上一篇我們已經完成一個具備訂閱功能的 Signal 核心,這一篇我們來實作 Effect,讓每個依賴項都能自動去追蹤,順利讓原本靜態的圖能具有響應性的動起來。
createEffect(fn):在追蹤區塊執行 fn,自動收集依賴邊。signal.set():通知相依的 effect,microtask 合併重跑一次。onCleanup(cb) 與 dispose():重跑前清理、手動解除依賴。我們透過這張圖,來先建立角色分工的基本認識:
run / schedule / dispose。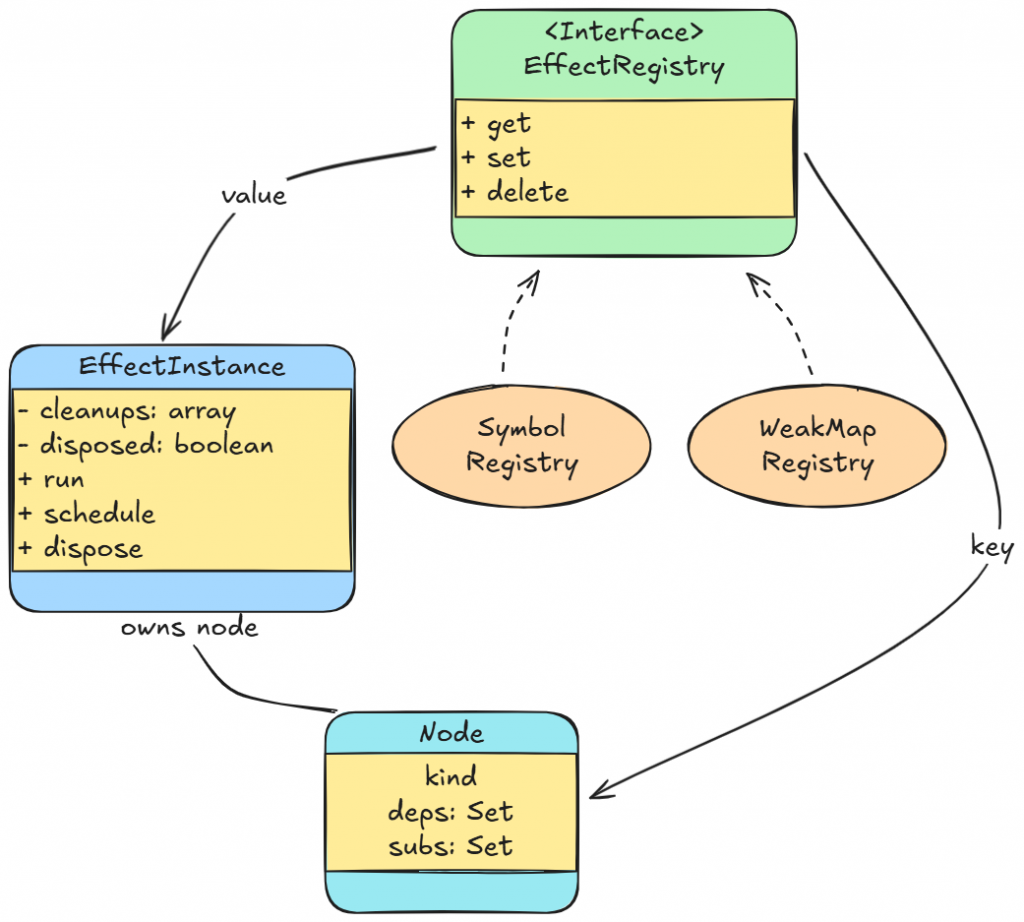
EffectInstance 擁有節點 (Node),Registry 只是「查表」讓我們從節點拿回實例。
這張描述建構與首次執行:
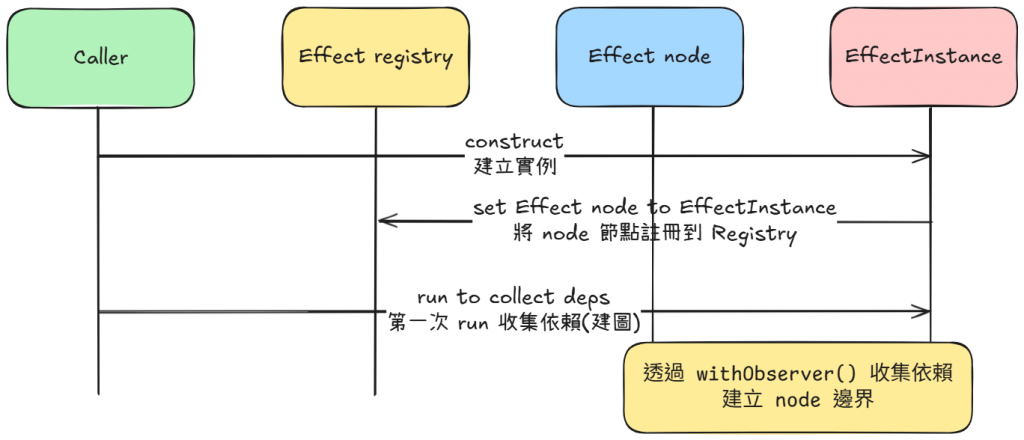
建圖先於通知。本篇的行為核心是「能重跑」;圖的維護(收集與解除)在
run()內部完成。
這張把「訊號更新 → 重跑」走完:
signal.set 更新值。subs(誰訂閱了這個 signal)。schedule。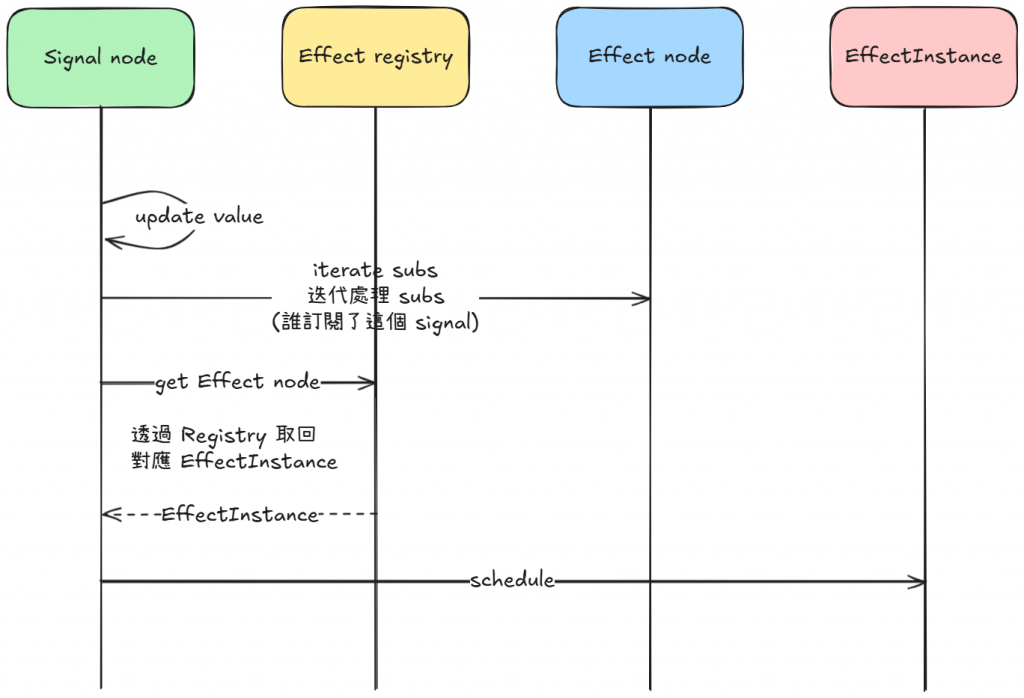
Registry 只是查表,真正「做事」的是
EffectInstance.schedule()(microtask 合併後呼叫run())。
// 上一篇的模型
// graph.ts
export type Kind = 'signal' | 'computed' | 'effect';
export interface Node {
kind: Kind;
deps: Set<Node>; // 我依賴了誰(effect / computed)
subs: Set<Node>; // 誰依賴我(signal / computed)
}
export function link(from: Node, to: Node) {
if (from.kind === 'signal') throw new Error('Signal nodes cannot depend on others');
from.deps.add(to);
to.subs.add(from);
}
export function unlink(from: Node, to: Node) {
from.deps.delete(to);
to.subs.delete(from);
}
// 追蹤:在觀察者上下文中讀取,會自動建邊界 Observer -> Trackable
let currentObserver: Node | null = null;
export function withObserver<T>(obs: Node, fn: () => T): T {
const prev = currentObserver;
currentObserver = obs;
try {
return fn();
} finally {
currentObserver = prev;
}
}
export function track(dep: Node) {
if (!currentObserver) return;
link(currentObserver, dep);
}
// registry.ts
import type { Node } from "./graph.js";
export interface EffectInstanceLike {
schedule(): void;
}
export const EffectSlot: unique symbol = Symbol("EffectSlot");
export interface EffectCarrier {
[EffectSlot]?: EffectInstanceLike;
}
export interface EffectRegistry {
get(node: EffectCarrier): EffectInstanceLike | undefined;
set(node: EffectCarrier, inst: EffectInstanceLike): void;
delete(node: EffectCarrier): void;
}
export const SymbolRegistry: EffectRegistry = {
get(node) {
return node[EffectSlot];
},
set(node, inst) {
Object.defineProperty(node, EffectSlot, {
value: inst,
enumerable: false,
configurable: true
});
},
delete(node) {
Reflect.deleteProperty(node, EffectSlot);
}
};
「Registry 負責維護 Node → EffectInstance 的關聯,讓
signal.set()能 O(1) 找到該重跑的 effect。
// effect.ts
import { unlink, withObserver, type Node } from "./graph.js";
import { SymbolRegistry, type EffectInstanceLike } from "./registry.js";
type Cleanup = () => void;
// 共用工具:LIFO 執行,確保最後清空
function drainCleanups(list: Cleanup[], onError?: (err: unknown) => void) {
// LIFO:從尾到頭執行
for (let i = list.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const cb = list[i];
try {
cb();
} catch (e) {
onError?.(e);
}
}
list.length = 0;
}
// microtask 合併
const pending = new Set<EffectInstance>();
let scheduled = false;
function schedule(inst: EffectInstance) {
if (inst.disposed) return;
pending.add(inst);
if (!scheduled) {
scheduled = true;
queueMicrotask(() => {
scheduled = false;
const list = Array.from(pending);
pending.clear();
for (const ef of list) ef.run();
});
}
}
let activeEffect: EffectInstance | null = null;
export function onCleanup(cb: Cleanup) {
if (activeEffect) activeEffect.cleanups.push(cb);
}
export class EffectInstance implements EffectInstanceLike {
node: Node = {
kind: 'effect',
deps: new Set(),
subs: new Set()
};
cleanups: Cleanup[] = [];
disposed = false;
constructor(private fn: () => void | Cleanup) {
SymbolRegistry.set(this.node, this); // 只碰 Registry
}
run() {
if (this.disposed) return;
// 1) 清理上次
drainCleanups(this.cleanups);
// 2) 解除舊依賴
for (const dep of [...this.node.deps]) unlink(this.node, dep);
// 3) 追蹤上下文執行,收集新依賴;支援回傳 cleanup
activeEffect = this;
try {
const ret = withObserver(this.node, this.fn);
if (typeof ret === 'function') this.cleanups.push(ret);
} finally {
activeEffect = null;
}
}
schedule() { schedule(this); }
dispose() {
if (this.disposed) return;
this.disposed = true;
drainCleanups(this.cleanups);
for (const dep of [...this.node.deps]) unlink(this.node, dep);
this.node.deps.clear();
SymbolRegistry.delete(this.node); // 只碰 Registry
}
}
export function createEffect(fn: () => void | Cleanup) {
const inst = new EffectInstance(fn);
inst.run(); // 先跑一次收集依賴
return () => inst.dispose();
}
// signal.ts
import { link, track, unlink, type Node } from "./graph.js";
import { SymbolRegistry } from "./registry.js";
type Comparator<T> = (a: T, b: T) => boolean;
const defaultEquals = Object.is;
export function signal<T>(initial: T, equals: Comparator<T> = defaultEquals) {
const node: Node & { kind: 'signal'; value: T; equals: Comparator<T> } = {
kind: 'signal',
deps: new Set(), // 由 link 規則保證為空
subs: new Set(),
value: initial,
equals,
};
const get = () => {
track(node);
return node.value;
};
const set = (next: T | ((p: T) => T)) => {
const nxtVal = typeof next === 'function' ? (next as (p: T) => T)(node.value) : next;
if (node.equals(node.value, nxtVal)) return;
node.value = nxtVal;
for (const sub of node.subs) {
if (sub.kind === 'effect') SymbolRegistry.get(sub)?.schedule();
}
};
const subscribe = (observer: Node) => {
link(observer, node);
return () => unlink(observer, node);
};
return { get, set, subscribe, peek: () => node.value };
}
import { signal } from './signal';
import { createEffect, onCleanup } from './effect';
const a = signal(1);
const b = signal(2);
const stop = createEffect(() => {
console.log('sum =', a.get() + b.get());
onCleanup(() => console.log('cleanup before rerun'));
});
a.set(10); // microtask:cleanup before rerun → sum = 12
b.set(20); // microtask:cleanup before rerun → sum = 30
stop(); // 解除訂閱與清理
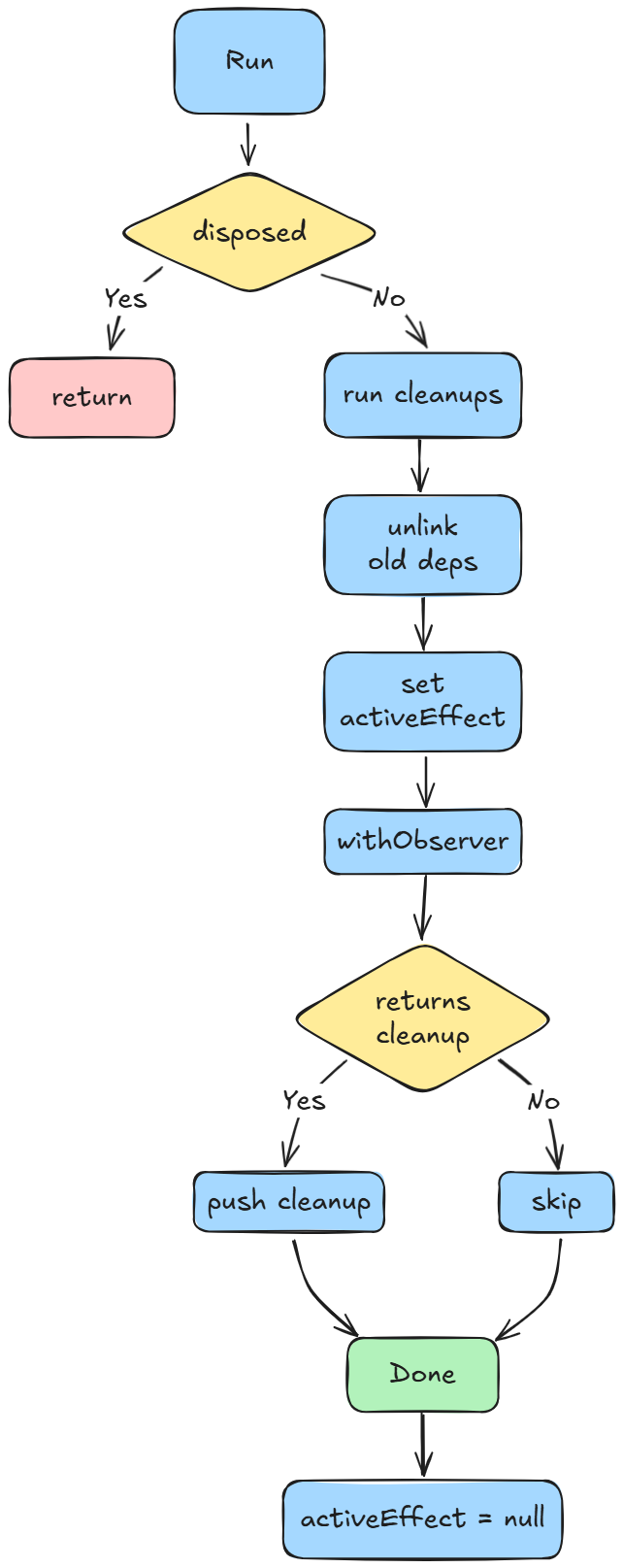
經過上述的流程,我們會建立一個可以符合運作的 Effect 核心,但還是要注意一些問題:
const v = a.get(); a.set(10); v 仍是舊值;要最新值請再呼叫 get()
set 合併:同一輪多次 set() 只重跑一次 effect(microtask 合併)。unlink 舊依賴再用 withObserver 收集新依賴,避免訂閱集合不斷增長。這一篇花了很多時間再製作圖表,也是希望能讓大家比較容易理解,畢竟牽扯到圖(Graph)這種資料結構,就會有很多細節需要處理。
下一篇,我們來討論 Effect 內部選型 (Symbol vs WeakMap),理解 WeakMap 的基礎,並嘗試另一種 WeakMapRegistry 的實踐方法。
