今天我們要實做 Feed Forward Network
前饋式神經網路是一種人工神經網路結構,也稱為前饋網路或前向傳播網路。
它是一種最基本的神經網路結構,通常由多個神經元層組成,信息傳遞方向是單向的,從輸入層經過中間隱藏層,最終到達輸出層。
在這種結構中,每一層的神經元與下一層的神經元之間建立權重連接,用於權重的調整和信息的傳遞。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import tqdm
首先我們先導入所需要的函式庫
train_x, train_y = np.load('/kaggle/input/custom-fnn/train_x.npy'), np.load('/kaggle/input/custom-fnn/train_y.npy')
test_x, test_y = np.load('/kaggle/input/custom-fnn/test_x.npy'), np.load('/kaggle/input/custom-fnn/test_y.npy')
checkpoint = np.load('/kaggle/input/custom-fnn/weights.npy', allow_pickle=True).item()
init_weights = checkpoint['w']
init_biases = checkpoint['b']
接著,我們讀取資料集 train_x.npy、train_y.npy、test_x.npy、test_y.npy
npy 檔是 numpy 專用的二進制文件,用於儲存數據
之後讀取初始網路權重 weight.npy
# number of layers: 3
# number of neurons in each layer (in order): 2048, 512, 5
# activation function for each layer (in order): relu, relu, softmax
# number of training epochs: 30
# learning rate: 0.01
# batch size: 200
cache = {}
params = {
"w1": init_weights[0], # shape: (784, 2048)
"b1": init_biases[0], # shape: (2048, 1)
"w2": init_weights[1], # shape: (2048, 512)
"b2": init_biases[1], # shape: (512, 1)
"w3": init_weights[2], # shape: (512, 5)
"b3": init_biases[2] # shape: (5, 1)
}
# define the activation function
def relu(x):
return np.maximum(0, x)
def softmax(x):
exps = np.exp(x - np.max(x, axis=1, keepdims=True))
return exps / np.sum(exps, axis=1, keepdims=True)
def drelu(x):
return np.where(x > 0, 1, 0)
def cross_entropy_loss(y_hat, y_true):
"""
y_hat: predicted label, shape: (batch_size, 5)
y_true: true label, shape: (batch_size, 5)
cross_entropy_loss = -1/m * np.sum(y_true * np.log(y_hat))
"""
y_true = np.eye(5)[y_true]
y_hat = softmax(y_hat)
return -1/y_true.shape[0] * np.sum(y_true * np.log(y_hat + 1e-8))
def accuracy(y_hat, y_true):
y_hat = np.argmax(y_hat, axis=1)
return np.sum(y_hat == y_true) / len(y_true)
def forward(x):
"""
x: input data, shape: (784, batch_size)
z = x @ w + b
a = relu(z)
"""
cache['x'] = x
cache['z1'] = cache['x'] @ params['w1'] + params['b1'] # (200, 784) @ (784, 2048) + (2048, 1) = (200, 2048)
cache['a1'] = relu(cache['z1']) # (200, 2048)
cache['z2'] = cache['a1'] @ params['w2'] + params['b2'] # (200, 2048) @ (2048, 512) + (512, 1) = (200, 512)
cache['a2'] = relu(cache['z2']) # (200, 512)
cache['z3'] = cache['a2'] @ params['w3'] + params['b3'] # (200, 512) @ (512, 5) + (5, 1) = (200, 5)
cache['a3'] = softmax(cache['z3']) # (200, 5)
return cache['a3']
def back_propagate(y, y_hat):
"""
y: true label, shape: (batch_size, 5)
y_hat: predicted label, shape: (batch_size, 5)
dz = (1./m) * (y_hat - y)
dw = a.T @ dz
"""
y = np.eye(5)[y]
dz3 = (1./y.shape[0]) * (y_hat - y) # (200, 5)
dw3 = cache['a2'].T @ dz3 # (512, 200) @ (200, 5) = (512, 5)
db3 = np.sum(dz3, axis=0).T # (5, 1)
dz2 = dz3 @ params['w3'].T * drelu(cache['z2']) # (200, 5) @ (5, 512) * (200, 512) = (200, 512)
dw2 = cache['a1'].T @ dz2 # (2048, 200) @ (200, 512) = (2048, 512)
db2 = np.sum(dz2, axis=0).T # (512, 1)
dz1 = dz2 @ params['w2'].T * drelu(cache['z1']) # (200, 512) @ (512, 2048) * (200, 2048) = (200, 2048)
dw1 = cache['x'].T @ dz1 # (784, 200) @ (200, 2048) = (784, 2048)
db1 = np.sum(dz1, axis=0).T # (2048, 1)
grads = {
"w1": dw1,
"b1": db1,
"w2": dw2,
"b2": db2,
"w3": dw3,
"b3": db3,
}
return grads
首先,定義神經網路的模型,這模型會用於分類問題:
接下來是模型的參數(權重和偏差)的初始化,這些參數將在訓練過程中逐漸調整以適應訓練數據。
程式碼中定義了幾個函數:
relu(x):計算 ReLU(修正線性單元)激活函數。softmax(x):計算 softmax 激活函數,用於將模型的輸出轉換為類別概率分佈。drelu(x):計算 ReLU 激活函數的導數。cross_entropy_loss(y_hat, y_true):計算交叉熵損失,用於評估模型的性能。accuracy(y_hat, y_true):計算模型的準確率。接下來是模型的前向傳播和反向傳播函數的定義:
forward(x):計算從輸入數據到模型輸出的前向傳播過程,包括線性計算和激活函數的應用。back_propagate(y, y_hat):計算反向傳播過程,用於計算梯度並更新模型的權重和偏差。反向傳播過程,我們使用 mini-batch SGD (stochastic gradient descent) 來更新參數
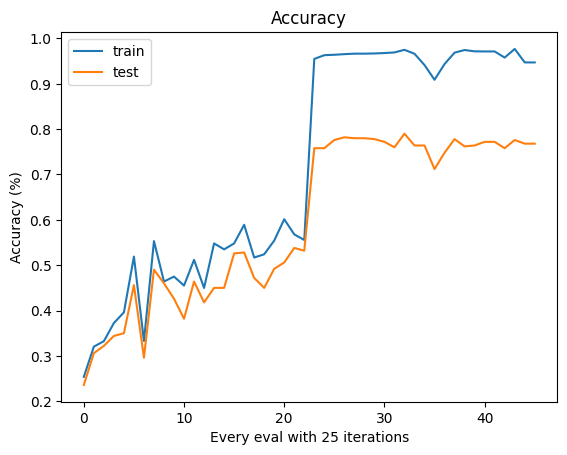
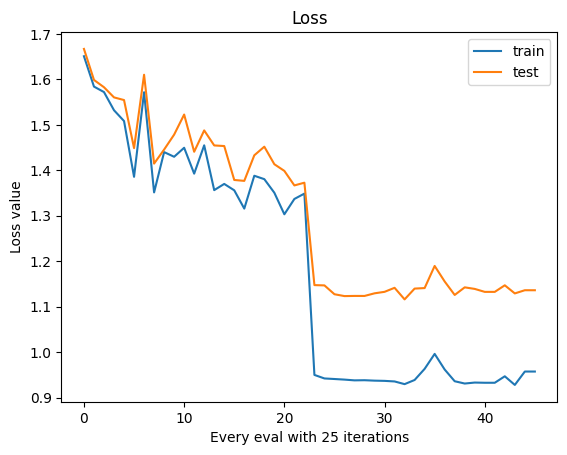
詳細 Notebook 可以參考 Kaggle Notebook
明天要進入真實實戰部份
我們會透過 Kaggle Dataset Natural Language Processing with Disaster Tweets 來演練
![]()
