原文題目
Given two integer arrays preorder and inorder where preorder is the preorder traversal of a binary tree and inorder is the inorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return the binary tree.
題目摘要
preorder 和 inorder,分別代表二元樹的前序遍歷和中序遍歷。Example 1: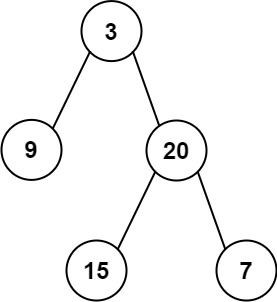
Input: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Example 2:
Input: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1]
Output: [-1]
解題思路一
理解前序、中序走訪的順序:
前序走訪的順序是「根節點 -> 左子樹 -> 右子樹」,中序走訪的順序是「左子樹 -> 根節點 -> 右子樹」。
找出根節點:
從前序走訪中拿到第一個元素,這就是根節點。
分清左右子樹:
在中序走訪中找到這個根節點,根節點左邊的部分就是左子樹,右邊的部分是右子樹。
重複過程:
對左子樹和右子樹重複相同的步驟,直到走訪完所有節點。
程式碼一
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return build(preorder, 0, preorder.length-1 , inorder, 0, inorder.length-1);
}
//preS為前序走訪索引值開始值
//preE為前序走訪索引值結束值
//inS為中序走訪索引值開始值
//inE為中序走訪索引值結束值
private TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int preS, int preE, int[] inorder, int inS, int inE){
//如果沒有節點,遞迴終止。
if (preS > preE || inS > inE) {
return null;
}
//根節點的值來自前序走訪的第一個元素
int rootVal = preorder[preS];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
//在中序走訪中找到根節點的Index
int rootIndex = 0;
for (int i = inS; i <= inE; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {
rootIndex = i;
break;
}
}
//左子樹的大小 = 根節點在中序走訪中的索引值 - 中序走訪開始值
//意即在中序走訪中根節點前半是左子樹,而右半(除了左子樹以及根節點以外的剩餘部分)是右子樹
int leftSize = rootIndex - inS;
//遞迴建立左子樹 --> 左子樹的範圍:
//前序走訪:(第一位應為根節點,故為第二位)開始值+1 ~ 開始值+左子樹大小
//中序走訪:開始值 ~ 根節點前一位
root.left = build(preorder, preS+1, preS+leftSize, inorder, inS, rootIndex-1);
//遞迴建立右子樹 --> 右子樹的範圍:
//前序走訪:開始值+左子樹大小+1(根節點後一位) ~ 前序走訪結束值
//中序走訪:根節點後一位 ~ 中序走訪結束值
root.right = build(preorder, preS+leftSize+1, preE, inorder, rootIndex+1, inE);
return root;
}
}
解題思路二
分析前序、中序走訪和二元樹的關係:
前序參訪順序:根節點 -> 左子樹 -> 右子樹。
中序參訪順序:左子樹 -> 根節點 -> 右子樹。
透過兩者走訪順序可已得出以下結論:
然後,在前序走訪中,根節點後面的元素會依次對應左子樹和右子樹,按照中序走訪中劃分的範圍來確定其子樹的結構。
初始化數據結構:
HashMap(inorderIndexMap)來記錄每個節點在中序遍歷中的索引位置,方便快速查找。preorderIndex 用於追蹤當前處理的前序遍歷節點索引。建立映射:
buildTree 主函數中,遍歷中序走訪數組,將每個節點值及其索引存入 inorderIndexMap。遞歸構建樹:
inorderStart 到 inorderEnd) 無效(即 inorderStart > inorderEnd),則返回 null。preorderIndex 獲取前序遍歷中的根節點值,並創建根節點。inorderIndexMap 查找根節點在中序遍歷中的位置(rootIndex)。inorderStart 到 rootIndex - 1,對應中序遍歷中根節點左側的部分。rootIndex + 1 到 inorderEnd,對應中序遍歷中根節點右側的部分。回傳結果:
程式碼二
class Solution {
private Map<Integer, Integer> inorderIndexMap; //用於記錄每個值在中序遍歷中的索引
private int preorderIndex; //追蹤當前處理的前序遍歷索引
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
//初始化inorderIndexMap並建立值到索引的映射
inorderIndexMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
inorderIndexMap.put(inorder[i], i);
}
preorderIndex = 0; //初始化preorderIndex
return buildTree(preorder, 0, inorder.length - 1); //開始構建樹,範圍是整個中序遍歷數組
}
//構建樹的遞迴函數
private TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int inorderStart, int inorderEnd) {
//當範圍無效時,返回 null
if (inorderStart > inorderEnd) {
return null;
}
int rootValue = preorder[preorderIndex++]; //獲取當前前序遍歷中的根節點值並增加索引
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootValue); //創建根節點
int rootIndex = inorderIndexMap.get(rootValue); //獲取根節點在中序遍歷中的索引
//遞迴構建左子樹,範圍是從 inorderStart 到 rootIndex - 1
root.left = buildTree(preorder, inorderStart, rootIndex - 1);
//遞迴構建右子樹,範圍是從 rootIndex + 1 到 inorderEnd
root.right = buildTree(preorder, rootIndex + 1, inorderEnd);
return root; //回傳建好的樹
}
}
結論
在解這道題時,最重要的當然是理解如何透過前序和中序的走訪特性來重新建構出二元樹,前序走訪提供了根節點的順序,而中序走訪則能幫助我們確定左右子樹的範圍。這題我和我的組員也分別用了不同的解法,第一種是純遞迴的解法,依賴前序和中序的特性重複建構二元樹。第二種解法則利用 HashMap 儲存中序遍歷中每個節點的索引,使得查找根節點位置的過程更為高效,這個解法同樣利用了前序走訪的特性,透過不斷遞迴構建左、右子樹,簡化了整體邏輯。通過這次的練習,我不僅了解根據前序和中序走訪構建二元樹的技巧,還學到了不同的解法。
