Python 是一個很好上手的程式語言,他是高階語言,程式碼簡潔易懂,接近人類的語言的表達邏輯,還有強大的函式庫(例如 TensorFlow、Keras 和 scikit-learn),豐富的開源套件和活躍的社群支持,而成為人工智慧程式設計的熱門選擇。Python 也憑藉 NLTK 和 spaCy 等函式庫在 AI NLP 中發揮至關重要的作用。
但缺點就是執行效率比較慢,低階語言是機器邏輯的語言,學起來較複雜,但相較高階語言執行速度較快。
Python 還可以做什麼?
總結來說,Python 是一個功能強大的程式語言,可用範圍十分的廣泛。
接下來就教大家如何安裝 Pytohn 和 一些簡易的語法:
1. 安裝 Python
官方網站下載 https://www.python.org/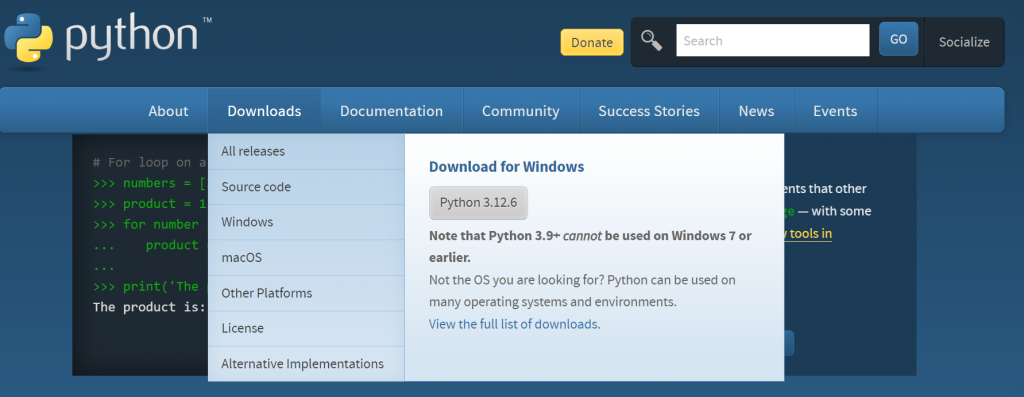
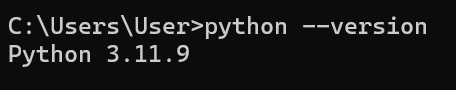
查看是否正確安裝,會看到類似 Python 3.x.x 的版本號
python --version
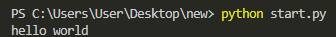
2. 基本的打印語句
print("hello world")
3. 變數資料型態
數字:整數3、長整數12345、浮點數(小數)3.14
字串:文字內容"Hello"
布林值:正確True、錯誤False
可變列表(List):有順序、可變動的資料集合[1,2,3] ["Hello","World"]
固定列表(Tuple):有順序、不可變動的資料集合(1,2,3) ("Hello","World")
集合:無順序的資料集合{1,2,3} {"Hello","World"}
字典:鍵值對(key - value)集合{"星期一":"Monday","星期二":"Tuesday"}
變數:可用來存放資料自訂名稱 x=3 print(x)
4. 列表 和 字典
可變列表(List):有順序、可變動的資料集合
fruits = ["banana", "cherry"]
fruits[0] = "apple" # 輸出 apple
print(fruits) # 輸出 ["apple", "cherry"]
固定列表(Tuple):有順序、不可變動的資料集合
tuple = (3, 4, 5)
tuple [0] = 5 # 錯誤 tuple 不可變動
集合:無順序的資料集合
# 判斷是否存在集合,使用 in 和 not in 運算符號
s1 = {1, 2, 3}
print(3 in s1) # 輸出 True
print(3 not in s1) # 輸出 False
s2 = {4, 5, 6, 7}
s3 = s1 & s2 # 交集:取兩個集合中,相同的資料 4.5
s4 = s1 | s2 # 聯集:取兩個集合中所有的資料,但不被重複 3.4.5.6.7
s5 = s1 - s2 # 差集:從s1減去和s2重疊部份 3
s6 = s1 ^ s2 # 反交集:取兩個集合中不重疊部份 3,6,7
# set (字串) 會自動把字串拆解成集合,重複部份不會計算
s = set("Hello") # 把字串的字幕拆解成集合:set (字串)
print(s) # set {'H', 'o', 'l', 'e'} 重複部份不會計算
print("H" in s) # 就可以測試H有沒有在s裡
字典:鍵值對(key - value)集合
dic = {"apple":"蘋果","banana":"香蕉"}
print(dic["apple"]) # 輸出 蘋果
dic["apple"] = "小蘋果"
print(dic["apple"]) # 輸出 小蘋果
print("apple" in dic) # 判斷 key 是否存在,只能判斷 key 不能判斷 value。 輸出 true
print("apple" not in dic) # 判斷 key 是否存在,只能判斷 key 不能判斷 value。輸出 false
5. 條件判斷if、elif、else
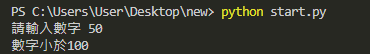
x = input("輸入數字")
x = int(x)
if x > 200:
print("數字大於200")
elif x > 100:
print("數字在100-200之間")
else:
print("數字小於100")
6. 流程控制:迴圈for 和 while 循環for 用於遍歷序列(列表、字符串等),並逐一取出處理
for x in [1, 2, 3]:
print(x) # 1 2 3
for x in "HELLO":
print(x) # H E L L O
while 循環在條件為 True 時重複執行
n = 1
sum = 0 # 紀錄累加的結果
while n <= 5:
sum += n
n += 1
print(sum) # 15
7. 函數
使用 def 建立函式
def people(name):
print('Hello ' + name) # Hello Bob
people("Bob")
8. 文件操作
mode = 讀取-r 寫入-w 讀寫-r+
with open(檔案路徑,mode=開啟模式)as檔案物件:
讀取或寫入檔案的程式
# 寫入文件
with open("data.txt",mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as file:
file.write("這是 Python 文件操作的範例。")
# 讀取文件
with open("data.txt",mode="r",encoding="utf-8") as file:
content = file.read()
print(content)
以上就是一些 Python的基本語法,明日就會學習如何用 Web 開發啦!
