程式環境都會用colab 來執行程式,如果要在其他環境執行,請自行修改哦
colab 事前準備:設定專案和 API 金鑰
載入gemini
#pip install -q -U google-generativeai
import google.generativeai as genai
API 金鑰
from google.colab import userdata
API_KEY=userdata.get('GOOGLE_API_KEY')
#genai.configure(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY")
# Configure the client library by providing your API key.
genai.configure(api_key=API_KEY)
import re
import tqdm
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, ConfusionMatrixDisplay
for m in genai.list_models():
if 'embedContent' in m.supported_generation_methods:
print(m.name)
回答
models/embedding-001
models/text-embedding-004
20 Newsgroups Text Dataset 包含 20 個主題的 18,000 個新聞群組貼文,分為訓練和測試集。
newsgroups_train = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='train')
# View list of class names for dataset
newsgroups_train.target_names
回答
['alt.atheism',
'comp.graphics',
'comp.os.ms-windows.misc',
'comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware',
'comp.sys.mac.hardware',
'comp.windows.x',
'misc.forsale',
'rec.autos',
'rec.motorcycles',
'rec.sport.baseball',
'rec.sport.hockey',
'sci.crypt',
'sci.electronics',
'sci.med',
'sci.space',
'soc.religion.christian',
'talk.politics.guns',
'talk.politics.mideast',
'talk.politics.misc',
'talk.religion.misc']
idx = newsgroups_train.data[0].index('Lines')
print(newsgroups_train.data[0][idx:])
回答
Lines: 15
I was wondering if anyone out there could enlighten me on this car I saw
the other day. It was a 2-door sports car, looked to be from the late 60s/
early 70s. It was called a Bricklin. The doors were really small. In addition,
the front bumper was separate from the rest of the body. This is
all I know. If anyone can tellme a model name, engine specs, years
of production, where this car is made, history, or whatever info you
have on this funky looking car, please e-mail.
Thanks,
# Apply functions to remove names, emails, and extraneous words from data points in newsgroups.data
newsgroups_train.data = [re.sub(r'[\w\.-]+@[\w\.-]+', '', d) for d in newsgroups_train.data] # Remove email
newsgroups_train.data = [re.sub(r"\([^()]*\)", "", d) for d in newsgroups_train.data] # Remove names
newsgroups_train.data = [d.replace("From: ", "") for d in newsgroups_train.data] # Remove "From: "
newsgroups_train.data = [d.replace("\nSubject: ", "") for d in newsgroups_train.data] # Remove "\nSubject: "
# Put training points into a dataframe
df_train = pd.DataFrame(newsgroups_train.data, columns=['Text'])
df_train['Label'] = newsgroups_train.target
# Match label to target name index
df_train['Class Name'] = df_train['Label'].map(newsgroups_train.target_names.__getitem__)
# Retain text samples that can be used in the gecko model.
df_train = df_train[df_train['Text'].str.len() < 10000]
df_train
回答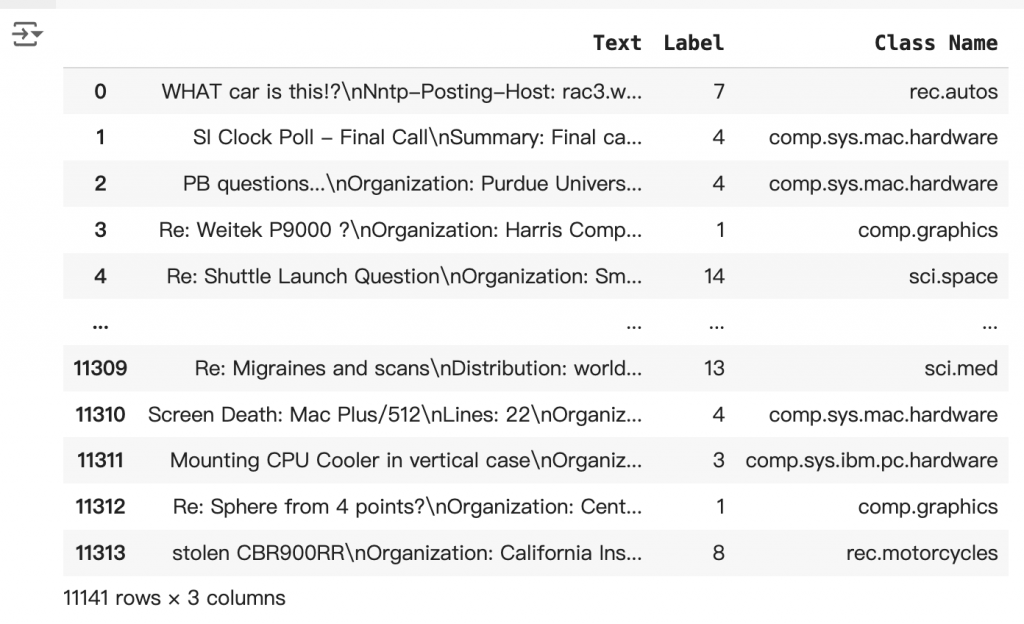
# Take a sample of each label category from df_train
SAMPLE_SIZE = 150
df_train = (df_train.groupby('Label', as_index = False)
.apply(lambda x: x.sample(SAMPLE_SIZE))
.reset_index(drop=True))
# Choose categories about science
df_train = df_train[df_train['Class Name'].str.contains('sci')]
# Reset the index
df_train = df_train.reset_index()
df_train
回答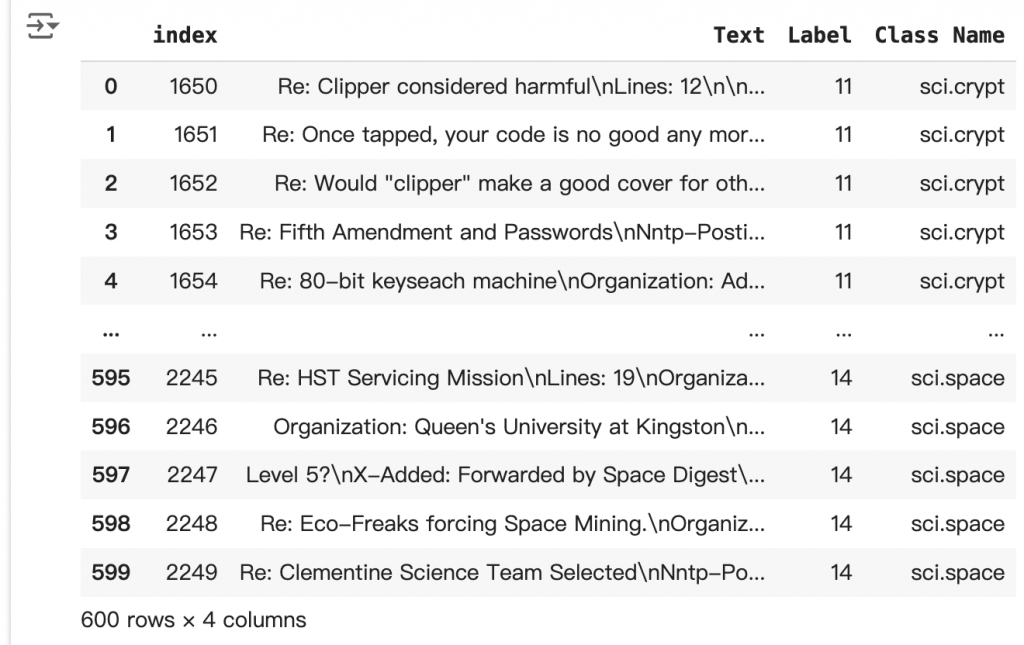
df_train['Class Name'].value_counts()
回答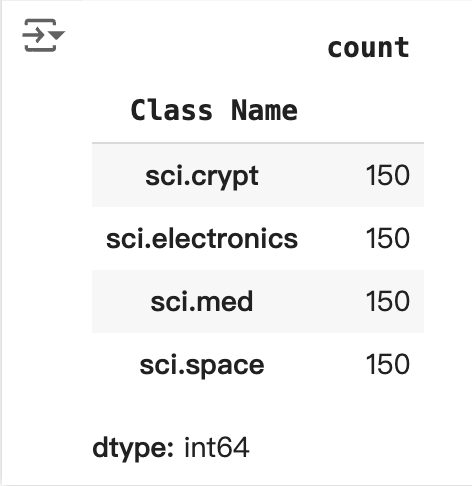
將 API 變更為使用模型嵌入功能 001 的嵌入 新的嵌入模型「embedding-001」其中有新的工作類型參數和選用標題 (僅適用於 task_type=RETRIEVAL_DOCUMENT)。
這些新參數僅適用於最新的嵌入模型。工作類型如下: 工作類型
文件嵌入向量的長度為 768 個字元。為了視覺化呈現內嵌文件的分組方式,您必須套用維度縮減功能,因為您只能在 2D 或 3D 空間中視覺化嵌入嵌入。
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
tqdm.pandas()
from google.api_core import retry
def make_embed_text_fn(model):
@retry.Retry(timeout=300.0)
def embed_fn(text: str) -> list[float]:
# Set the task_type to CLUSTERING.
embedding = genai.embed_content(model=model,
content=text,
task_type="clustering")
return embedding["embedding"]
return embed_fn
def create_embeddings(df):
model = 'models/text-embedding-004'
df['Embeddings'] = df['Text'].progress_apply(make_embed_text_fn(model))
return df
df_train = create_embeddings(df_train)
回答
100% 600/600 [10:10<00:00, 1.04it/s]
len(df_train['Embeddings'][0])
回答
768
# Convert df_train['Embeddings'] Pandas series to a np.array of float32
X = np.array(df_train['Embeddings'].to_list(), dtype=np.float32)
X.shape
回答
(600, 768)
tsne = TSNE(random_state=0, n_iter=1000)
tsne_results = tsne.fit_transform(X)
回答
/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/sklearn/manifold/_t_sne.py:1162: FutureWarning: 'n_iter' was renamed to 'max_iter' in version 1.5 and will be removed in 1.7.
warnings.warn(
df_tsne = pd.DataFrame(tsne_results, columns=['TSNE1', 'TSNE2'])
df_tsne['Class Name'] = df_train['Class Name'] # Add labels column from df_train to df_tsne
df_tsne
回答
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,6)) # Set figsize
sns.set_style('darkgrid', {"grid.color": ".6", "grid.linestyle": ":"})
sns.scatterplot(data=df_tsne, x='TSNE1', y='TSNE2', hue='Class Name', palette='hls')
sns.move_legend(ax, "upper left", bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1))
plt.title('Scatter plot of news using t-SNE');
plt.xlabel('TSNE1');
plt.ylabel('TSNE2');
plt.axis('equal')
回答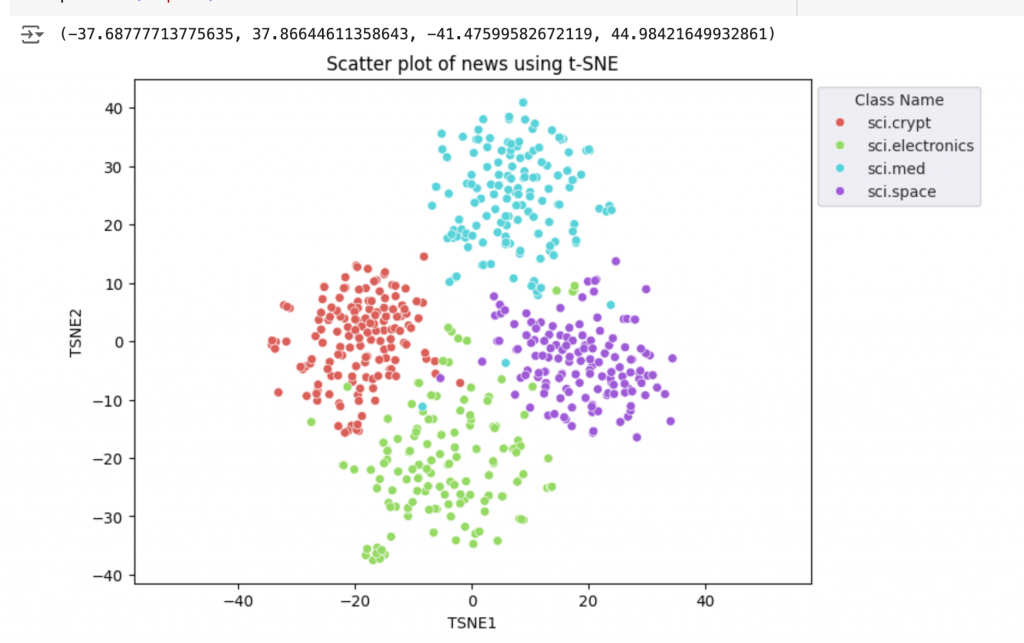
KMeans 分群法是一種熱門的分群演算法,通常用於非監督式學習。疊代決定最佳的 k 中心點,並將每個範例指派給最接近的質心。直接將嵌入項目輸入 KMeans 演算法,比較嵌入的視覺化效果與機器學習演算法的成效。
# Apply KMeans
kmeans_model = KMeans(n_clusters=4, random_state=1, n_init='auto').fit(X)
labels = kmeans_model.fit_predict(X)
df_tsne['Cluster'] = labels
df_tsne
回答
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,6)) # Set figsize
sns.set_style('darkgrid', {"grid.color": ".6", "grid.linestyle": ":"})
sns.scatterplot(data=df_tsne, x='TSNE1', y='TSNE2', hue='Cluster', palette='magma')
sns.move_legend(ax, "upper left", bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1))
plt.title('Scatter plot of news using KMeans Clustering');
plt.xlabel('TSNE1');
plt.ylabel('TSNE2');
plt.axis('equal')
回答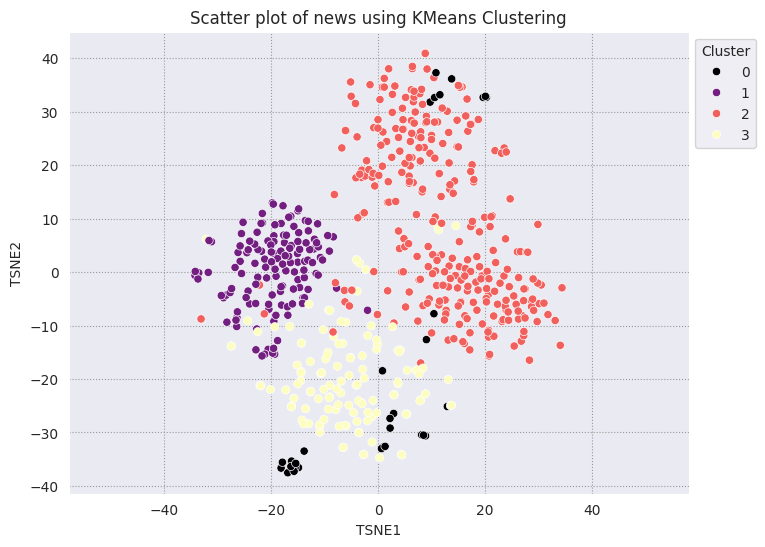
def get_majority_cluster_per_group(df_tsne_cluster, class_names):
class_clusters = dict()
for c in class_names:
# Get rows of dataframe that are equal to c
rows = df_tsne_cluster.loc[df_tsne_cluster['Class Name'] == c]
# Get majority value in Cluster column of the rows selected
cluster = rows.Cluster.mode().values[0]
# Populate mapping dictionary
class_clusters[c] = cluster
return class_clusters
classes = df_tsne['Class Name'].unique()
class_clusters = get_majority_cluster_per_group(df_tsne, classes)
class_clusters
回答
{'sci.crypt': 1, 'sci.electronics': 3, 'sci.med': 2, 'sci.space': 2}
# Convert the Cluster column to use the class name
class_by_id = {v: k for k, v in class_clusters.items()}
# df_tsne['Predicted'] = df_tsne['Cluster'].map(class_by_id.__getitem__)
df_tsne['Predicted'] = df_tsne['Cluster'].map(lambda x: class_by_id.get(x, 'Unknown'))
# Filter to the correctly matched rows
correct = df_tsne[df_tsne['Class Name'] == df_tsne['Predicted']]
# Summarise, as a percentage
acc = correct['Class Name'].value_counts() / SAMPLE_SIZE
acc
回答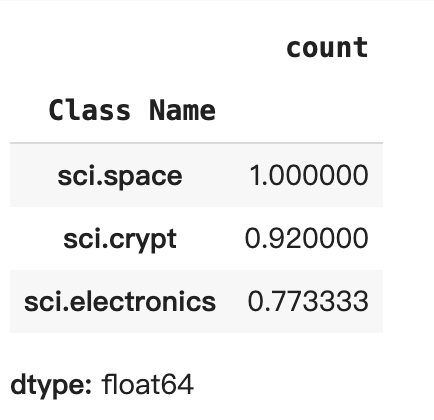
# Get predicted values by name
df_tsne['Predicted'] = ''
for idx, rows in df_tsne.iterrows():
cluster = rows['Cluster']
# Get key from mapping based on cluster value
# key = list(class_clusters.keys())[list(class_clusters.values()).index(cluster)]
# df_tsne.at[idx, 'Predicted'] = key
if cluster in class_clusters.values():
# Get key from mapping based on cluster value
key = list(class_clusters.keys())[list(class_clusters.values()).index(cluster)]
df_tsne.at[idx, 'Predicted'] = key
else:
# Handle the case where the cluster value is not found
df_tsne.at[idx, 'Predicted'] = 'Unknown'
df_tsne
回答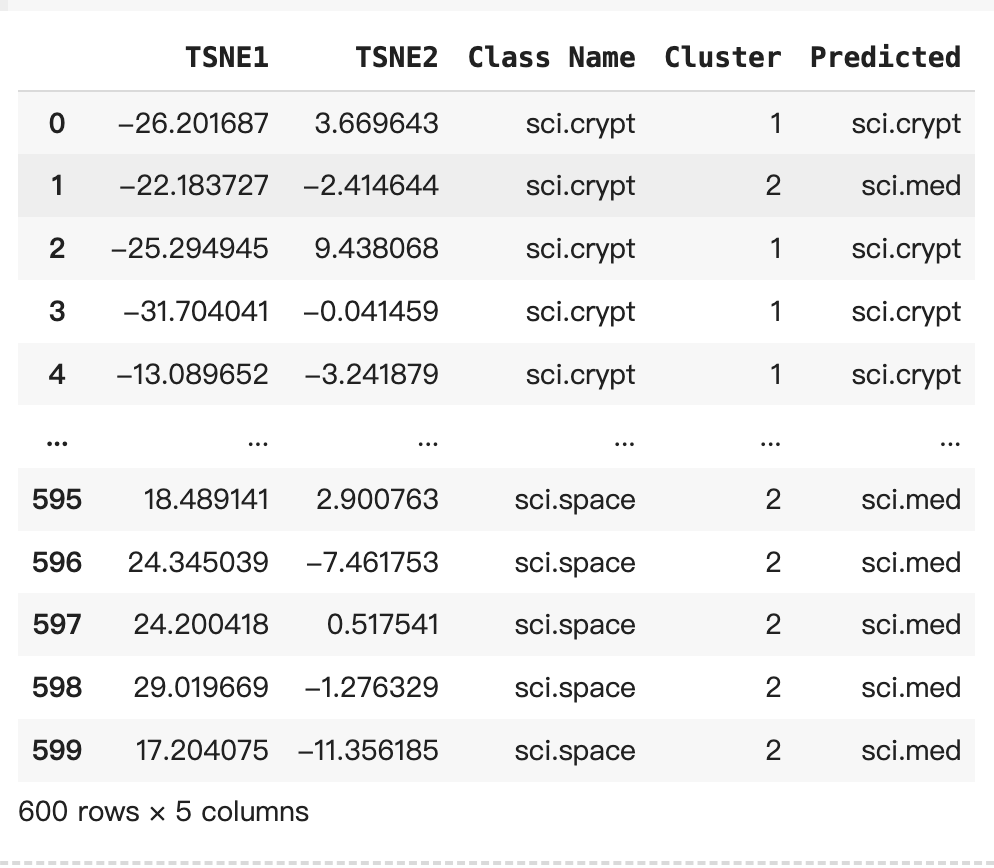
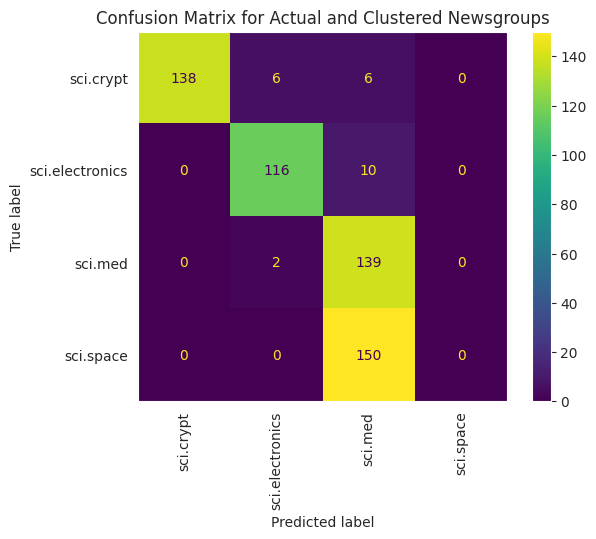
# cm = confusion_matrix(df_tsne['Class Name'].to_list(), df_tsne['Predicted'].to_list())
cm = confusion_matrix(df_tsne['Class Name'].to_list(), df_tsne['Predicted'].to_list(), labels=classes)
disp = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix=cm,
display_labels=classes)
disp.plot(xticks_rotation='vertical')
plt.title('Confusion Matrix for Actual and Clustered Newsgroups');
plt.grid(False)
回答