在設計完畫面後,也大概確認了整個專案的頁面功能,在設置完資料夾結構後,就是進入前端後端實作的階段,大部分的頁面我是前後端功能同步進行,但為了避免畫面凌亂,會以前後端分離的方式做介紹。接下來的步驟我會先進行後端,包括 Model 的架構介紹、 API 需求與格式、錯誤處理的方向說明。
在 Prisma 的章節中有稍微帶過 Model 的設置方式,以及簡短的展示了我專案中資料庫所需要的 Table 及欄位,這段落中會詳細的說明各個資料的用意,以及資料間的關聯。
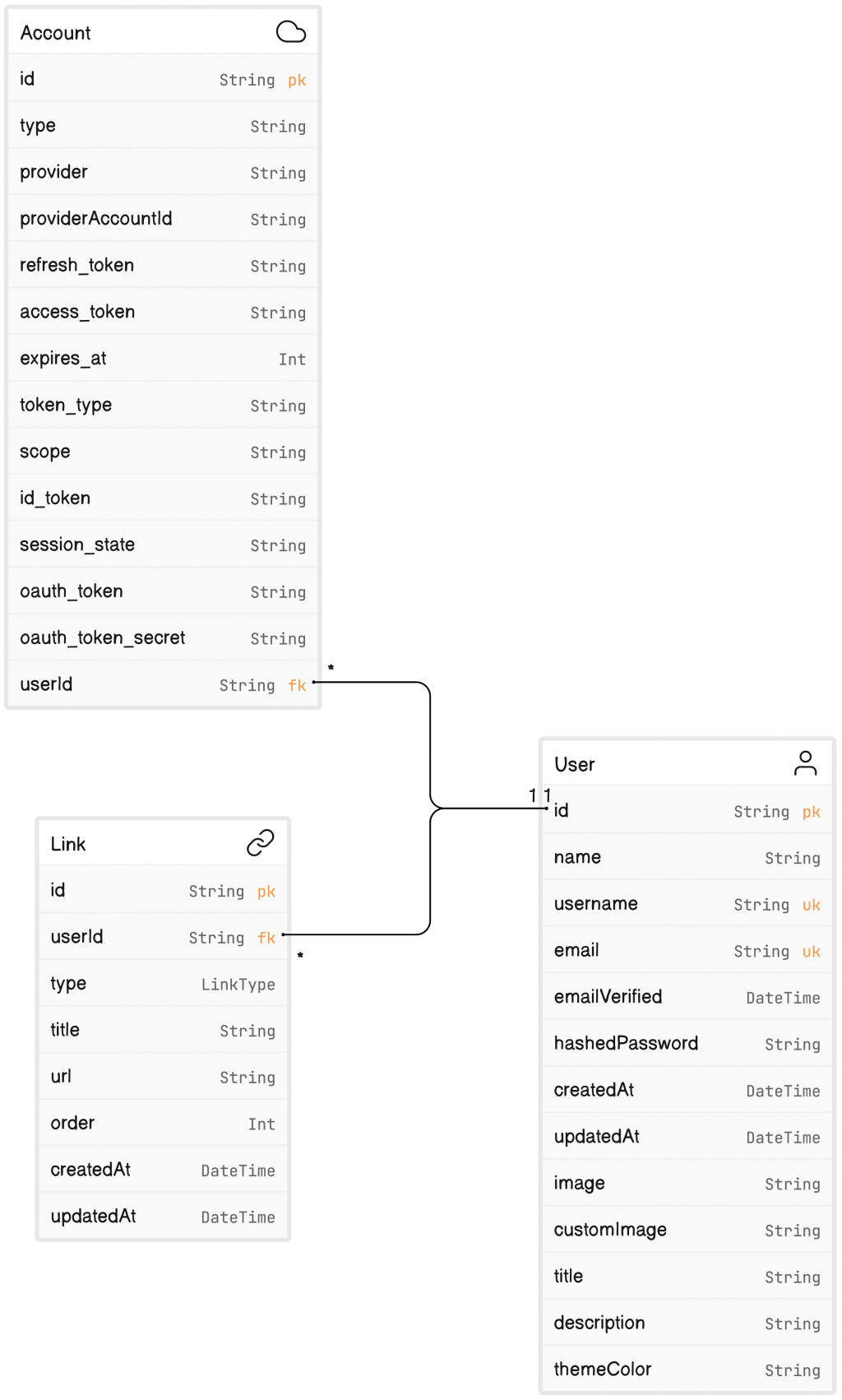
在 MongoDB 中一張 Table 以 Collection 為定義,在專案中設置了三個 Collection,User、Account 及 Link:
定義用戶的個人資訊,其中 username 及 email 為唯一值
| Index | Data Type | Field Name | Nullable | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Key | ObjectId | id | False | 唯一且作為用戶的識別碼 |
| String | name | False | 用戶的名字,此為第三方驗證所設定的 name | |
| Unique | String | username | False | 用戶名,唯一值 |
| Unique | String | False | 用戶的電子郵件,也是唯一值 | |
| DateTime | emailVerified | True | 用戶驗證其電子郵件的日期和時間 | |
| String | hashedPassword | True | 用戶的加密密碼 | |
| DateTime | createdAt | False | 用戶建立的日期和時間 | |
| DateTime | updatedAt | False | 用戶最後更新的日期和時間 | |
| String | image | True | 用戶的圖片,此為第三方驗證所設定的圖片 | |
| String | customImage | True | 用戶的自定義圖片 | |
| String | title | True | 用戶的標題 | |
| String | description | True | 用戶的描述或簡介 | |
| String | themeColor | True | 用戶設定的主題顏色 |
定義用戶的帳戶資訊,主要作為第三方驗證的帳戶設置。一個 user 可以有多個 account,並以 userId 與 User 的 id 做對應。
| Index | Data Type | Field Name | Nullable | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Key | ObjectId | id | False | 唯一且作為帳戶識別碼 |
| Foreign Key | ObjectId | userId | False | 與 User 表的 id field 相關聯,表示這個帳戶屬於哪個用戶 |
| String | type | False | NextAuth.js 定義的帳戶類型 | |
| 例如:"oauth" | "email" | "credentials” | ||
| String | provider | False | 帳戶的提供商(例如,Google、Facebook 等) | |
| String | providerAccountId | False | 提供商給該帳戶的獨特識別碼 |
定義一個連結的資訊。一個 user 可以有多個 link,並以 userId 與 User 的 id 做對應。
| Index | Data Type | Field Name | Nullable | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Key | ObjectId | id | False | 唯一且作為連結的識別碼 |
| Foreign Key | ObjectId | userId | False | 與 User 表的 id field 相關聯,表示這個連結屬於哪個用戶 |
| String | type | False | 連結的類型。website 或是各種社群類型 | |
| String | title | Depends | 連結的標題。若 type 為 website 則需自定義,如果是社群,標題為社群的名稱。 | |
| String | url | False | 實際的連結網址 | |
| Integer | order | False | 表示連結排序順序的數字 | |
| DateTime | createdAt | False | 連結建立的日期和時間 | |
| DateTime | updatedAt | False | 連結最後更新的日期和時間 |
當我們完成資料庫的 Collections / Table 定義後,下一步是根據具體需求來設計 API。根據 Next.js 的 Data Fetching 章節,由於 Prisma ORM 不支援 Server Component 的 fetch 功能,我們選擇直接從資料庫獲取資料以實現 GET 方法。對於其他方法,我們採用 RESTful API 作為我們的通訊協議風格,並在 Route Handler 中進行具體實現。
依據頁面的需求,將分為三個部分,登入/註冊、後台設定及前台呈現。
登入註冊的需求除了已經在 NextAuth 中示範過的 OAuth 還需要以帳號密碼的註冊 API,需要接收 username、email、password 作為 request body,其中 password 必須經過加密處理後再寫入資料庫。
後台設定頁面分為基本設定、帳號設定及連結設定,其中基本設定與帳號設定的資料來源皆為 User Collection,而連結設定則是與 Link Collection 相關。
前台設定相對簡單,目前只需要顯示用戶的圖片、標題、簡介、主題色及所有設定的連結,主要是以用戶的 username 獲得這些資訊。
以下列出目前除了 GET 以外的 API 設計。
POST /register:建立一個新的用戶,用於註冊用戶。
PUT /users/{id}:更新特定 ID 的用戶資訊,用於基本設定及帳戶設定
POST /users/{id}/links:新增特定 ID 用戶下的一個連結,用於連結設定新增連結。
PATCH /users/{id}/links:更新特定 ID 用戶下的所有連結,用於連結設定中更新連結順序。
PUT /users/{id}/links/{linkId}:更新特定 ID 用戶下的指定連結,用於連結設定編輯指定連結。
DELETE /users/{id}/links/{linkId}:刪除特定 ID 用戶下的指定連結,用於連結設定的刪除指定連結。
除了 GET 之外的請求皆會以 Next.js 13 的 Route Handler 完成,在設置時非常簡單,只需要在 route.ts 檔案中定義請求方式 GET / POST / PUT / DELETE 等等方法,其中接收 request 及 params 即可編寫其中的業務邏輯,最後回傳 NextResponse.json,在開發上相對變得非常直觀。接下來就依序上方的 API 設計進行實作吧!
getCurrentUser在建立 API 之前先介紹專案中進行身分驗證的方法,從 session 中取得當前活躍的 user,NextAuth.js 章節中有介紹在 server 端以 getServerSession 取得 session,所以相同的藉由這個方法取得當前 user 並回傳。
import { getServerSession } from 'next-auth'
import { authOptions } from '@/app/api/auth/[...nextauth]/route'
import prisma from '@/libs/prismadb'
export async function getSession() {
return await getServerSession(authOptions)
}
export async function getCurrentUser() {
try {
const session = await getSession()
// 驗證是否有取得 session 資料
if (!session?.user?.email) return null
// 以 session 取得的資料再回去資料庫中比對並找到該 user
const currentUser = await prisma.user.findUnique({
where: {
email: session.user.email as string
}
})
// 找不到一樣回傳 null
if (!currentUser) return null
// 由 server 端傳給 client 端的資料必須為可序列化,所以要將日期轉為一般 string
return {
...currentUser,
createdAt: currentUser.createdAt.toISOString(),
updatedAt: currentUser.updatedAt.toISOString(),
emailVerified: currentUser.emailVerified?.toISOString() || null
}
} catch (error) {
// 這不是串接 API 而是直接與 db 溝通,所以直接回傳 null
return null
}
}
POST /register首先定義 request Method PUT ,由 request 取得 body ,經過業務邏輯處理後再回傳資料庫結果至 NextResponse.json 並設定回傳 message。在實作時會以 try…catch 進行錯誤捕捉,所以若有錯誤時,以建立一個 response 實例,設定錯誤訊息及 status code。
import bcrypt from 'bcrypt'
import prisma from '@/libs/prismadb'
import { NextResponse } from 'next/server'
export async function POST(request: Request) {
try {
const body = await request.json()
const { email, username, password } = body
<-------- 業務邏輯 -------->
const user = await prisma.user.create({
...
})
return NextResponse.json(user, {message:'success'})
} catch (error) {
// 建立一個 response 實例,status code 為 500
return new NextResponse('Internal Error', { status: 500 })
}
}
在處理資料時可以先將 request 中取得的資料先驗證,將請求的資料一律當作未知的,經過一層的過濾,逐一檢查後再接續著業務邏輯處理。
首先註冊的邏輯中,email, username, password 三位一體,缺一不可,所以先進行第一階段驗證,並回傳錯誤。
if (!email || !username || !password)
return new NextResponse('Missing Info', { status: 400 })
接下來確認來源資料的型別,這時候我們又可以使用 zod 幫我們驗證!
const validateSchema = z.object({
email: z.string().email(),
username: z.string(),
password: z.string(),
})
// 將 body 進行驗證,由於需要知道錯誤訊息,所以使用 safeParse
const result = validateSchema.safeParse(body)
if(!result){
throw new z.ZodError(result.error.issues)
}
密碼是極其敏感的資料,需要嚴格保護。在將密碼存入資料庫前,我使用 bcrypt 套件進行 hash 加密。此套件不僅加密密碼,還自動提供了加鹽(salting)功能,以增強安全性。
const hashedPassword = await bcrypt.hash(password, 12)
當經過驗證及加密處理,最後就可以將資料寫進資料庫中,這邊以 prisma 提供的 create 方法作為資料新增。
const user = await prisma.user.create({
data: {
email,
username,
hashedPassword
}
})
PUT /users/{id}一樣先定義 request Method PUT ,參數除了 request 之外,因為有傳 id 所以要定義 params 的型別。{id} 中的變數是什麼 params 的屬性就是什麼。getCurrentUser 確認身分後再取得 body 資料。
import { NextResponse } from 'next/server'
import { getCurrentUser } from '@/actions/getCurrentUser'
import prisma from '@/libs/prismadb'
export async function PUT(
req: Request,
{ params }: { params: { id: string } }
) {
const currentUser = await getCurrentUser()
if (!currentUser) return new NextResponse('Unauthorized', { status: 401 })
<-------- 業務邏輯 -------->
return NextResponse.json({ data, message: 'success' })
}
驗證方法如同註冊的驗證方法,但這支 API 比較特別的是基本設定及帳戶設定都會用到,而且值為 optional 所以只需要驗證類型跟特殊設定即可。
更新資料的方法以 update 實現,而且先必須先以識別碼 - id 搜尋指定用戶(使用 where 語法),再寫入更新的值:
const data = await prisma.user.update({
where: {
id: params.id // 指定特定 id user
},
data: {
title,
description,
customImage,
themeColor,
updatedAt: new Date() // 每次更新都寫入新的更新時間
}
})
POST /users/{id}/links建立設定及 getCurrentUser 的身分驗證如同上面的方法,這部分不再贅述。直接跳到驗證的步驟,比較需要注意的是 order 的驗證,排序的功能在後端邏輯中只做驗證不做排序,而驗證方法是在資料庫中搜尋同一用戶的 links 中是否有相同 order 的 link,如果有就回傳錯誤:
const checkOrder = await prisma.link.findFirst({
where: {
order: order,
userId: params.id,
},
});
if (checkOrder) return new NextResponse("order is duplicate", { status: 400 });
PATCH /users/{id}/links由於是更新連結中單一欄位,所以可以使用 for loop 做修改更新:
const updatedLinks = [];
for (const link of links) {
const updatedLink = await prisma.link.update({
where: {
id: link.id,
},
data: {
order: link.order,
},
});
updatedLinks.push(updatedLink);
}
// 前端需要取得更新後的資料,所以要回傳結果
return NextResponse.json({ data: updatedLinks, message: "success" });
PUT /users/{id}/links/{linkId}相同的基本建立及身分驗證,此處因為有回傳兩個 params - id 及 linkId ,所以驗證步驟需要確保這兩個值都有收到才能繼續執行:
if (!id || !linkId) return new NextResponse("Bad Request", { status: 400 });
而此處 id 主要用途為確認請求方的 id 等於當前用戶的 id ,所以多這一層驗證:
if (id !== currentUser.id)
return new NextResponse("Bad Request", { status: 400 });
接著通過驗證後,就可以將尋找指定 linkId 更新 link Collection
const data = await prisma.link.update({
where: {
id: linkId,
},
data: {
order,
title,
type,
url,
},
});
DELETE /users/{id}/links/{linkId}刪除的 API 不需要傳遞 request body 只需要由 params 的值來執行,同樣的經過身分驗證後再確認 PUT 方法的 step 1 及 step 2 後,即可調用 prisma 的 delete 方法將指定的 link 刪除:
const data = await prisma.link.delete({
where: {
id: linkId,
},
});
由於 prisma 等 ORM 尚為支援 server component 的 fetch 功能,而專案中幾乎所有資料取得皆在 server 端執行,所以取得資料的部分會以 get action 的方法實作,如同上一段落中的 getCurrentUser 我們還需要在連結設定的部分取得 links 以及前台頁面以 username 取得當前頁面所有資訊:
如同其他 HTTP 請求,在取得 links 之前也需要進行身分驗證,在這些 actions 中,由於不是 API 請求,所以如有任何錯誤都將回傳 null 。在驗證通過後,我們就以 findMany 語法搜尋特定 user id 的所有 link,並且!回傳時依據 link 的 order 屬性,以 orderBy 語法排列後回傳:
const links = await prisma.link.findMany({
where: {
userId: currentUser.id,
},
orderBy: {
order: "asc",
},
});
前台是所有訪客皆可以訪問的頁面,而取得資料的方法是將頁面網址取得的 params - username 作為 getUserByUsername action 的參數,並且取得 User 及 Link 兩個 collection 再一並回傳資料:
以 username 先取得 user 的資料
const user = await prisma.user.findUnique({
where: {
username,
},
});
if (!user) return null // 錯誤由前端進行判斷
由取得的 user 再去搜尋該 user 的所有 links,再回傳兩者的結合。
const links = await prisma.link.findMany({
where: {
userId: user.id,
},
});
全文可參考 github:
https://github.com/ysl0628/2023-ithelp/tree/main/day-20
範例程式碼:
在後端的世界,雖然有接觸過一點 Node.js 的基礎,但實戰以及規範都不是這麼熟悉,請教隊友後,得到的結論是越嚴謹越好,把所有來源當作未知的未知,所以必須經過層層的把關驗證,而這些驗證只是經過一層過濾,濾紙不夠細膩還是會放走那些危險因子,所以下章節除了接續這篇的錯誤處理之外,也要帶讀者們了解使用 headers 增加應用程式的安全性!

