row >= 0 and row < SIZE and \
col >= 0 and col < SIZE and \
board[row][col] == 0:
board[row][col] = step
if step == SIZE * SIZE:
global total
total += 1
print(f'第 {total} 種走法: ')
print_board(board)
patrol(board, row - 2, col - 1, step + 1)
patrol(board, row - 1, col - 2, step + 1)
patrol(board, row + 1, col - 2, step + 1)
patrol(board, row + 2, col - 1, step + 1)
patrol(board, row + 2, col + 1, step + 1)
patrol(board, row + 1, col + 2, step + 1)
patrol(board, row - 1, col + 2, step + 1)
patrol(board, row - 2, col + 1, step + 1)
board[row][col] = 0
def main():
board = [[0] * SIZE for _ in range(SIZE)]
patrol(board, SIZE - 1, SIZE - 1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
共有 304 種走法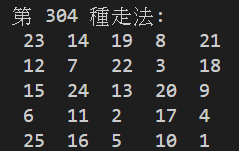
動態規劃
斐波那契數列 (Fibonacci sequence)。
def fib(num, temp = {}):
if num in (1, 2):
return 1
try:
return temp[num]
except KeyError:
temp[num] = fib(num - 1) + fib(num - 2)
return temp[num]
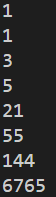
print(fib(1))
print(fib(2))
print(fib(4))
print(fib(5))
print(fib(8))
print(fib(10))
print(fib(12))
print(fib(20))
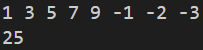
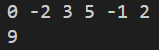
子列表元素之和的最大值。(使用動態規劃可以避免二重循環)
def main():
# 輸入數字 (以空格分開)
items = list(map(int, input().split()))
size = len(items) # 6
overall, partial = {}, {}
overall[size - 1] = partial[size - 1] = items[size - 1]
# 由倒數第 2 項後往前推
for i in range(size - 2, -1, -1):
# 比較目前值和目前值 + 下一項的值誰大
partial[i] = max(items[i], partial[i + 1] + items[i])
# 再比較和目前值的下一項誰大
overall[i] = max(partial[i], overall[i + 1])
print(overall[0])
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()