以下是使用 POSIX 執行緒(pthread)的簡單範例,展示了如何創建和管理多個執行緒。
posix-sched.c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // 引入此標頭以使用 malloc 和 free
#include <unistd.h> // 引入此標頭以使用 getpid 和 sleep
#define NUM_THREADS 5
/* the thread runs in this function */
void *runner(void *param);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) // 修正 main 函數的返回類型
{
int i, scope;
pthread_t tid[NUM_THREADS]; /* the thread identifier */
pthread_attr_t attr; /* set of attributes for the thread */
/* get the default attributes */
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
/* first inquire on the current scope */
if (pthread_attr_getscope(&attr, &scope) != 0)
fprintf(stderr, "Unable to get scheduling scope.\n");
else {
if (scope == PTHREAD_SCOPE_PROCESS)
printf("PTHREAD_SCOPE_PROCESS\n");
else if (scope == PTHREAD_SCOPE_SYSTEM)
printf("PTHREAD_SCOPE_SYSTEM\n");
else
fprintf(stderr, "Illegal scope value.\n");
}
/* set the scheduling algorithm to PCS or SCS */
if (pthread_attr_setscope(&attr, PTHREAD_SCOPE_SYSTEM) != 0)
printf("unable to set scheduling policy.\n");
/* create the threads */
for (i = 0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++) {
int *arg = malloc(sizeof(*arg)); // 動態分配記憶體以傳遞執行緒編號
if (arg == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate memory.\n");
exit(1);
}
*arg = i; // 傳遞執行緒編號
pthread_create(&tid[i], &attr, runner, arg);
}
/**
* Now join on each thread
*/
for (i = 0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++)
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
}
/**
* The thread will begin control in this function.
*/
void *runner(void *param)
{
int thread_id = *((int *)param); // 取得執行緒編號
free(param); // 釋放動態分配的記憶體
// 獲取當前進程的 PID
pid_t pid = getpid();
printf("Thread %d running in process with PID: %d\n", thread_id, pid);
// 根據執行緒編號執行不同的工作
printf("Thread %d is doing some work...\n", thread_id);
sleep(1); // 模擬工作延遲
pthread_exit(0);
}
Terminal
編譯並執行
gcc posix-sched.c -o posix-sched -lpthread
./posix-sched
結果: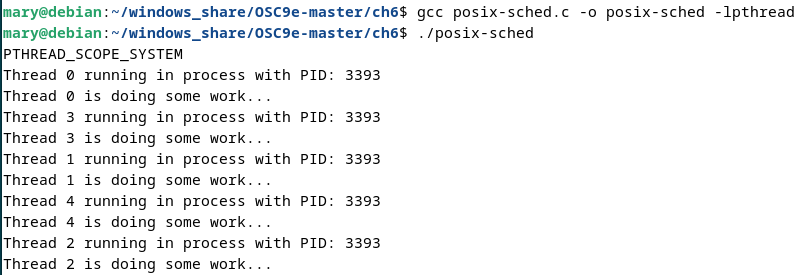
參考:greggagne/OSC9e/ch6/posix-sched.c
