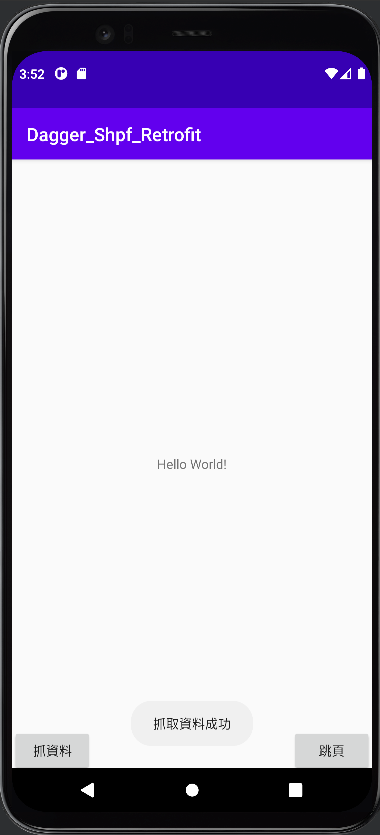
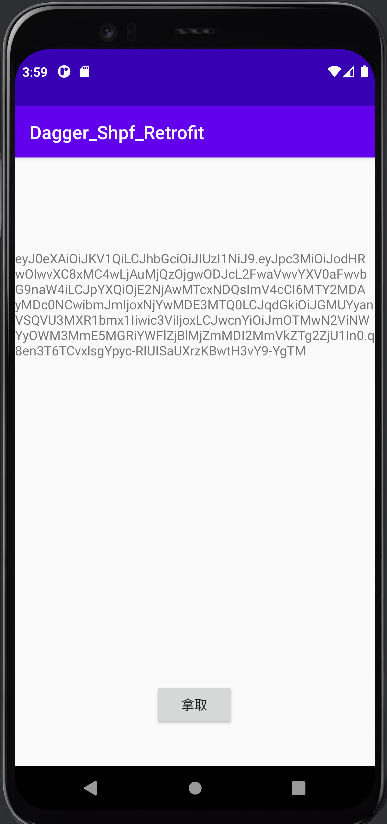
今天要接續上次所講解的Dagger2繼續延伸,而今天要介紹的是@Singleton單例的用法和@Scope的用法,下面我們講解完這兩個註解後,就來用一個簡單的抓資料存資料範例,而這個範例會使用之前講解的 Retrofit和SharedPreferences 合併!!
下面是範例建立的各個class和分類。
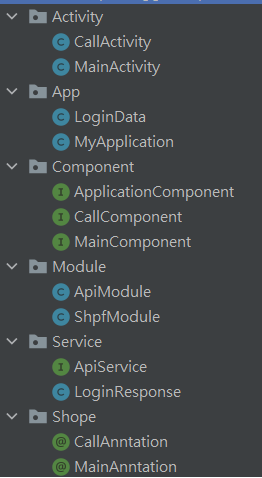
這邊我建立了兩個Scope分別是CallAnntation和MainAnntation。
看到下面的註解這三個是綁在一起的。
給CallActivity使用。
@Scope
@Documented
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface CallAnntation {
}
給MainActivity使用。
@Scope
@Documented
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface MainAnntation {
}
抓取資料的方法。
public interface ApiService {
//登入Token資料
@POST("auth/login")
Call<LoginResponse> login(@Body LoginResponse loginResponse);
}
要抓取的資料。
public class LoginResponse {
private String token;
private String account;
private String password;
//這裡是要讓上方抓API時需要帳號密碼,所以這裡我建立一個方法把帳密包起來,讓上方可以用@Body拿取帳密。
public LoginResponse(String account,String password){
this.account=account;
this.password=password;
}
/**--------------get方法---------------------*/
public String getToken() {
return token;
}
}
用來提供"建立Retrofit"的實例化,而且因為這裡使用單例的方法,所以自每次叫API都不會再build一次Retrofit。
public class APIModule {
private ApiServise apiServise;
private Retrofit retrofit;
@Singleton
@Provides
ApiServise providesApiservise(Retrofit retrofit){
return apiServise=retrofit.create(ApiServise.class);
}
@Singleton
@Provides
Retrofit providesClient(){
return retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com")
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.build();
}
這一個Module是用來實例化"LoginData"這一個class。
@Module
public class ShpfModule {
@Singleton
@Provides
LoginData provicesLoginData(){
return new LoginData();
}
}
這裡是讓Application和要使用的主件(Module)建立橋樑。
//加上單例
@Singleton
@Component(modules = {ApiModule.class, ShpfModule.class})
public interface ApplicationComponent {
void inject(MyApplication application);
/**等等會看到其他的Component想要dependencies這一個Component,
並且它們想使用這個Component所連接的Module裡實例的方法時,就必
須讓要使用的方法暴露出來。*/
ApiService providesApiService();
LoginData provicesLoginData();
}
用來連接 CallComponen和它要用的主件。
//這邊加入了先前設定的@Scope,代表這一個Component只給有註解@CallAnntation的頁面使用
@CallAnntation
//這裡用的就是dependencies不同於modules,是用來依賴於其他的Componen
@Component(dependencies =ApplicationComponent.class)
public interface CallComponent {
void inject(CallActivity callActivity);
}
用來連接 MainComponent和它要用的主件。
//跟上面一樣,這一個Component只給有註解@MainAnntation的頁面使用
@MainAnntation
//一樣的是用來依賴於ApplicationComponent的
@Component(dependencies = {ApplicationComponent.class})
public interface MainComponent {
void inject(MainActivity mainActivity);
}
這裡是實作SharedPreferences的地方,這裡之前講解過就快速帶過。
public class LoginData {
private static String TOKEN="token";
private SharedPreferences shpf;
private Context context;
/**MODE_PRIVATE 只允許該APP存取
MODE_WORLD_READABLE 所有APP都能讀取
MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE 所有APP都能存取、寫入
MODE_MULTI_PROCESS 允許多個process 同時存取*/
public void getShpf(Context context){
this.context=context;
shpf=this.context.getSharedPreferences(String.valueOf(R.string.app_name), Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
}
//存取TOKEN
public void setToken(String token){
shpf.edit().putString(TOKEN,token).apply();
}
//拿取TOKEN
public String getToken(){
return shpf.getString(TOKEN,"");
}
}
用來實現單例模式。
public class MyApplication extends Application {
//單利模式
private static MyApplication instance;
private static ApplicationComponent apiService;
private static ApplicationComponent loginData;
@Override
public void onCreate(){
super.onCreate();
instance=this;
//builder出DaggerApplicationComponent,並注入到此。
apiService =DaggerApplicationComponent.builder().apiModule(new ApiModule()).build();
apiService.inject(this);
//builder出DaggerApplicationComponent,並將注入到此。
loginData=DaggerApplicationComponent.builder().shpfModule(new ShpfModule()).build();
loginData.inject(this);
}
public static MyApplication getInstance(){
// 第一次被呼叫的時候再建立物件
if(instance==null)
instance=new MyApplication();
return instance;
}
//建立getApiService方法
public ApplicationComponent getApiService(){
return apiService;
}
//建立getLoginData方法
public ApplicationComponent getLoginData(){
return loginData;
}
}
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//設定context
private Context context = this;
ApiService apiService;
//把依賴注入
@Inject
ApiService apiService;
@Inject
LoginData loginData;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
init();
}
public void init(){
//
DaggerMainComponent.builder()
.applicationComponent(MyApplication.getInstance().getApiService())
.build()
.inject(this);
DaggerMainComponent.builder()
.applicationComponent(MyApplication.getInstance().getLoginData())
.build()
.inject(this);
apiService=apiClient.getApiService();
//把context傳入loginData。
loginData.getShpf(context);
}
按下"Button"抓取API
public void buttonClick(View view){
//呼叫API,並把帳密傳入
apiService.login(new LoginResponse("e1001","e1001"))
.enqueue(new Callback<LoginResponse>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Call<LoginResponse> call, Response<LoginResponse> response) {
//把API存入SharedPreferences
loginData.setToken(response.body().getToken());
//判斷是否抓取成功
if(response.body()!=null)
Toast.makeText(context,"抓取資料成功",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Call<LoginResponse> call, Throwable t) {
}
});
}
//按下"Button"跳到CallActivity
public void nextPage(View view){
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,CallActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
按下抓取資料 按下拿取資料