回溯法(backtracking)是一種用解決問題的演算法,它通常會窮舉不同的可能性,並在達到某條件時回退(backtrack)到達之前的狀態,接著繼續搜索。因為它達到特定條件會退回的特性,它會比單純的窮舉法(brute force)來得快。透過state space tree可能更容易理解: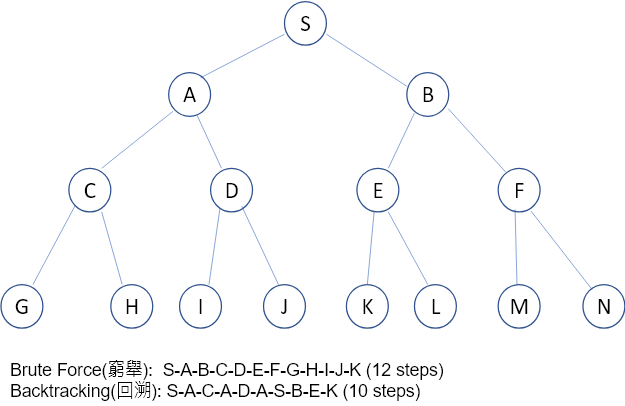
圖1,假使我們今天要從S點到K點,如果是窮舉法需要12步,如果是回溯法只需要10步。
回溯法比較經典的問題應該就是N Queens problem(N個皇后問題):
今天我們要放N個皇后在NxN的棋盤上,為了不使皇后間打架,規則是皇后們1.不能在同一列 2.不能在同一行 3.不能彼此的對角線上。我們直接來看程式碼:
class NQueens:
def __init__(self,n):
self.n=n
self.chess_table=[[0 for i in range(n)] for j in range(n)]
def __str__(self):
res=''
for i in range(self.n):
for j in range(self.n):
if self.chess_table[i][j]==1:
res+=' Q '
else:
res+=' - '
res+='\n'
return res
# 檢查是否可以放queen,回傳True-> safe 可以; False -> 不行
def is_place_safe(self,row_index,col_index):
# 檢查同一行
for i in range(self.n):
if self.chess_table[row_index][i]==1:
return False
# top left to right bottom (左上對角線)
j=col_index
for i in range(row_index,-1,-1):
if i<0:
break
if self.chess_table[i][j]==1:
return False
j=j-1
# top right to bottom left (從點到左下)
j=col_index
for i in range(row_index,self.n):
if i<0:
break
if self.chess_table[i][j]==1:
return False
j=j-1
return True
def solve(self,col_index):
# 0,1,2,3
if col_index==self.n:
return True
for row_index in range(self.n):
if self.is_place_safe(row_index,col_index):
self.chess_table[row_index][col_index]=1
if self.solve(col_index+1):
return True
self.chess_table[row_index][col_index]=0
return False
def solve_NQueens(self):
if self.solve(0):
print(self)
else:
print('There is no solution for the problem')
test=NQueens(4)
test.solve_NQueens()
>> - - Q -
Q - - -
- - - Q
- Q - -
參考資料:
The Complete Data Structures and Algorithms Course in Python (udemy)
