You are given a doubly linked list, which contains nodes that have a next pointer, a previous pointer, and an additional child pointer. This child pointer may or may not point to a separate doubly linked list, also containing these special nodes. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure as shown in the example below.
Given the head of the first level of the list, flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level, doubly linked list. Let curr be a node with a child list. The nodes in the child list should appear after curr and before curr.next in the flattened list.
Return the head of the flattened list. The nodes in the list must have all of their child pointers set to null.
Example 1:
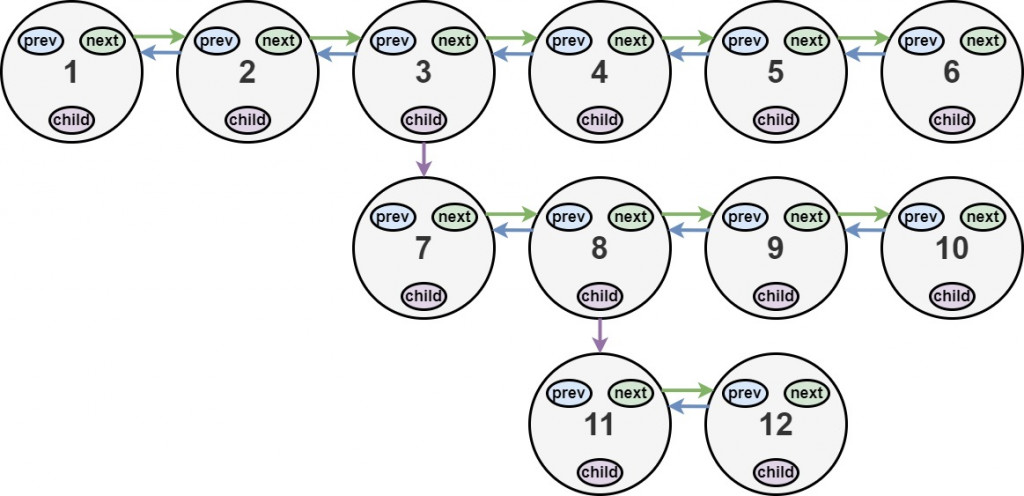
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12]
Output: [1,2,3,7,8,11,12,9,10,4,5,6]
Explanation: The multilevel linked list in the input is shown.
After flattening the multilevel linked list it becomes:

Example 2:
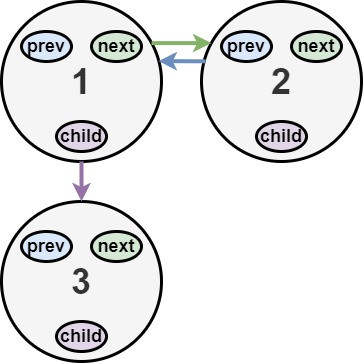
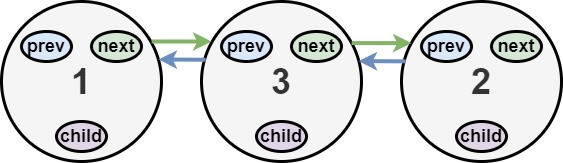
Input: head = [1,2,null,3]
Output: [1,3,2]
Explanation: The multilevel linked list in the input is shown.
After flattening the multilevel linked list it becomes:
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Explanation: There could be empty list in the input.
Constraints:
1000.1 <= Node.val <= 105
How the multilevel linked list is represented in test cases:
We use the multilevel linked list from Example 1 above:
1---2---3---4---5---6--NULL
|
7---8---9---10--NULL
|
11--12--NULL
The serialization of each level is as follows:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null]
[7,8,9,10,null]
[11,12,null]
To serialize all levels together, we will add nulls in each level to signify no node connects to the upper node of the previous level. The serialization becomes:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, null]
|
[null, null, 7, 8, 9, 10, null]
|
[ null, 11, 12, null]
Merging the serialization of each level and removing trailing nulls we obtain:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12]
這個題目是雙向鏈結陣列的變形,題目給的鏈結陣列是單向的,解題的時候除了多了一個child要進行判斷,回傳值還要變成雙向,但解法也不難,看到這種階層感的題目第一個想法就是要用遞迴,遞迴寫好接下來就補一些小判斷。
Runtime: 0 ms (100%)
Memory Usage: 40.3 MB (68.81%)
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node prev;
public Node next;
public Node child;
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node flatten(Node head) {
if (head != null) {
Node temp = head;
getChild(temp);
}
return head;
}
public Node getChild(Node node) {
Node curr = node;
Node prevCurr = curr.prev;
Node nextCurr = curr.next;
Node child = null;
while (curr.next != null) {
if (curr.child != null) {
child = curr.child;
child.prev = curr;
Node childTail = getChild(child);
curr.next = child;
curr.child = null;
childTail.next = nextCurr;
curr = childTail;
}
prevCurr = curr;
if (nextCurr != null) {
nextCurr.prev = curr;
nextCurr = nextCurr.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
curr.prev = prevCurr;
}
if (curr.child != null) {
child = curr.child;
child.prev = curr;
Node childTail = getChild(child);
curr.next = child;
curr.prev = prevCurr;
curr.child = null;
curr = childTail;
prevCurr = curr;
return prevCurr;
}
return curr;
}
}
開始有一些變形題了,這題應該算是簡單的Medium 題目,大概一個多小時就解完了,接下來先跳過Copy List with Random Pointer,還沒想出解法,先講Rotate List。
