Linked list是一種線性序列,其將資料儲存於節點(Node),隨機且不連續的存於記憶體中,每一個節點有指向下一個節點的指標。(見圖1)其好處是,不像前面講的陣列、列表或是tuple需要連續的記憶體空間或預設陣列大小,Linked list可以充分利用記憶體空間。(見圖2)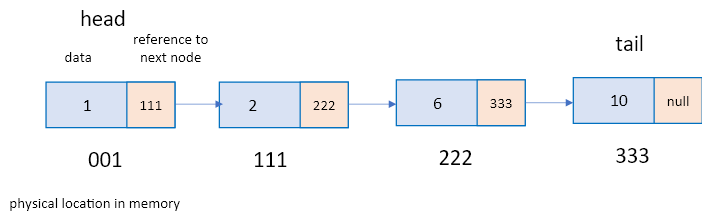
圖1.Linked list 的每個節點會有個資料(value)和指標(Pointer)描述下一個節點的位子(指向下一個節點)。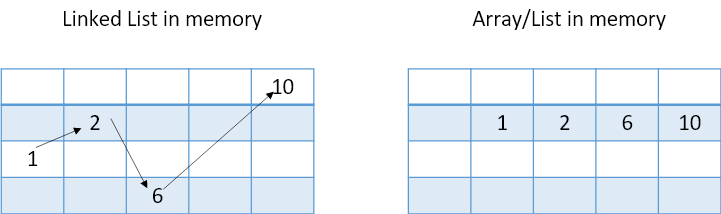
圖2.陣列在記憶體中需要資料為連續儲存,且需要預定陣列的大小。而Linked List 的資料在記憶體中儲存位子為隨機且不需連續。
今天就先帶大家看Singly Linked List(單向鏈結串列)和Circular Singly Linked List(環狀單向鏈結串列),兩者差異如圖所示環狀單向鏈結串列最後一筆資料,會指向最前面一筆資料,因如環狀,故得其名。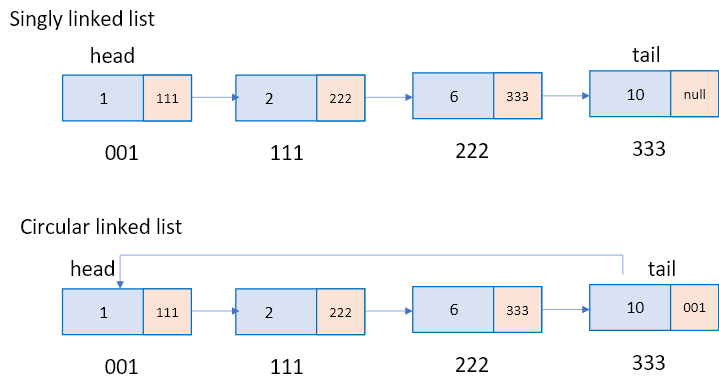
圖3.單向鏈結串列和環狀單向鏈結串列。
Singly Linked List (單向鏈結串列)
下面我們來看一下Singly Linked List(單向鏈結串列)的程式碼,大家可以自己在VScode或是jupyter notebook玩一次,建議一個方法一個方法的自己試一次
# 節點(Node)內除了有資料(value)外還需要有個pointer指向下個 Node
class Node:
def __init__(self,value):
self.value=value
self.next=None
class singly_linked_list:
def __init__(self):
self.head=None
self.tail=None
self.length=0
# 附加新的值在linked list的最後 time complexity: O(1), space complexity: O(1):
def append(self,value):
new_node=Node(value)
#假使linked list是空的,head和tail都會指向這個新增加的節點
if self.head is None:
self.head=new_node
self.tail=new_node
else:
#改tail的指向和重新把tail定位新增的節點就行囉~
self.tail.next=new_node
self.tail=new_node
self.length+=1
# 附加新的值在linked list的最前面: time complexity: O(1), space complexity: O(1)
def prepend(self,value):
new_node=Node(value)
if self.head is None:
self.head=new_node
self.tail=new_node
else:
new_node.next=self.head
self.head=new_node
self.length+=1
#插入值在linked list中: time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def insert(self,index,value):
new_node=Node(value)
if index<0 or index>self.length:
return False
#time complexity: O(1)
elif self.length==0:
self.head=new_node
self.tail=new_node
#time complexity: O(1)
elif index==0:
new_node.next=self.head
self.head=new_node
else:
#time complexity: O(n)因為有個loop
temp_node=self.head
for _ in range(index-1):
temp_node=temp_node.next
new_node.next=temp_node.next
temp_node.next=new_node
self.length+=1
return True
#將linked list中的值全部讀取一遍: time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def traverse(self):
current=self.head
while current:
print(current.value)
current=current.next
#在linked list中搜尋特定值回傳其位子: time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def search(self,target):
current=self.head
index=0
while current:
if current.value==target:
return index
current=current.next
index+=1
return -1
#在linked list中取得特定位置的值(according to index):time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def get(self,index):
if index==-1:
return self.tail
elif index < 0 or index >= self.length:
return None
else:
current=self.head
for _ in range(index):
current=current.next
return current
#更改值:time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def set_value(self,index,value):
temp=self.get(index)
if temp:
temp.value=value
return True
return False
#刪除linked list第一個值並回傳: time complexity: O(1), space complexity: O(1)
def pop_first(self):
if self.length==0:
return None
popped_node=self.head
if self.length==1:
self.head=None
self.tail=None
else:
self.head=self.head.next
popped_node.next=None
self.length -= 1
return popped_node
#刪除linked list的末端值並回傳: time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def pop(self):
popped_node=self.tail
if self.length==1:
self.head=self.tail=None
else:
temp=self.head
while temp.next is not self.tail:
temp=temp.next
self.tail=temp
temp.next=None
self.length-=1
return popped_node
# 移除linked list中特定位置的值: time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def remove(self,index):
if index>=self.length or index<0:
return None
if index ==0:
return self.pop_first()
if index==self.length-1 or index==-1:
return self.pop()
prev_node=self.get(index-1)
popped_node=prev_node.next
prev_node.next=popped_node.next
popped_node.next = None
self.length -= 1
return popped_node
# 刪除整個linked list
def delete_all(self):
self.head=None
self.tail=None
self.length=0
return 'The linked list got empty !!!'
# 設定print function 要印出的東西 (optional)
def __str__(self):
temp_node=self.head
result=''
while temp_node:
result+=str(temp_node.value)
if temp_node.next is not None:
result+='->'
temp_node=temp_node.next
return result
# 設定物件在for loop要吐出的element
def __iter__(self):
temp_node=self.head
while temp_node:
yield temp_node
if temp_node ==self.tail:
break
else:
temp_node=temp_node.next
SLL=singly_linked_list()
SLL.append(10)
SLL.append(20)
SLL.append(30)
print(SLL)
SLL.prepend(40)
SLL.prepend(50)
print(SLL)
SLL.insert(3,70)
print(SLL)
SLL.set_value(2,100)
print(SLL)
print(SLL.search(100))
print(SLL.pop_first().value)
print(SLL)
print(SLL.pop().value)
print(SLL)
SLL.remove(2)
print(SLL)
print(SLL.delete_all())
print(SLL)
>> 10->20->30
>> 50->40->10->20->30
>> 50->40->10->70->20->30
>> 50->40->100->70->20->30
>> 2
>> 50
>> 40->100->70->20->30
>> 30
>> 40->100->70->20
>> 40->100->20
>> The linked list got empty !!!
# 這裡順便複習一下昨天的__iter__,它定義loop裡要output的東西
SLL=singly_linked_list()
SLL.append(10)
SLL.append(20)
SLL.append(30)
[x.value for x in SLL]
>>[10, 20, 30]
Circular Singly Linked list (環狀單向鏈結串列)
其self.tail會指向self.head,見下面程式碼
class Node:
def __init__(self,value):
self.value=value
self.next=None
class circular_singly_linked_list:
def __init__(self):
self.head=None
self.tail=None
#time complexity: O(1), space complexity: O(1)
def append(self,value):
new_node=Node(value)
if self.head==None:
self.head=new_node
self.tail=new_node
else:
self.tail.next=new_node
new_node.next=self.head
self.tail=new_node
#time complexity: O(1), space complexity: O(1)
def prepend(self,value):
new_node=Node(value)
if self.head==None:
self.head=new_node
self.tail=new_node
else:
new_node.next=self.head
self.tail.next=new_node
self.head=new_node
#time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def insert(self,index,value):
new_node=Node(value)
if index==0:
self.prepend(value)
elif index==-1:
self.append(value)
else:
temp_node=self.head
for i in range(index-1):
temp_node=temp_node.next
new_node.next=temp_node.next
temp_node.next=new_node
# time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def get(self,index):
if self.head==None:
return 'There is no value in CSLL'
elif index==-1:
return self.tail
else:
loc=0
temp_node=self.head
while temp_node:
if loc==index:
return temp_node
elif temp_node==self.tail:
return False
else:
loc+=1
temp_node=temp_node.next
#time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def set_value(self,index,value):
node=self.get(index)
if node:
node.value=value
return 'The value is set'
else:
return 'The index is out of range'
#time complexity: O(1), space complexity: O(1)
def pop_first(self):
if self.head==None:
return 'There is no value in CSLL'
else:
popped_value=self.head.value
self.tail.next=self.head.next
self.head=self.head.next
return popped_value
#time complexity:O(n), space complexity:O(1)
def pop(self):
if self.head==None:
return 'There is no value in CSLL'
else:
temp_node=self.head
while temp_node.next is not self.tail:
temp_node=temp_node.next
popped_value=self.tail.value
temp_node.next=self.head
self.tail=temp_node
return popped_value
# time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def traverse(self):
if self.head==None:
return 'There is no value in CSLL'
else:
temp_node=self.head
while temp_node:
print(temp_node.value)
if temp_node==self.tail:
break
else:
temp_node=temp_node.next
# time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def search(self,target):
if self.head==None:
return 'There is no value in CSLL'
else:
temp_node=self.head
index=0
while temp_node:
if temp_node.value==target:
return index
elif temp_node.next==self.head:
break
else:
index+=1
temp_node=temp_node.next
return 'There is no such value in this CSLL'
#time complexity: O(n), space complexity: O(1)
def delete(self,target):
if self.head==None:
return 'There is no value in CSLL'
else:
temp_node=self.head
while temp_node is not self.tail:
if temp_node.next.value==target:
temp_node.next=temp_node.next.next
return 'The value got successfully deleted!'
else:
temp_node=temp_node.next
return 'There is no such value in the list'
# time complexity: O(1)
def deleteall(self):
self.head=None
self.tail=None
return 'The linked list got clear successfully!'
# print function-time complexity: O(n), space: O(1)
def __str__(self):
result=''
temp_node=self.head
while temp_node:
result+=str(temp_node.value)
if temp_node==self.tail:
return result
else:
result+='->'
temp_node=temp_node.next
return result
CSLL=circular_singly_linked_list()
CSLL.append(10)
CSLL.append(20)
CSLL.append(30)
print(CSLL)
CSLL.prepend(40)
CSLL.prepend(50)
print(CSLL)
CSLL.insert(3,70)
print(CSLL)
>>10->20->30
>>50->40->10->20->30
>>50->40->10->70->20->30
介紹完singly linked list由於篇幅關係,明天再為大家介紹doubly linked list,大家可以先消化一下。
參考資料:
The Complete Data Structures and Algorithms Course in Python from Udemy
