給定一個價錢數列,prices[i]代表第i天的股票價錢。
需求是求出最大利潤,一次只能持有一張股票,但可以隨買隨賣,即允許今天賣掉馬上又買
Example 1:
Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4]
Output: 7
Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 3 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
Then buy on day 4 (price = 3) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-3 = 3.
Total profit is 4 + 3 = 7.
Example 2:
Input: prices = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 4
Explanation: Buy on day 1 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
Total profit is 4.
Example 3:
Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
Output: 0
Explanation: There is no way to make a positive profit, so we never buy the stock to achieve the maximum profit of 0.
這題應用到Greedy(貪婪演算法),詳可見維基百科
簡單來說,就是每一步都貪心的選擇最好答案(局部最佳解),那結果就會是最好的(全局最佳解)
根據此演算法理論,每一天是否有正利潤(有的話就是局部最佳解),加總每一天的正利潤就得到最大利潤(全局最佳解)。
畫成下圖更容易了解,紅色部分全部加起來就是。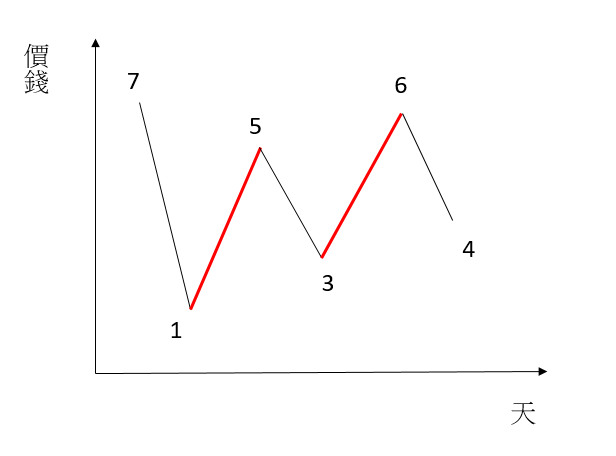
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int maxProfit = 0;
for (int i=1; i<prices.size(); i++) {
if (prices[i] > prices[i-1])
maxProfit += prices[i] - prices[i-1];
}
return maxProfit;
}
};
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
maxProfit = 0
for i in range(1, len(prices)):
if prices[i] > prices[i-1]:
maxProfit += prices[i] - prices[i-1]
return maxProfit
