我們一樣打開我們的專案
我們先把List<Product> products 刪除
然後清空GetProduct 跟 CreateProduct兩個方法的程式碼
順便將前天範例的CreateProduct方法的[FromQuery]刪掉
所以目前程式碼會像
ProductControlle.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using MyFirstApi.Model;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
namespace MyFirstApi.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ProductController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
[Route("GetProduct")]
public List<Product> GetProducts()
{
}
[HttpPost]
[Route("CreateProduct")]
public string CreateProduct(Product product)
{
}
}
}
刪完之後會出現紅色小蚯蚓是正常的
兩個方法都有要求返回值
但我們並沒有return任何東西
接著我們在GetProducts程式碼中填入
[HttpGet]
[Route("GetProduct")]
public List<Product> GetProducts()
{
using (ProductContext context = new ProductContext())
{
return context.Products.ToList();
}
}
第一行的using ProductContext context = new ProductContext();
指的是在這個區塊的程式碼執行完成之後
context這個物件就會從記憶體中被釋放
通常對於DB連線或者是WebClient連線等等的方式
因為DB在處理系統的連線數是有限的
所以我們要確保在執行完動作之後馬上釋放連線
才能夠讓DB處理更多請求
我們先讓CreateProduct 回傳空值
[HttpPost]
[Route("CreateProduct")]
public string CreateProduct(Product product)
{
return null;
}
然後執行專案
一樣用POST去呼叫 GetProduct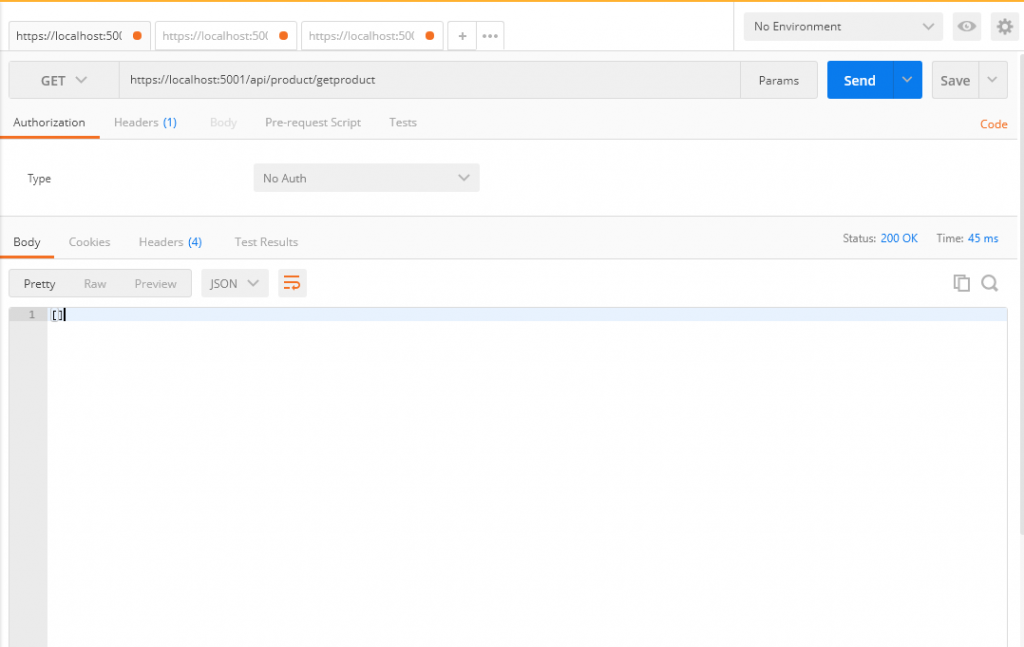
因為資料庫裏面沒有東西
所以我們得到空的List
所以我們來實作CreateProduct
[HttpPost]
[Route("CreateProduct")]
public string CreateProduct(Product product)
{
using ProductContext context = new ProductContext();
context.Products.Add(product);
context.SaveChanges();
return $"{JsonConvert.SerializeObject(product)}商品已加入清單";
}
context指的是你的資料庫
products 是資料庫中的資料表
我們在資料表中加入了一筆product
但是在執行context.SaveChanges();之前
通通都只是在記憶體中
直到我們執行這行才會把所有變更存到資料庫中
我們一樣執行專案
然後一樣用PostMan測試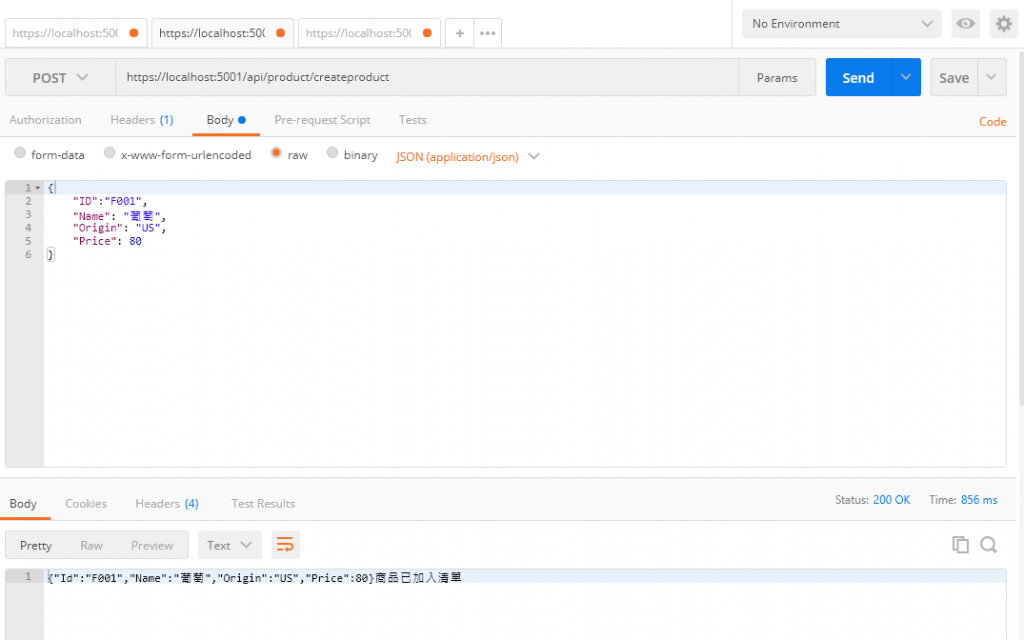
可以看見成功訊息
我們再用GetProducts看看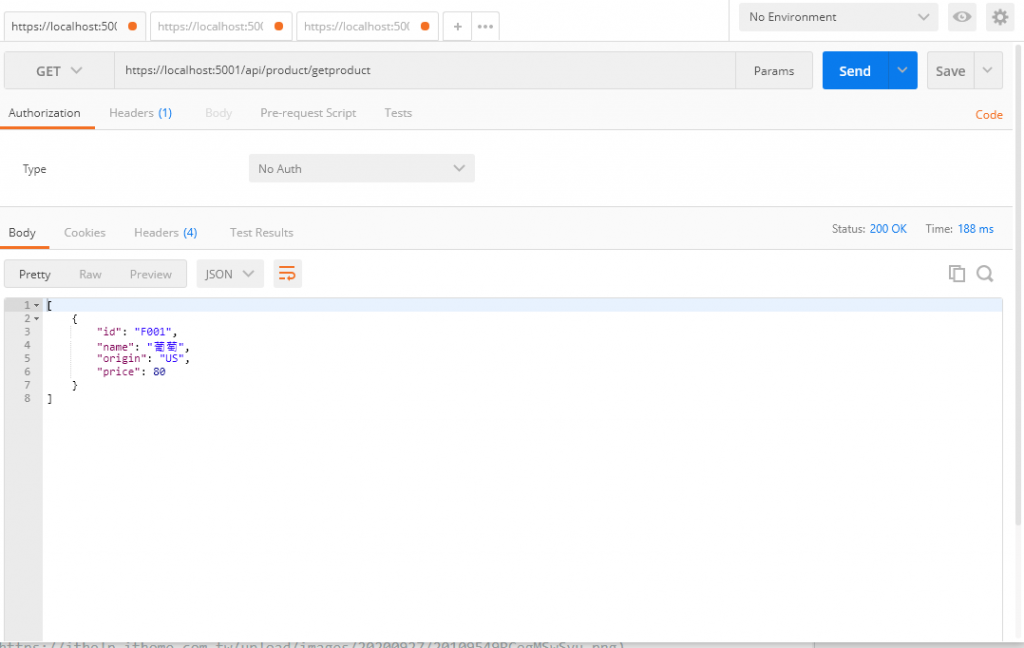
可以成功地看見物品清單
有了新增查詢
接著我們來實作修改與刪除
我們先新增一個修改的方法
[HttpPut]
[Route("UpdateProduct/{id}")]
public ActionResult CreateProduct(string id,[FromBody]Product product)
{
using ProductContext context = new ProductContext();
Product originProduct = context.Products.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == id);
if (originProduct == null) return BadRequest("if not found");
if (product.Id != id) return BadRequest("不可修改ID");
originProduct.Name = product.Name;
originProduct.Price = product.Price;
originProduct.Origin = product.Origin;
context.SaveChanges();
return Ok($"{JsonConvert.SerializeObject(originProduct)}已被修改}");
}
[Route("UpdateProduct/{id}")]
{id}表示這是必填欄位
他為綁定到傳入參數中的id
Product originProduct = context.Products.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == id);
if (originProduct == null) return BadRequest("if not found");
if (product.Id != id) return BadRequest("不可修改ID");
這三行是從根據ID從資料庫中找到要修改的資料
如果找不到資料就回傳 BadRequest
通常ID是不會被修改的
他通常是資料庫的主鍵
所以要修改的ID跟原本資料的ID對不上的話我也會回傳BadRequest
不熟HttpCode可以參考
https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10242055
剩下就是進行修改的動作
當然我們也可以把資料刪掉再塞一筆新的進去假裝他被修改了
不過外部使用者只要在乎資料有被修改
不用在乎你實作的細節
這就是封裝的重要性
我們一樣執行專案
在網址列輸入
https://localhost:5001/api/product/updateproduct/F001
F001是我上面示範的商品編號
記得將方法改為PUT
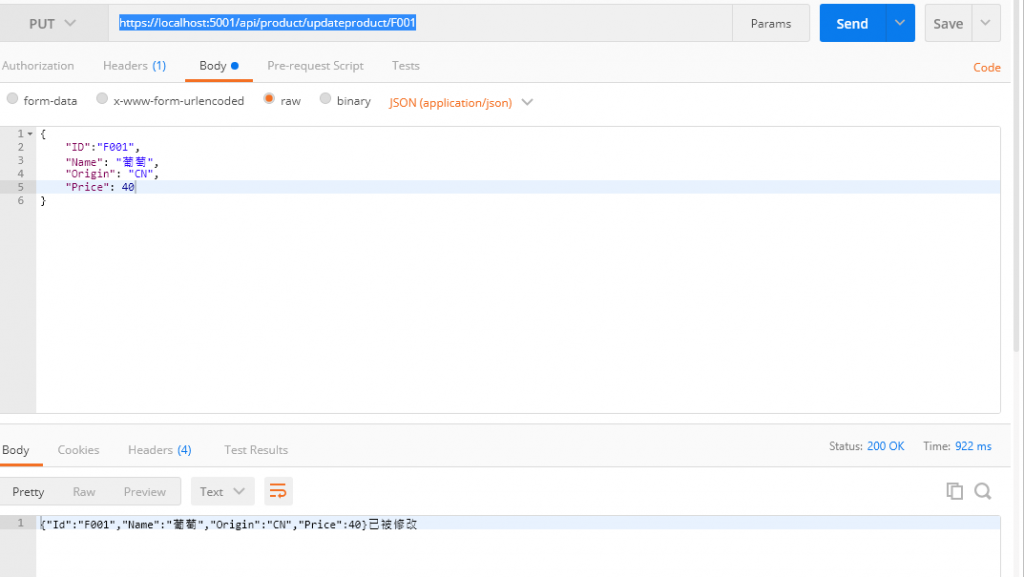
然後我們用GetProduct
可以看見物品確實被修改了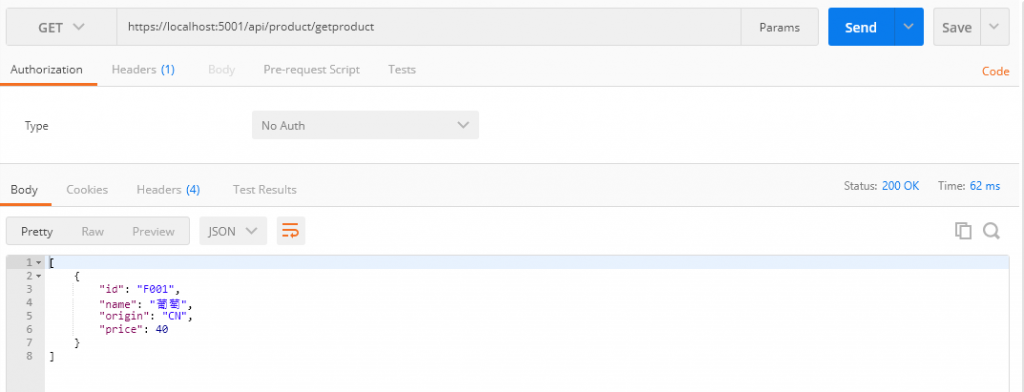
我們再建立一個DeleteProduct Method
[HttpDelete]
[Route("DeleteProduct/{id}")]
public ActionResult DeleteProduct(string id)
{
using ProductContext context = new ProductContext();
Product originProduct = context.Products.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == id);
if (originProduct == null) return BadRequest("if not found");
context.Products.Remove(originProduct);
context.SaveChanges();
return Ok($"{JsonConvert.SerializeObject(originProduct)}已被刪除");
}
一樣開啟專案測試
網址輸入https://localhost:5001/api/product/deleteproduct/F001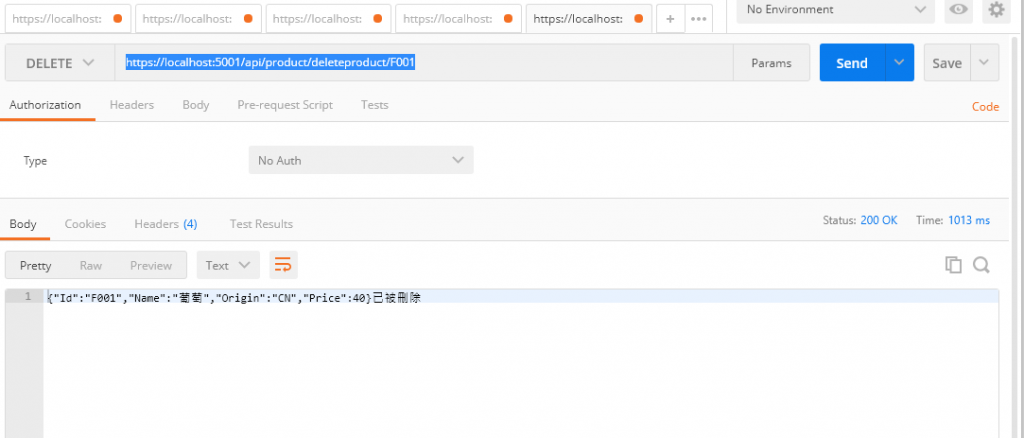
物品被刪了
Get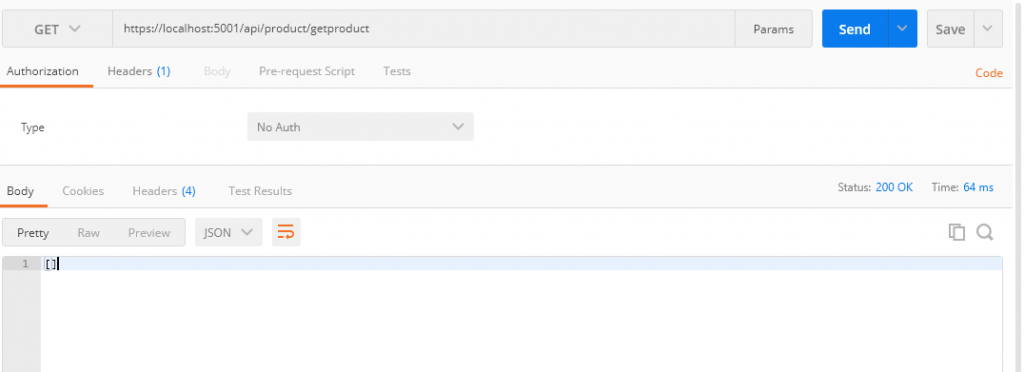
神摸也沒有
原始程式碼(https://github.com/peace920902/ApiTutorial)
