x=6
y=10
eval('100 * x +300 +y +9')
>> 919
exec('''
for i in range(5):
print (f"iter time: {i}" )
''')
>> iter time: 0
iter time: 1
iter time: 2
iter time: 3
iter time: 4
A. 解方程式 (預設右側為0)
from sympy.solvers import solve
from sympy import Symbol
x = Symbol('x')
print(solve(x**2 - 1, x))
>> [-1, 1]
B 產生上標 (jupyter 有效 QQ)
from sympy.solvers import solve
from sympy import Symbol
x = Symbol('x')
x**4+2*x**2+3
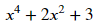
C. 直接解方程式
from sympy.core import sympify
x, y = sympify('x, y')
print(solve([x + y + 2, 3*x + 2*y], dict=True))
>> [{x: 4, y: -6}]
# 求 20 個 x 點對應的 y 值
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df = pd.DataFrame ({'x': range(-10, 11)})
df['y'] = (3*df['x'] - 4) / 2
# 作圖
plt.plot(df.x, df.y, color="0.5")
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.grid()
plt.axhline()
plt.axvline()
x_i = [(1.33, 0), (0, 0)]
y_i = [[0, 0], [0, -2]]
plt.annotate('x-intercept',(1.333, 0))
plt.annotate('y-intercept',(0,-2))
plt.plot(x_i[0], x_i[1], color="r")
plt.plot(y_i[0], y_i[1], color="y
plt.show()
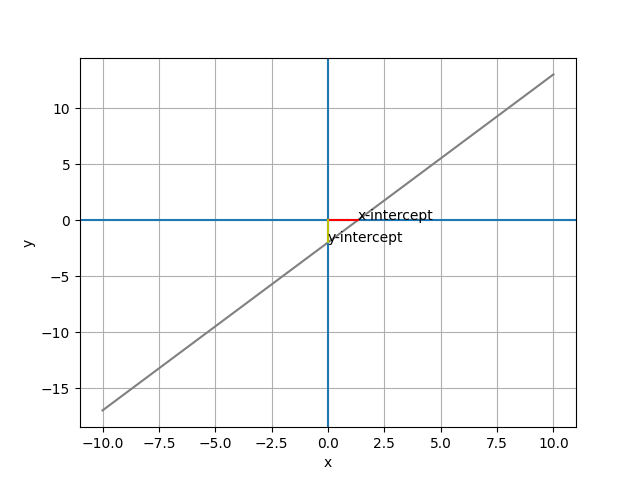 ")
")
# 作圖
plt.plot(df.x, df.y, color="0.5")
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.grid()
plt.axhline()
plt.axvline()
# the slope
slope = 1.5
x_slope = [0, 1]
y_slope = [-2, -2 + slope]
plt.plot(x_slope, y_slope, color='red', lw=5)
plt.savefig('pic 03.png')
plt.show()
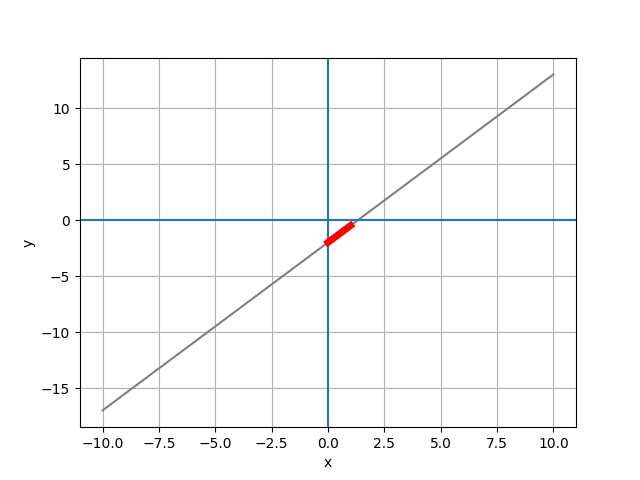
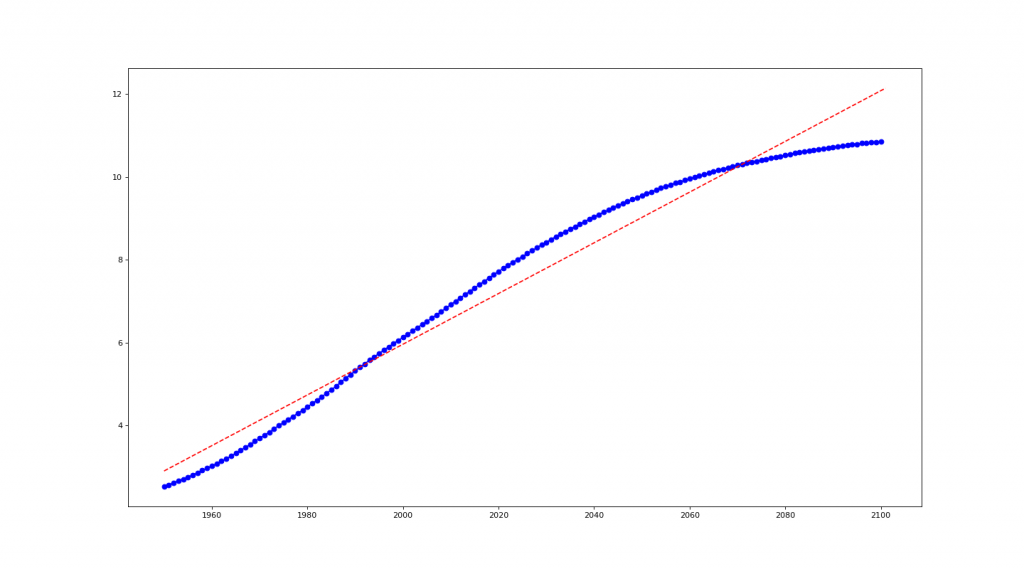
# 世界人口預測
year=[1950, 1951, 1952, 1953, 1954, ...2100]
pop=[2.53, 2.57, 2.62, 2.67, 2.71, ...10.85]
# 1. Numpy regression
x1 = np.linspace(1950, 2101, 2000)
fit = np.polyfit(year, pop, 1)
y1 = np.poly1d(fit)(x1)
# 作圖
plt.figure(num=None, figsize=(18, 10), dpi=80, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
plt.plot(year, pop, 'b-o', x1, y1, 'r--')
plt.show()
# 2. LinearRegression
X = np.array(year).reshape(len(year), 1)
y = np.array(pop)
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression as LR
clf = LR()
clf.fit(X, y) # 線性迴歸
print(f'y = {clf.coef_[0]:.2f} * x + {clf.intercept_:.2f}')
>> y = 0.06 * x + -116.36
# 作圖
plt.figure(num=None, figsize=(18, 10), dpi=80, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
x1 = np.arange(1950, 2101)
y1 = clf.coef_[0] * x1 - clf.intercept_
plt.plot(year, pop, 'b-o', x1, y1, 'r--')
plt.show()
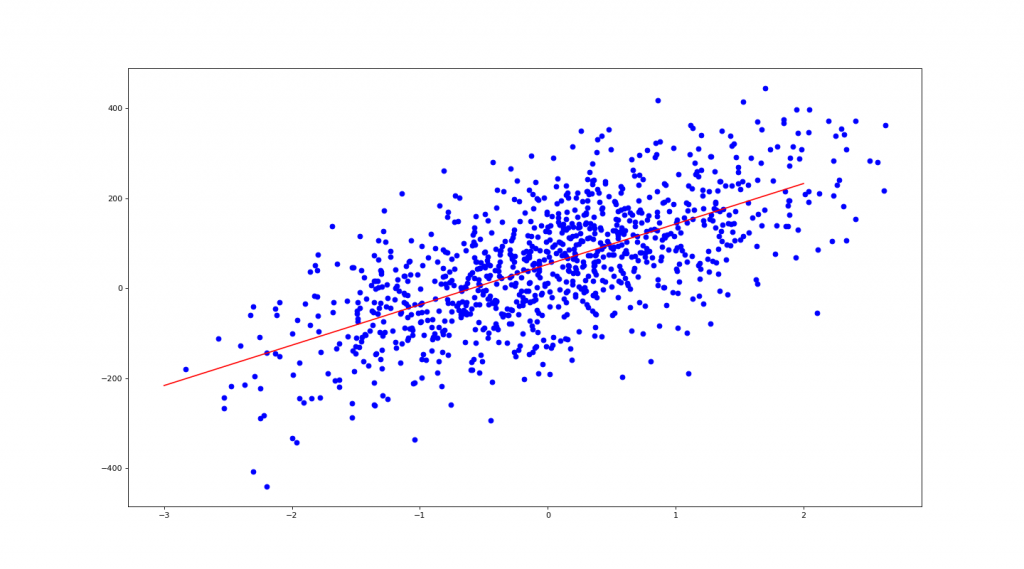
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression as mr
# n_features= : 幾個 x
# noise= : 雜訊量
# bias= : 截距
X, y= mr(n_samples=1000, n_features=1, noise=10, bias=50)
# use sklearn LinearRegression
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression as LR
clf = LR()
clf.fit(X, y)
coe = clf.coef_[0]
ic = clf.intercept_
print(f' y = {coe:.2f} * x + {ic:.2f}') # 1 + {clf.coef_[1]:.2f} * x2
>> y = 89.69 * x + 52.88
# 作圖
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(num=None, figsize=(18, 10), dpi=80, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
plt.scatter(X, y, c='b') # 畫出 X, y 點點
X1 = np.linspace(-3, 2, 100)
plt.plot(X1, coe*X1 + ic, 'r') # 畫出迴歸紅線
plt.show()
Numpy 線性代數解聯立方程式
EX1. 4x - 5y = -13
-2x + 3y = 9
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[4, -5], [-2, 3]])
b = np.array([-13, 9])
print(np.linalg.solve(a, b))
>> [3. 5.]
EX2. x + 2y = 5
y - 3z = 5
3x - z = 4
a = np.array([[1, 2, 0], [0, 1, -3], [3, 0, -1]])
b = np.array([5, 5, 4])
print(np.linalg.inv(a) @ b)
>> [ 1. 2. -1.]
import math
# 16 是 4 的幾次方
print(math.log(16, 4))
>> 2.0
# 100 是 log10 的幾次方
print(math.log10(100))
>> 2.0
# e & pi
print(math.e, math.pi) # 等同於 np.e, np.pi
>> 2.718281828459045 3.141592653589793
# 100 是 e 的幾次方
print(math.log(100, math.e))
>> 4.605170185988092
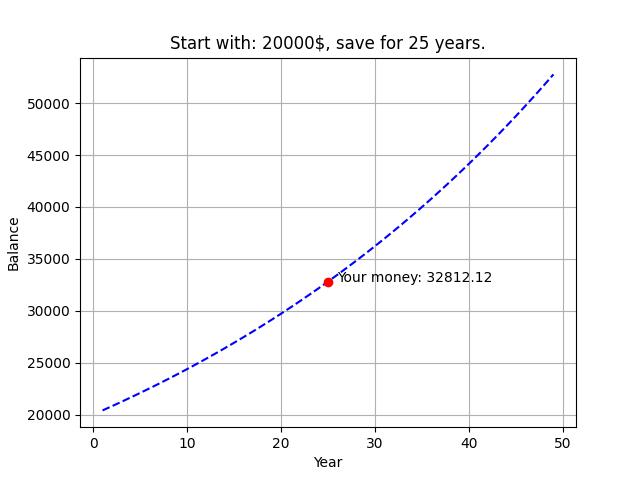
複利計算
import pandas as pd
m = int(input('請輸入你想存多少 (錢): '))
i = int(input('請輸入你想存多久 (年): '))
total_monety = m*(1.02**i)
df = pd.DataFrame ({'Year': range(1, 50)})
df['Balance'] = m*(1.02**df['Year'])
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.plot(df.Year, df.Balance, 'b--', i, total_monety, 'ro')
plt.xlabel('Year')
plt.ylabel('Balance')
plt.grid()
plt.title(f'Start with: {m}$, save for {i} years.')
plt.annotate(f'Your money: {total_monety:.2f}',(i+1, total_monety))
plt.show()
Greatest Common Factor (最大公因數)
a = int(input('數字1: '))
b = int(input('數字2: '))
def GCD(x, y):
while True:
if y == 0:
print(x)
break
else:
return GCD(y, x%y)
GCD(a, b)
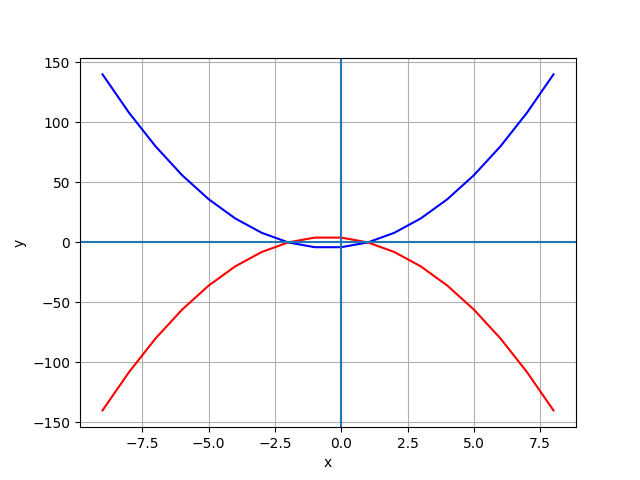
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
df = pd.DataFrame ({'x': range(-9, 9)})
df['y1'] = 2*df['x']**2 + 2 *df['x'] - 4
df['y2'] = -(2*df['x']**2 + 2*df['x'] - 4)
# 作圖
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.plot(df.x, df.y1, 'b', df.x, df.y2, 'r')
plt.plot()
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.grid()
plt.axhline()
plt.axvline()
plt.show()
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
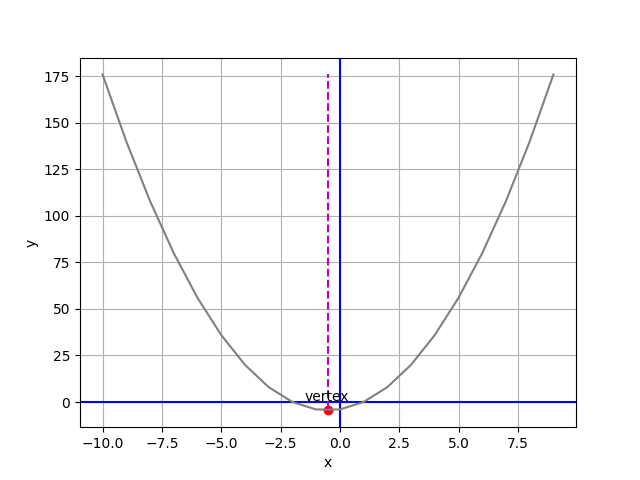
def plot_parabola(a, b, c): # 代入 (2, 2, -4)
vx = (-1*b)/(2*a) # 極值點斜率必為0,f(x)'=2ax+b=0,x=(-b/2a)
vy = a*vx**2 + b*vx + c # 代入 f(x) 求極值 y 座標
df = pd.DataFrame ({'x': np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)})
df['y'] = a*df['x']**2 + b*df['x'] + c # 把 x, y 輸入進 df
# 作圖
plt.xlabel('x') # x 軸名稱
plt.ylabel('y') # y 軸名稱
plt.grid() # 灰色格線
plt.axhline(c='b') # 水平基準線
plt.axvline(c='b') # 垂直基準線
xp = [vx, vx]
yp = [df.y.min(), df.y.max()]
plt.plot(df.x, df.y, '0.5', xp, yp, 'm--') # 劃出拋物線 / y 最小垂直線
plt.scatter(vx, vy, c='r') # 劃出 y 最小點
plt.annotate('vertex', (vx, vy), xytext=(vx - 1, (vy + 5)* np.sign(a)))
plt.savefig('pic 10.png')
plt.show()
plot_parabola(2, 2, -4)
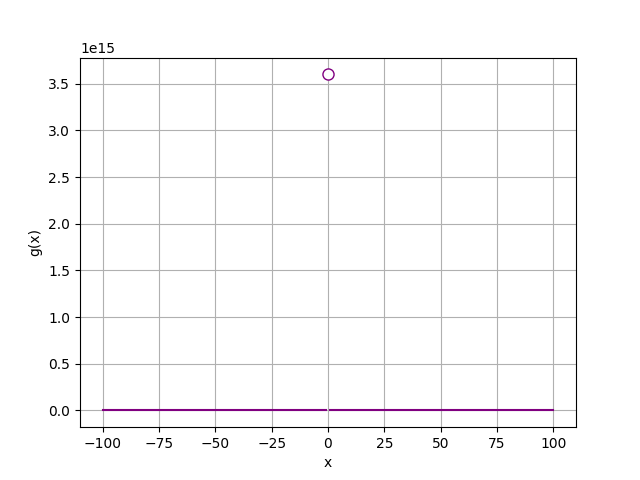
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(x):
return x**2 + 2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def g(x):
if x != 0:
return (12/(2*x))**2
x = range(-100, 101)
y = [g(a) for a in x]
# 作圖
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('g(x)')
plt.grid()
plt.plot(x,y, color='purple')
plt.plot(0, g(0.0000001), c='purple', marker='o', markerfacecolor='w', markersize=8)
plt.show()
.
.
.
.
.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
ds = datasets.load_wine()
X =pd.DataFrame(ds.data, columns=ds.feature_names)
y = ds.target
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split as tts
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = tts(X, y, test_size=0.1)
A. 使用 KNN 驗算法:
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier as KNN
clf = KNN(n_neighbors=3)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
clf.score(X_test, y_test)
>> 0.78
B. 使用 LogisticRegression 驗算法:
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression as lr
clf2 = lr(solver='liblinear')
clf2.fit(X_train, y_train)
clf2.score(X_test, y_test)
>> 1.0
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
ds = datasets.load_diabetes()
# 注意此處 X 的數值經過 standardization,固有出現年齡負值的情況。
# (X-m)/sigma,平均為 0 / 標準差為 1
X = pd.DataFrame(ds.data, columns=ds.feature_names)
y = ds.target
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split as tts
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = tts(X, y, test_size=0.2)
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
clf = LinearRegression()
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
clf.score(X_test, y_test)
>> 0.46
額外補充:求 MSE & Coefficients
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
# Coefficients (一次項式係數)
# y = w1*x1 + w2*x2 + w3*x3 ... w10*x10 + b
print('Coefficients: ', clf.coef_)
>> Coefficients: [ -42.4665896 -278.41905956 519.81553297 346.25936576 -836.62271952
494.18394438 135.91708785 164.44984594 795.02484868 69.8608995 ]
print('Intercept: ', clf.intercept_)
>> Intercept: 152.2877890433722
# MSE (均方誤差):1/n * sum(y_pred-y_test)
print(f'MSE: {mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)}')
>> MSE: 3161.582266519054
# Coefficient of determination (判定係數):越接近 1 越好
print(f'Coefficient of determination: {r2_score(y_test, y_pred)}')
>> Coefficient of determination: 0.4556662437750665
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
df = pd.read_csv('tips.csv')
print(df.head())
X = df.drop('tip', axis=1) # 把'tip'丟棄
y = df['tip'] # y 為要分析的資料
# 顯示 'sex' 欄位不同的項目
print(X['sex'].unique())
>> ['Female' 'Male']
解決方式如下:
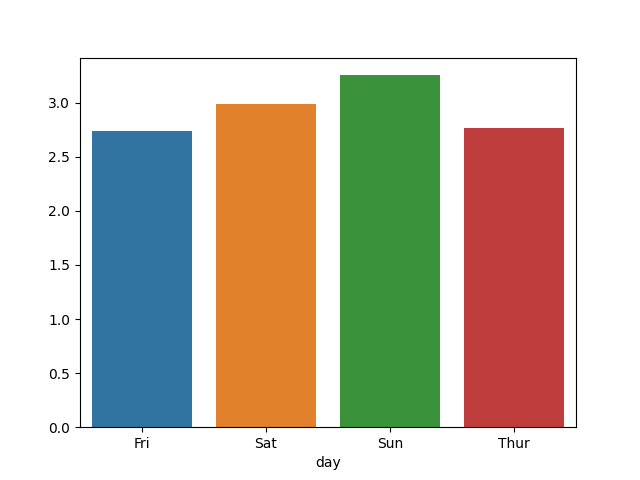
gb = df.groupby(['day'])['tip'].mean()
print(gb)
>> Fri 2.73
Sat 2.99
Sun 3.26
Thur 2.77
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sns.barplot(gb.index, gb.values)
plt.show()
# 把所有值換成數字才能分析
X['sex'].replace({'Female' : 0, 'Male' : 1}, inplace=True)
X['smoker'].replace({'Yes' : 0, 'No' : 1}, inplace=True)
X['day'].replace({'Thur' : 0, 'Fri' : 0, 'Sat' : 2, 'Sun' : 3}, inplace=True)
X['time'].replace({'Lunch' : 0, 'Dinner' : 1}, inplace=True)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split as tts
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = tts(X, y, test_size = 0.2)
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
clf = LinearRegression()
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
clf.score(X_test, y_test)
>> 0.4
